Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)No...
Start Learning for Free
Biogas is which type of natural resources
- a)Non- Renewable
- b)Exhaustible
- c)Non-conventional
- d)Human
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible...
Key Points
- Biogasis an emerging renewable, non-conventional energy source that is obtained through the degradation of organic matter by bacteria under anaerobic conditions.
- The major constituent of biogas is Methane.
- Biogasis usuallymade up of around 50-70% methane(CH4) and25-45% carbon dioxide(CO2), with other gases such ashydrogen(H2),hydrogen sulphide(H2S),watervapour(H2O),Nitrogen(N2),oxygen(O2),ammonia(NH3) making up the rest.
- It is released when Cow, Buffalo, and Pig manureis processed anaerobicallyi.e. in the absence of Oxygen.
- Biogas can be used for Space Heating, Generation of Electricity, Fuel for Cooking, etc.
Important Points
Advantages of Biogas -
- Biogas burns without smoke; hence no harmful gas such as CO2, CO, NO2, and SO2 are evolved.
- The slurry produced after the production of biogas is used as manure in fields.
- The method of disposal is safe and efficient and hence no space is wasted in the form of landfills.
- Biogas plants require very little installation costs and become self-sufficient in a span of 3-4 months.
- Work opportunity for thousands of people is created, especially in rural areas.
Thus, Biogas is a non-conventional type of natural resource.
Additional Information
There are basically two sources of energy:
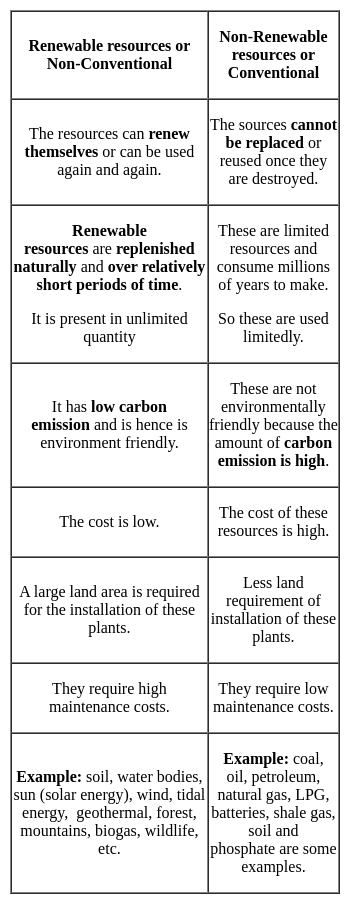
Most Upvoted Answer
Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible...
Understanding Biogas as a Resource
Biogas is primarily classified as a non-conventional natural resource. Here's a detailed explanation of why this classification is appropriate:
Definition of Biogas
- Biogas is generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, and plant material.
- It primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), making it a renewable source of energy.
Non-Conventional Resource
- Non-conventional energy resources are those that are not typically utilized in mainstream energy production. They often include renewable energy sources that are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Biogas fits this definition since it is derived from organic waste, which is continuously produced and can be replenished over time.
Renewability Factor
- Unlike fossil fuels (non-renewable) which can deplete over time, biogas production relies on ongoing processes of organic waste decomposition.
- The sustainable nature of biogas production is supported by agricultural and biological cycles, making it a viable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact
- Utilizing biogas helps in waste management and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. By converting waste into energy, it provides an eco-friendly solution to energy needs.
Conclusion
- Therefore, biogas is classified as a non-conventional natural resource. It is renewable, sustainable, and plays a crucial role in the transition towards greener energy solutions.
Biogas is primarily classified as a non-conventional natural resource. Here's a detailed explanation of why this classification is appropriate:
Definition of Biogas
- Biogas is generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, and plant material.
- It primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), making it a renewable source of energy.
Non-Conventional Resource
- Non-conventional energy resources are those that are not typically utilized in mainstream energy production. They often include renewable energy sources that are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Biogas fits this definition since it is derived from organic waste, which is continuously produced and can be replenished over time.
Renewability Factor
- Unlike fossil fuels (non-renewable) which can deplete over time, biogas production relies on ongoing processes of organic waste decomposition.
- The sustainable nature of biogas production is supported by agricultural and biological cycles, making it a viable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact
- Utilizing biogas helps in waste management and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. By converting waste into energy, it provides an eco-friendly solution to energy needs.
Conclusion
- Therefore, biogas is classified as a non-conventional natural resource. It is renewable, sustainable, and plays a crucial role in the transition towards greener energy solutions.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Question Description
Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Biogas is which type of natural resourcesa)Non- Renewableb)Exhaustible c)Non-conventional d)HumanCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















