Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniforml...
Start Learning for Free
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now be
- a)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3
- b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2
- c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3
- d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive ch...
Please refer to the figure below..
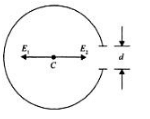
Initially the charge on the ring was 'Q' and we now have removed a section of the ring of length 'd', as shown above.
Now, the charge in the removed section will be
q = Q.(d/2πR)
it stems from the fact that the (linear) charge density remains the same in both the ring and the removed section [q/d = Q/2πR]
The electric field at the center would be zero as it gets cancelled out. After removing the section we have to fields being developed; E1 and E2.
Here,
E1 is the electric field due to the removed section
and
E2 is the electric field due to the remaining ring
Now, for the net electric field at the center to be zero,
E1 = E2
or
E2 = kq/R^2
so, [ q = Q.(d/2πR)]
E2 = kQd / 2πR^3
thus,
electric field is directed towards the gap and is proportional to R^3, so
correct answer - option (a)
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive ch...
Since the ring has uniform charge distribution, we can treat it as a collection of infinitesimally small charged elements. Let's consider an element of length $dl$ on the ring, and let its position be denoted by the angle $\theta$ (measured from some reference point on the ring). The charge on this element is then:
$$dq = \frac{Q}{2\pi R} dl$$
where $\frac{Q}{2\pi R}$ is the charge density of the ring.
Now, let's consider the electric field due to this element at a point P located a distance $x$ from the center of the ring, as shown in the diagram below:

The electric field due to this element can be found using Coulomb's law:
$$dE = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{dq}{r^2}$$
where $r$ is the distance from the element to point P. Using the diagram, we can see that:
$$r^2 = x^2 + R^2 - 2xR\cos\theta$$
Substituting in the expressions for $dq$ and $r^2$ and integrating over the length of the ring, we get:
$$E = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \int_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2} \frac{Q}{2\pi R} \frac{dl}{(x^2 + R^2 - 2xR\cos\theta)^{3/2}}$$
where $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$ are the angles corresponding to the beginning and end of the removed section of the ring.
To evaluate this integral, we can make use of the substitution $u = \cos\theta$, $du = -\sin\theta d\theta$, and the fact that $dl = Rd\theta$. This gives:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R} \int_{-1}^{a} \frac{Rd\theta}{(x^2 + R^2 - 2xRu)^{3/2}}$$
where $a = \cos(\theta_1)$, and we've used the fact that $\cos(\theta_2) = \cos(\theta_1 + d) = \cos(\theta_1)$, since $d$ is small.
Making the substitution $t = x/Ru$, we get:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R^2} \int_{x/R}^{x/(R\cos\theta_1)} \frac{dt}{(1 + t^2 - 2t)^{3/2}}$$
Simplifying the denominator using the identity $1 - 2t + t^2 = (1-t)^2$, we get:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R^2} \int_{x/R}^{x/(R\cos\theta_1)} \frac{dt}{
$$dq = \frac{Q}{2\pi R} dl$$
where $\frac{Q}{2\pi R}$ is the charge density of the ring.
Now, let's consider the electric field due to this element at a point P located a distance $x$ from the center of the ring, as shown in the diagram below:

The electric field due to this element can be found using Coulomb's law:
$$dE = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{dq}{r^2}$$
where $r$ is the distance from the element to point P. Using the diagram, we can see that:
$$r^2 = x^2 + R^2 - 2xR\cos\theta$$
Substituting in the expressions for $dq$ and $r^2$ and integrating over the length of the ring, we get:
$$E = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \int_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2} \frac{Q}{2\pi R} \frac{dl}{(x^2 + R^2 - 2xR\cos\theta)^{3/2}}$$
where $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$ are the angles corresponding to the beginning and end of the removed section of the ring.
To evaluate this integral, we can make use of the substitution $u = \cos\theta$, $du = -\sin\theta d\theta$, and the fact that $dl = Rd\theta$. This gives:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R} \int_{-1}^{a} \frac{Rd\theta}{(x^2 + R^2 - 2xRu)^{3/2}}$$
where $a = \cos(\theta_1)$, and we've used the fact that $\cos(\theta_2) = \cos(\theta_1 + d) = \cos(\theta_1)$, since $d$ is small.
Making the substitution $t = x/Ru$, we get:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R^2} \int_{x/R}^{x/(R\cos\theta_1)} \frac{dt}{(1 + t^2 - 2t)^{3/2}}$$
Simplifying the denominator using the identity $1 - 2t + t^2 = (1-t)^2$, we get:
$$E = -\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{Q}{2\pi R^2} \int_{x/R}^{x/(R\cos\theta_1)} \frac{dt}{

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now bea)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















