Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a...
Start Learning for Free
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:
- a)Porphyrin
- b)Corrin
- c)Phthalocyanine
- d)Crown ether
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phtha...
The core of the molecule vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is a corrin structure (depicted in red) with at its center a cobalt ion. One of the nitrogen atoms on the imidazole is a fifth nitrogen ligand for the cobalt atom.
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phtha...
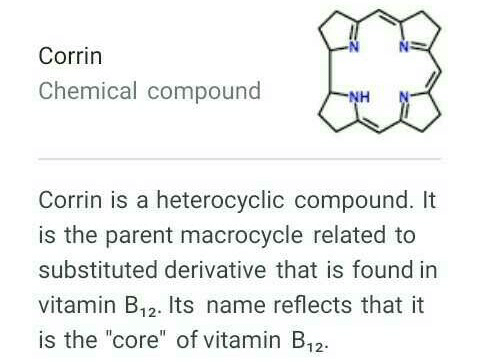
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is Corrin.
Explanation:
- Vitamin B12, also known as Cobalamin, is a complex organic compound that is essential for various biological processes in the human body.
- The central atom in vitamin B12 is Cobalt, which is coordinated to a complex ligand system called Corrin.
- Corrin is a macrocyclic ligand that is derived from porphyrin, which is the same ligand present in hemoglobin and chlorophyll.
- The Corrin ligand in vitamin B12 consists of a tetrapyrrole ring with a cobalt ion coordinated to the center.
- The Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 is responsible for its biological activity, which includes the transport and metabolism of various molecules in the body, such as amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleic acids.
- The Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 also plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous system.
- The unique properties of the Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 make it an important molecule in both biochemistry and medicine.
- The deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to various health problems, such as anemia, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
Explanation:
- Vitamin B12, also known as Cobalamin, is a complex organic compound that is essential for various biological processes in the human body.
- The central atom in vitamin B12 is Cobalt, which is coordinated to a complex ligand system called Corrin.
- Corrin is a macrocyclic ligand that is derived from porphyrin, which is the same ligand present in hemoglobin and chlorophyll.
- The Corrin ligand in vitamin B12 consists of a tetrapyrrole ring with a cobalt ion coordinated to the center.
- The Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 is responsible for its biological activity, which includes the transport and metabolism of various molecules in the body, such as amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleic acids.
- The Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 also plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous system.
- The unique properties of the Corrin ligand system in vitamin B12 make it an important molecule in both biochemistry and medicine.
- The deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to various health problems, such as anemia, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phtha...

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Question Description
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The ligand system present in vitamin B12 is:a)Porphyrinb)Corrinc)Phthalocyanined)Crown etherCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.