Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Questions > What is different between computers organisat...
Start Learning for Free
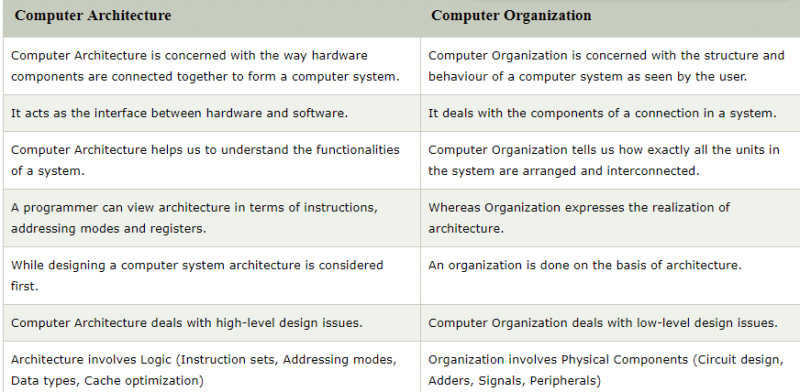
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?
Verified Answer
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Computer Science Engineering (CSE) courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Computer Science Engineering (CSE) courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?
Computer Organization
Definition:
Computer organization refers to the way a computer's hardware components work together to perform tasks and execute instructions. It focuses on the physical aspects of a computer system, including the design and arrangement of its components.
Components:
1. Memory: It is responsible for storing and retrieving data and instructions.
2. Processor: Also known as the central processing unit (CPU), it carries out instructions and performs calculations.
3. Input and Output: These components facilitate communication between the computer and external devices, such as keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers.
4. Control Unit: It manages the flow of instructions and data within the computer system.
5. Bus: This component enables communication between different hardware components.
Functionality:
1. Instruction Execution: Computer organization determines how instructions are fetched, decoded, and executed by the processor.
2. Data Storage and Access: It defines how data is stored in memory and accessed by the processor.
3. Input and Output Operations: Computer organization determines how input and output devices communicate with the processor and memory.
Performance Optimization:
Computer organization plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of a computer system. By designing efficient memory hierarchies, utilizing parallel processing techniques, and optimizing data transfer rates, the overall performance of the system can be improved.
Computer Architecture
Definition:
Computer architecture refers to the conceptual structure and functional behavior of a computer system. It focuses on the logical design and implementation of a computer's hardware and software interface.
Design Principles:
1. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): It defines the set of instructions that a processor can execute and the addressing modes available.
2. Memory Hierarchy: It involves the organization of memory into multiple levels, such as cache, main memory, and secondary storage, to improve performance.
3. Pipeline Processing: It involves breaking down instructions into smaller stages and executing them concurrently to improve throughput.
4. Parallel Processing: It involves the use of multiple processors or cores to execute instructions simultaneously, enhancing performance.
Software and Hardware Interface:
Computer architecture defines the interface between the software and hardware components of a computer system. It specifies how programs interact with the processor, memory, and input/output devices.
Role in Performance Optimization:
Computer architecture plays a crucial role in optimizing performance by designing efficient instruction sets, memory hierarchies, and parallel processing techniques. It also considers factors such as power consumption, scalability, and reliability.
In summary, computer organization focuses on the physical aspects and interconnections of a computer's hardware components, while computer architecture deals with the logical design, interface, and functionality of the system. Both disciplines are essential for understanding and designing efficient and high-performance computer systems.
Definition:
Computer organization refers to the way a computer's hardware components work together to perform tasks and execute instructions. It focuses on the physical aspects of a computer system, including the design and arrangement of its components.
Components:
1. Memory: It is responsible for storing and retrieving data and instructions.
2. Processor: Also known as the central processing unit (CPU), it carries out instructions and performs calculations.
3. Input and Output: These components facilitate communication between the computer and external devices, such as keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers.
4. Control Unit: It manages the flow of instructions and data within the computer system.
5. Bus: This component enables communication between different hardware components.
Functionality:
1. Instruction Execution: Computer organization determines how instructions are fetched, decoded, and executed by the processor.
2. Data Storage and Access: It defines how data is stored in memory and accessed by the processor.
3. Input and Output Operations: Computer organization determines how input and output devices communicate with the processor and memory.
Performance Optimization:
Computer organization plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of a computer system. By designing efficient memory hierarchies, utilizing parallel processing techniques, and optimizing data transfer rates, the overall performance of the system can be improved.
Computer Architecture
Definition:
Computer architecture refers to the conceptual structure and functional behavior of a computer system. It focuses on the logical design and implementation of a computer's hardware and software interface.
Design Principles:
1. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): It defines the set of instructions that a processor can execute and the addressing modes available.
2. Memory Hierarchy: It involves the organization of memory into multiple levels, such as cache, main memory, and secondary storage, to improve performance.
3. Pipeline Processing: It involves breaking down instructions into smaller stages and executing them concurrently to improve throughput.
4. Parallel Processing: It involves the use of multiple processors or cores to execute instructions simultaneously, enhancing performance.
Software and Hardware Interface:
Computer architecture defines the interface between the software and hardware components of a computer system. It specifies how programs interact with the processor, memory, and input/output devices.
Role in Performance Optimization:
Computer architecture plays a crucial role in optimizing performance by designing efficient instruction sets, memory hierarchies, and parallel processing techniques. It also considers factors such as power consumption, scalability, and reliability.
In summary, computer organization focuses on the physical aspects and interconnections of a computer's hardware components, while computer architecture deals with the logical design, interface, and functionality of the system. Both disciplines are essential for understanding and designing efficient and high-performance computer systems.
Attention Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Computer Science Engineering (CSE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Computer Science Engineering (CSE).

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Similar Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Doubts
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?
Question Description
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?.
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?.
Solutions for What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is different between computers organisation and architecture ?, a detailed solution for What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? has been provided alongside types of What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is different between computers organisation and architecture ? tests, examples and also practice Computer Science Engineering (CSE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























