Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > In a transformer, the load current is kept co...
Start Learning for Free
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observed
- a)independent of load power factor
- b)load power factor is leading
- c)load power factor is lagging
- d)at power factor equal to unity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power f...
Voltage regulation is the change in secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load at a specific power factor of load and the change is expressed in percentage.
E2 = no-load secondary voltage
V2 = full load secondary voltage
Voltage regulation for the transformer is given by the ratio of change in secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load to no load secondary voltage.
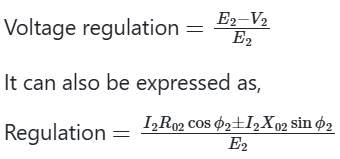
+ sign is used for lagging loads and
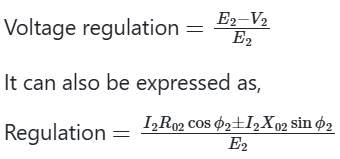
+ sign is used for lagging loads and
- ve sign is used for leading loads
Hence voltage regulation can be negative only for capacitive loads
In transformer minimum voltage regulation occurs when the power factor of the load is leading.
The voltage regulation of the transformer is zero at a leading power factor load such as a capacitive load.
For zero voltage regulation, E2 = V2
> IR cos φ = IX sin φ (negative sign represents leading power factor loads)
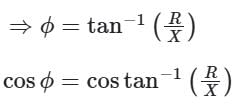
This is the leading power factor at which voltage regulation becomes zero while supplying the load.
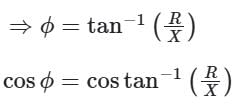
This is the leading power factor at which voltage regulation becomes zero while supplying the load.
Most Upvoted Answer
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power f...
Understanding Transformer Voltage Regulation
In a transformer, voltage regulation refers to the change in secondary voltage as the load varies. When the load current is constant, the power factor plays a crucial role in determining voltage regulation.
Impact of Load Power Factor on Voltage Regulation
- Leading Power Factor: When the load power factor is leading, the current lags behind the voltage. This causes the transformer to behave like it is supplying reactive power, which can lead to a reduction in the voltage drop across the transformer’s impedance. As a result, the secondary voltage can either remain constant or even increase, achieving zero voltage regulation.
- Lagging Power Factor: Conversely, with a lagging power factor, the current leads the voltage. This situation increases the voltage drop across the transformer impedance, resulting in a decrease in secondary voltage, thus causing negative voltage regulation.
- Unity Power Factor: At unity power factor, the current and voltage are in phase. The voltage drop is present but remains relatively stable, leading to a certain level of voltage regulation, but not zero.
Conclusion
In summary, the condition for achieving zero voltage regulation in a transformer with constant load current is primarily linked to the power factor.
- A leading power factor ensures that the reactive power effects counteract the resistive drops, stabilizing the voltage.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B: zero voltage regulation is observed when the load power factor is leading.
In a transformer, voltage regulation refers to the change in secondary voltage as the load varies. When the load current is constant, the power factor plays a crucial role in determining voltage regulation.
Impact of Load Power Factor on Voltage Regulation
- Leading Power Factor: When the load power factor is leading, the current lags behind the voltage. This causes the transformer to behave like it is supplying reactive power, which can lead to a reduction in the voltage drop across the transformer’s impedance. As a result, the secondary voltage can either remain constant or even increase, achieving zero voltage regulation.
- Lagging Power Factor: Conversely, with a lagging power factor, the current leads the voltage. This situation increases the voltage drop across the transformer impedance, resulting in a decrease in secondary voltage, thus causing negative voltage regulation.
- Unity Power Factor: At unity power factor, the current and voltage are in phase. The voltage drop is present but remains relatively stable, leading to a certain level of voltage regulation, but not zero.
Conclusion
In summary, the condition for achieving zero voltage regulation in a transformer with constant load current is primarily linked to the power factor.
- A leading power factor ensures that the reactive power effects counteract the resistive drops, stabilizing the voltage.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B: zero voltage regulation is observed when the load power factor is leading.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observeda)independent of load power factorb)load power factor is leadingc)load power factor is laggingd)at power factor equal to unityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























