Economics Exam > Economics Questions > Explain one process of price determination un...
Start Learning for Free
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule
?
?
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition w...
Price Determination under Perfect Competition:
Under perfect competition, many factors influence the determination of the price of goods. In this article, we will look at the equilibrium of the industry and the equilibrium of a firm as important factors behind price determination under perfect competition.
Equilibrium of the Industry under Perfect Competition:
In economic terms, an industry consists of many independent firms. Each firm has a number of factories, farms or mines, as required. Each such firm in industry produces a homogeneous product. Equilibrium of the industry happens when the total output of the industry is equal to the total demand. In such a scenario, the prevailing price of a commodity is its equilibrium price.
We know that under competitive conditions, the interaction of demand and supply determines the equilibrium price as shown below:
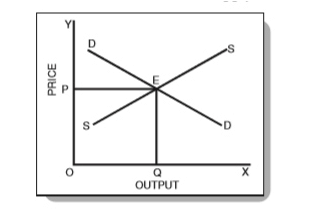
In Fig. 1 above, OP is the equilibrium price. Further, OQ is the equilibrium quantity sold at that price. Now, the equilibrium price is the price at which both the demand and supply are equal. In other words, no buyer, who wanted to buy at that price, goes dissatisfied and no seller, who wanted to sell his goods at that price, goes dissatisfied either.
Note that with the demand remaining the same, if the price is higher or lower than OP, then the market is not in equilibrium. Also, if goods are lesser or higher than the demand, the equilibrium is not attained.
Equilibrium of the Firm under Perfect Competition
A firm is in equilibrium when it maximizes its profits. Hence, the output that offers maximum profit to a firm is the equilibrium output. When a firm is in equilibrium, there is no reason to increase or decrease the output.
In a competitive market, firms are price-takers. The reason being the presence of a large number of firms who produce homogeneous products. Therefore, firms cannot influence the price in their individual capacities. They have to follow the price determined by the industry.
The following figure shows a firm’s demand curve under perfect competition:
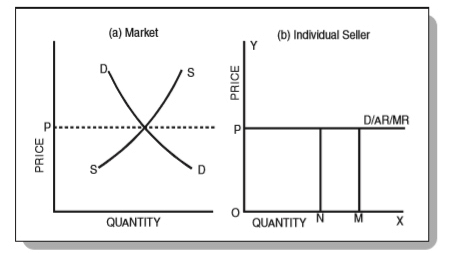
From Fig. 2 above, you can see that the industry price, OP, is fixed throughout the interaction of demand and supply of the industry. Firms have to accept this price. Hence, they are price-takers and not price-makers. Hence, they cannot increase or decrease the price OP.
Therefore, the line P acts as a demand curve for such firms. Hence, in perfect competition, the demand curve of an individual firm is a horizontal line at the level of the industry-set market price. Firms have to choose the level of output that yields maximum profit.
Conditions for the equilibrium of a firm
To attain an equilibrium position, a firm must satisfy the following two conditions:
1.They must ensure that the marginal revenue is equal to the marginal cost (MR = MC).
a.If MR > MC, the firm has an incentive to expand its production and sell additional units.
b.If MR < MC, the firm must reduce the output since additional units add more cost than revenue.
c.The firm gets maximum profits only when MR = MC.
2.The MC curve must have a positive slope and cut the MR curve from below.
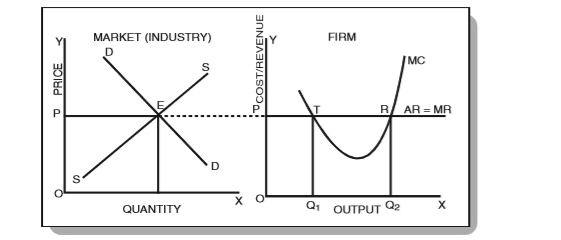
In Fig. 3 above, DD is the demand curve and SS is the supply curve. They equilibrate at point E and set the market price as OP. Under perfect competition, firms adopt OP as the industry price and consider the P-line as the demand curve or AR – average revenue curve (perfectly elastic at P).
Since all units are equally priced, the MR curve is a horizontal line and is equal to the AR line. Observe that the curve MC cuts the MR curve at two points – T and R. At point T, the MC curve cuts the MR curve from above whereas at point R it cuts the MR curve from below. Therefore, according to the conditions of equilibrium of a firm, point R is the point of equilibrium and OQ2 is the equilibrium level of output.
Community Answer
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition w...
Process of Price Determination Under Perfect Competition
The process of price determination under perfect competition is driven by the interaction of demand and supply in the market. In a perfectly competitive market, there are numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, and free entry and exit of firms. This leads to a situation where no individual buyer or seller has the power to influence the market price.
