Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-...
Start Learning for Free
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Young's modulus of copper as 42 × 10
9
Pa- a)3.65 × 10-8
- b)3.65 × 10-3
- c)3.65 × 10-9
- d)3.65 × 10-2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm ×...
Given Data,
Length of the piece of copper = l = 19.1 mm = 19.1 × 10-3m
Breadth of the piece of copper = b = 15.2 mm = 15.2× 10-3m
Tension force applied on the piece of cooper, F = 44500N
Area of rectangular cross section of copper piece,
Area = l× b
⇒ Area = (19.1 × 10-3m) × (15.2× 10-3m)
⇒ Area = 2.9 × 10-4 m2
Modulus of elasticity of copper from standard list, η = 42× 109 N/m2
By definition, Modulus of elasticity, η = stress/strain
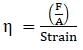
⇒ Strain = F/Aη
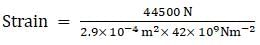
⇒ Strain = 3.65 × 10-3
Hence, the resulting strain is 3.65 × 10-3
Length of the piece of copper = l = 19.1 mm = 19.1 × 10-3m
Breadth of the piece of copper = b = 15.2 mm = 15.2× 10-3m
Tension force applied on the piece of cooper, F = 44500N
Area of rectangular cross section of copper piece,
Area = l× b
⇒ Area = (19.1 × 10-3m) × (15.2× 10-3m)
⇒ Area = 2.9 × 10-4 m2
Modulus of elasticity of copper from standard list, η = 42× 109 N/m2
By definition, Modulus of elasticity, η = stress/strain
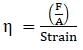
⇒ Strain = F/Aη
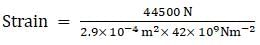
⇒ Strain = 3.65 × 10-3
Hence, the resulting strain is 3.65 × 10-3
Most Upvoted Answer
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm ×...
X 20.3 mm is being stretched in a tensile testing machine. The original gauge length of the specimen is 50.8 mm and the machine applies a force of 50 kN. Determine the engineering stress and strain, as well as the true stress and strain.
First, we need to calculate the cross-sectional area of the specimen:
A = (15.2 mm) x (20.3 mm) = 308.56 mm^2
Next, we can calculate the engineering stress:
σ = F/A = 50 kN / 308.56 mm^2 = 161.9 MPa
To calculate the engineering strain, we need to know the change in length of the specimen. Let's say the machine stretches the specimen to a final length of 55.8 mm.
ε = (ΔL / L0) = (55.8 mm - 50.8 mm) / 50.8 mm = 0.098
Now, we can calculate the true stress and strain. To do this, we need to know the true cross-sectional area of the specimen, which changes as the specimen is stretched. We can use the equation:
A' = A x (1 + ε)
where A' is the true cross-sectional area and ε is the engineering strain.
A' = 308.56 mm^2 x (1 + 0.098) = 338.1 mm^2
The true stress is then:
σ' = F/A' = 50 kN / 338.1 mm^2 = 147.9 MPa
The true strain is:
ε' = ln (L / L0) = ln (55.8 mm / 50.8 mm) = 0.096
So the engineering stress and strain are 161.9 MPa and 0.098, respectively, while the true stress and strain are 147.9 MPa and 0.096, respectively.
First, we need to calculate the cross-sectional area of the specimen:
A = (15.2 mm) x (20.3 mm) = 308.56 mm^2
Next, we can calculate the engineering stress:
σ = F/A = 50 kN / 308.56 mm^2 = 161.9 MPa
To calculate the engineering strain, we need to know the change in length of the specimen. Let's say the machine stretches the specimen to a final length of 55.8 mm.
ε = (ΔL / L0) = (55.8 mm - 50.8 mm) / 50.8 mm = 0.098
Now, we can calculate the true stress and strain. To do this, we need to know the true cross-sectional area of the specimen, which changes as the specimen is stretched. We can use the equation:
A' = A x (1 + ε)
where A' is the true cross-sectional area and ε is the engineering strain.
A' = 308.56 mm^2 x (1 + 0.098) = 338.1 mm^2
The true stress is then:
σ' = F/A' = 50 kN / 338.1 mm^2 = 147.9 MPa
The true strain is:
ε' = ln (L / L0) = ln (55.8 mm / 50.8 mm) = 0.096
So the engineering stress and strain are 161.9 MPa and 0.098, respectively, while the true stress and strain are 147.9 MPa and 0.096, respectively.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Question Description
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Youngs modulus of copper as 42 × 109Paa)3.65 × 10-8b)3.65 × 10-3c)3.65 × 10-9d)3.65 × 10-2Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















