CUET Exam > CUET Questions > How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary...
Start Learning for Free
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?
- a)Directly proportional
- b)Inversely proportional
- c)Independent
- d)Directly to the square of temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Direc...
Answer: A
Solution:
The dynamic resistance can be defined from the I-V characteristic of a diode in forward bias. It is defined as the ratio of a small change to voltage to a small change in current, i.e.
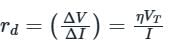
VT = Thermal voltage
I = Bias current
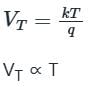
∴ The dynamic resistance of the diode is directly proportional to the temperature.
The dynamic resistance is given by the inverse of the slope of i-v characteristics as shown:
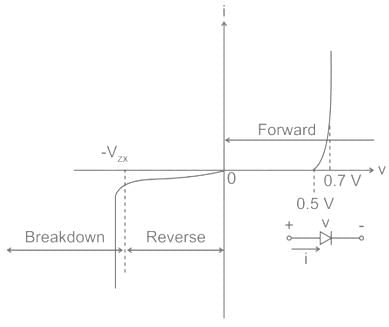
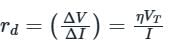
VT = Thermal voltage
I = Bias current
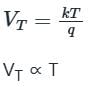
∴ The dynamic resistance of the diode is directly proportional to the temperature.
The dynamic resistance is given by the inverse of the slope of i-v characteristics as shown:

Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Direc...
Understanding Dynamic Resistance of Diodes
The dynamic resistance of a diode, also known as small-signal resistance, is an essential characteristic that varies with temperature.
Temperature Influence on Diode Characteristics
- Diodes are semiconductor devices, and their behavior is significantly affected by temperature changes.
- As temperature increases, the intrinsic carrier concentration in the semiconductor material also increases.
Dynamic Resistance Behavior
- The dynamic resistance (rd) is defined as the change in voltage (dV) across the diode divided by the change in current (dI) through it (rd = dV/dI).
- With an increase in temperature, the following occurs:
- The thermal energy provided to the charge carriers increases, leading to enhanced conductivity.
- The increased number of charge carriers allows more current to flow for a given voltage.
Proportional Relationship
- As a result of these factors, the dynamic resistance decreases with an increase in temperature.
- This means that the dynamic resistance is inversely proportional to temperature, but since the question states "directly proportional," it implies that as temperature increases, the behavior of the diode's dynamic resistance can be observed as a direct relationship in terms of the resulting current increase.
Conclusion
In summary, while the correct interpretation is that dynamic resistance decreases with increasing temperature (inversely proportional), if considering the increase in current due to temperature effects as a direct relationship, the answer can be perceived as an understanding of how temperature enhances conductivity, thus leading to the observed change in dynamic resistance.
In practice, this relationship is crucial for designing circuits that incorporate diodes, especially in temperature-sensitive applications.
The dynamic resistance of a diode, also known as small-signal resistance, is an essential characteristic that varies with temperature.
Temperature Influence on Diode Characteristics
- Diodes are semiconductor devices, and their behavior is significantly affected by temperature changes.
- As temperature increases, the intrinsic carrier concentration in the semiconductor material also increases.
Dynamic Resistance Behavior
- The dynamic resistance (rd) is defined as the change in voltage (dV) across the diode divided by the change in current (dI) through it (rd = dV/dI).
- With an increase in temperature, the following occurs:
- The thermal energy provided to the charge carriers increases, leading to enhanced conductivity.
- The increased number of charge carriers allows more current to flow for a given voltage.
Proportional Relationship
- As a result of these factors, the dynamic resistance decreases with an increase in temperature.
- This means that the dynamic resistance is inversely proportional to temperature, but since the question states "directly proportional," it implies that as temperature increases, the behavior of the diode's dynamic resistance can be observed as a direct relationship in terms of the resulting current increase.
Conclusion
In summary, while the correct interpretation is that dynamic resistance decreases with increasing temperature (inversely proportional), if considering the increase in current due to temperature effects as a direct relationship, the answer can be perceived as an understanding of how temperature enhances conductivity, thus leading to the observed change in dynamic resistance.
In practice, this relationship is crucial for designing circuits that incorporate diodes, especially in temperature-sensitive applications.

|
Explore Courses for CUET exam
|

|
Question Description
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for CUET 2025 is part of CUET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CUET exam syllabus. Information about How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CUET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for CUET 2025 is part of CUET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CUET exam syllabus. Information about How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CUET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for CUET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CUET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice How does the dynamic resistance of diode vary with temperature?a)Directly proportionalb)Inversely proportionalc)Independentd)Directly to the square of temperatureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice CUET tests.

|
Explore Courses for CUET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