Supply Schedule:
The supply schedule represents the relationship between the quantity of a product supplied by producers and the corresponding prices at which they are willing to sell. The supply schedule is typically upward sloping, indicating that as the price of the product increases, producers are willing to supply more of it.
For example, let's consider the supply schedule for wheat:
Price per bushel (in $) | Quantity supplied (in bushels)
--------------------------------------------------------
5 | 100
10 | 200
15 | 300
20 | 400
25 | 500
In the above schedule, as the price of wheat increases from $5 to $25, the quantity supplied increases from 100 bushels to 500 bushels.
Demand Schedule:
The demand schedule represents the relationship between the quantity of a product demanded by buyers and the corresponding prices at which they are willing to purchase. The demand schedule is typically downward sloping, indicating that as the price of the product decreases, buyers are willing to purchase more of it.
Let's consider the demand schedule for wheat:
Price per bushel (in $) | Quantity demanded (in bushels)
--------------------------------------------------------
25 | 100
20 | 200
15 | 300
10 | 400
5 | 500
In the above schedule, as the price of wheat decreases from $25 to $5, the quantity demanded increases from 100 bushels to 500 bushels.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity:
The equilibrium price and quantity are determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves. It is the price and quantity at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
Equilibrium is reached when the market clears, i.e., there is no excess demand or excess supply. At any price above the equilibrium price, there will be excess supply, and at any price below the equilibrium price, there will be excess demand.
In the diagram below, the demand curve (D) and supply curve (S) intersect at point E, determining the equilibrium price (P*) and equilibrium quantity (Q*) of wheat.
[Diagram]
At the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded by buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers. Any deviation from this equilibrium price will result in market forces pushing the price back towards the equilibrium.
Conclusion:
The process of price determination under perfect competition involves the interaction of demand and supply. The supply schedule represents the quantity of a product supplied at different prices, while the demand schedule represents the quantity demanded at different prices. The equilibrium price and quantity are determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves, where there is no excess demand or supply. This process ensures that the market operates efficiently and allocates resources effectively.
The process of price determination under perfect competition is driven by the interaction of demand and supply in the market. In a perfectly competitive market, there are numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, and free entry and exit of firms. This leads to a situation where no individual buyer or seller has the power to influence the market price.
Supply Schedule:
The supply schedule represents the relationship between the quantity of a product supplied by producers and the corresponding prices at which they are willing to sell. The supply schedule is typically upward sloping, indicating that as the price of the product increases, producers are willing to supply more of it.
For example, let's consider the supply schedule for wheat:
Price per bushel (in $) | Quantity supplied (in bushels)
--------------------------------------------------------
5 | 100
10 | 200
15 | 300
20 | 400
25 | 500
In the above schedule, as the price of wheat increases from $5 to $25, the quantity supplied increases from 100 bushels to 500 bushels.
Demand Schedule:
The demand schedule represents the relationship between the quantity of a product demanded by buyers and the corresponding prices at which they are willing to purchase. The demand schedule is typically downward sloping, indicating that as the price of the product decreases, buyers are willing to purchase more of it.
Let's consider the demand schedule for wheat:
Price per bushel (in $) | Quantity demanded (in bushels)
--------------------------------------------------------
25 | 100
20 | 200
15 | 300
10 | 400
5 | 500
In the above schedule, as the price of wheat decreases from $25 to $5, the quantity demanded increases from 100 bushels to 500 bushels.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity:
The equilibrium price and quantity are determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves. It is the price and quantity at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
Equilibrium is reached when the market clears, i.e., there is no excess demand or excess supply. At any price above the equilibrium price, there will be excess supply, and at any price below the equilibrium price, there will be excess demand.
In the diagram below, the demand curve (D) and supply curve (S) intersect at point E, determining the equilibrium price (P*) and equilibrium quantity (Q*) of wheat.
[Diagram]
At the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded by buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers. Any deviation from this equilibrium price will result in market forces pushing the price back towards the equilibrium.
Conclusion:
The process of price determination under perfect competition involves the interaction of demand and supply. The supply schedule represents the quantity of a product supplied at different prices, while the demand schedule represents the quantity demanded at different prices. The equilibrium price and quantity are determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves, where there is no excess demand or supply. This process ensures that the market operates efficiently and allocates resources effectively.

|
Explore Courses for Economics exam
|

|
Similar Economics Doubts
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule?
Question Description
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? for Economics 2025 is part of Economics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Economics exam syllabus. Information about Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? covers all topics & solutions for Economics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule?.
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? for Economics 2025 is part of Economics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Economics exam syllabus. Information about Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? covers all topics & solutions for Economics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule?.
Solutions for Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Economics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Economics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule?, a detailed solution for Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? has been provided alongside types of Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain one process of price determination under perfect competition with the help of diagram and schedule? tests, examples and also practice Economics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Economics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















