Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected...
Start Learning for Free
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?
- a)Young's modulus
- b)Shear modulus
- c)Poisson's ratio
- d)Both Young's modulus and shear modulus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Whi...
Both Poison’s ratio and Young’s Modulus are required to calculate the lateral strain in rod Now m,E and N are related by
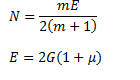
So E and G are required if
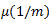
is given
Most Upvoted Answer
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Whi...
Calculating Change in Diameter of a Rod under Tensile Load
When a rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P, it results in a change in its dimensions. The change in diameter can be calculated using the following formula:
ΔD = (PD) / (πE (L+δ))
where ΔD is the change in diameter, P is the tensile load, D is the original diameter, E is the Young's modulus of the material, L is the original length of the rod, and δ is the change in length due to the load.
Sufficient Parameters to Calculate Change in Diameter
To calculate the change in diameter of the rod under tensile load, we need to know the following parameters:
1. Young's Modulus
Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material. It is defined as the ratio of stress to strain within the elastic limit of the material. Young's modulus is necessary to calculate the change in diameter of the rod because it relates the stress applied to the rod to the strain that it produces.
2. Shear Modulus
Shear modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to deformation by shear stress. It relates the shear stress applied to the rod to the resulting shear strain. Although shear strain does not contribute to the change in diameter, it is necessary to calculate the change in length of the rod under tensile load. Therefore, shear modulus is also required to calculate the change in diameter.
3. Poisson's Ratio
Poisson's ratio is a measure of the ratio of lateral strain to axial strain in a material. It is defined as the negative ratio of the change in diameter to the change in length under a tensile load. Although Poisson's ratio can be used to calculate the change in diameter, it cannot be determined independently of the other two parameters.
Hence, both Young's modulus and shear modulus are required to calculate the resulting change in diameter of a rod under tensile load.
When a rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P, it results in a change in its dimensions. The change in diameter can be calculated using the following formula:
ΔD = (PD) / (πE (L+δ))
where ΔD is the change in diameter, P is the tensile load, D is the original diameter, E is the Young's modulus of the material, L is the original length of the rod, and δ is the change in length due to the load.
Sufficient Parameters to Calculate Change in Diameter
To calculate the change in diameter of the rod under tensile load, we need to know the following parameters:
1. Young's Modulus
Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material. It is defined as the ratio of stress to strain within the elastic limit of the material. Young's modulus is necessary to calculate the change in diameter of the rod because it relates the stress applied to the rod to the strain that it produces.
2. Shear Modulus
Shear modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to deformation by shear stress. It relates the shear stress applied to the rod to the resulting shear strain. Although shear strain does not contribute to the change in diameter, it is necessary to calculate the change in length of the rod under tensile load. Therefore, shear modulus is also required to calculate the change in diameter.
3. Poisson's Ratio
Poisson's ratio is a measure of the ratio of lateral strain to axial strain in a material. It is defined as the negative ratio of the change in diameter to the change in length under a tensile load. Although Poisson's ratio can be used to calculate the change in diameter, it cannot be determined independently of the other two parameters.
Hence, both Young's modulus and shear modulus are required to calculate the resulting change in diameter of a rod under tensile load.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Whi...
Calculation of Diameter Change in a Tensile Loaded Rod:
When a rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P, it will experience a change in both length and diameter. The change in length can be calculated using the formula:
ΔL = PL / AE
Where ΔL is the change in length, P is the tensile load, L is the length of the rod, A is the cross-sectional area of the rod, and E is the Young's modulus.
However, the change in diameter cannot be calculated using this formula alone. We need to consider the effect of Poisson's ratio and shear modulus on the change in diameter.
Poisson's Ratio:
Poisson's ratio is the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain when a material is subjected to a tensile load. It is denoted by the symbol ν (nu). Poisson's ratio is a measure of how much a material will compress in the transverse direction when it is stretched in the axial direction.
The formula for Poisson's ratio is:
ν = -εt / εa
Where ν is Poisson's ratio, εt is the transverse strain, and εa is the axial strain.
The transverse strain can be calculated using the formula:
εt = -ν εa
In the case of a rod under tensile load, the transverse strain can be considered as the change in diameter.
Shear Modulus:
Shear modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to shearing forces. It is denoted by the symbol G. Shear modulus is a measure of how much a material will deform when it is subjected to a shearing force.
The formula for shear modulus is:
G = τ / γ
Where G is the shear modulus, τ is the shearing stress, and γ is the shearing strain.
In the case of a rod under tensile load, the shearing stress can be considered as the force acting parallel to the cross-section of the rod and the shearing strain can be considered as the change in diameter.
Conclusion:
To calculate the change in diameter of a rod under tensile load, we need to consider the effect of Poisson's ratio and shear modulus, in addition to Young's modulus. Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Both Young's modulus and shear modulus.
When a rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P, it will experience a change in both length and diameter. The change in length can be calculated using the formula:
ΔL = PL / AE
Where ΔL is the change in length, P is the tensile load, L is the length of the rod, A is the cross-sectional area of the rod, and E is the Young's modulus.
However, the change in diameter cannot be calculated using this formula alone. We need to consider the effect of Poisson's ratio and shear modulus on the change in diameter.
Poisson's Ratio:
Poisson's ratio is the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain when a material is subjected to a tensile load. It is denoted by the symbol ν (nu). Poisson's ratio is a measure of how much a material will compress in the transverse direction when it is stretched in the axial direction.
The formula for Poisson's ratio is:
ν = -εt / εa
Where ν is Poisson's ratio, εt is the transverse strain, and εa is the axial strain.
The transverse strain can be calculated using the formula:
εt = -ν εa
In the case of a rod under tensile load, the transverse strain can be considered as the change in diameter.
Shear Modulus:
Shear modulus is a measure of a material's resistance to shearing forces. It is denoted by the symbol G. Shear modulus is a measure of how much a material will deform when it is subjected to a shearing force.
The formula for shear modulus is:
G = τ / γ
Where G is the shear modulus, τ is the shearing stress, and γ is the shearing strain.
In the case of a rod under tensile load, the shearing stress can be considered as the force acting parallel to the cross-section of the rod and the shearing strain can be considered as the change in diameter.
Conclusion:
To calculate the change in diameter of a rod under tensile load, we need to consider the effect of Poisson's ratio and shear modulus, in addition to Young's modulus. Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Both Young's modulus and shear modulus.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A rod of length L and diameter D is subjected to a tensile load P. Which of the following is sufficient to calculate the resulting change in diameter?a)Young's modulusb)Shear modulusc)Poisson's ratiod)Both Young's modulus and shear modulusCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























