Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both ena...
Start Learning for Free
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give
- a)a pure enantiomer
- b)a racemic mixture
- c)a pair of diastereomers
- d)an achiral alcohol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereom...
Explanation:
Enantiomerism:
Enantiomerism refers to the phenomenon where two molecules are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. In this case, compound A shows enantiomerism, which means it exists in two different mirror-image forms.
Diastereomerism:
Diastereomerism refers to the phenomenon where two molecules have the same connectivity but are not mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. In this case, compound A shows diastereomerism, which means it exists in multiple forms that are not mirror images of each other.
Reaction 1: Treatment of A with Na2CrO4/Dil. H2SO4:
When compound A is treated with Na2CrO4 and dilute H2SO4, it undergoes oxidation reaction and gives compound B. The reaction is as follows:
C7H16O (A) + Na2CrO4 / Dil. H2SO4 → C7H14O (B)
Reaction 2: Dehydration of A with concentrated H2SO4:
When compound A is dehydrated with concentrated H2SO4, it undergoes elimination reaction and gives a single alkene C. The reaction is as follows:
C7H16O (A) + H2SO4 (conc.) → C7H14 (C)
Reaction 3: Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O:
When alkene C is subjected to ozonolysis followed by treatment with Zn-H2O, it undergoes oxidative cleavage and gives compound D as one of the products. The reaction is as follows:
C7H14 (C) + O3 → C5H10O (D)
Reaction 4: Reduction of D with NaBH4:
When compound D is reduced with NaBH4, it undergoes reduction reaction and gives a racemic mixture. This means that both enantiomers of D are formed in equal amounts. The reaction is as follows:
C5H10O (D) + NaBH4 → Racemic mixture of D
Reaction 5: Reduction of B with LiAlH4 followed by acid hydrolysis:
When compound B is reduced with LiAlH4 followed by acid hydrolysis, it undergoes reduction reaction and gives a pair of diastereomers. This means that two different diastereomers of B are formed. The reaction is as follows:
C7H14O (B) + LiAlH4 → Diastereomers of B
Therefore, the correct answer is option c) a pair of diastereomers.
Enantiomerism:
Enantiomerism refers to the phenomenon where two molecules are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. In this case, compound A shows enantiomerism, which means it exists in two different mirror-image forms.
Diastereomerism:
Diastereomerism refers to the phenomenon where two molecules have the same connectivity but are not mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. In this case, compound A shows diastereomerism, which means it exists in multiple forms that are not mirror images of each other.
Reaction 1: Treatment of A with Na2CrO4/Dil. H2SO4:
When compound A is treated with Na2CrO4 and dilute H2SO4, it undergoes oxidation reaction and gives compound B. The reaction is as follows:
C7H16O (A) + Na2CrO4 / Dil. H2SO4 → C7H14O (B)
Reaction 2: Dehydration of A with concentrated H2SO4:
When compound A is dehydrated with concentrated H2SO4, it undergoes elimination reaction and gives a single alkene C. The reaction is as follows:
C7H16O (A) + H2SO4 (conc.) → C7H14 (C)
Reaction 3: Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O:
When alkene C is subjected to ozonolysis followed by treatment with Zn-H2O, it undergoes oxidative cleavage and gives compound D as one of the products. The reaction is as follows:
C7H14 (C) + O3 → C5H10O (D)
Reaction 4: Reduction of D with NaBH4:
When compound D is reduced with NaBH4, it undergoes reduction reaction and gives a racemic mixture. This means that both enantiomers of D are formed in equal amounts. The reaction is as follows:
C5H10O (D) + NaBH4 → Racemic mixture of D
Reaction 5: Reduction of B with LiAlH4 followed by acid hydrolysis:
When compound B is reduced with LiAlH4 followed by acid hydrolysis, it undergoes reduction reaction and gives a pair of diastereomers. This means that two different diastereomers of B are formed. The reaction is as follows:
C7H14O (B) + LiAlH4 → Diastereomers of B
Therefore, the correct answer is option c) a pair of diastereomers.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereom...
Since, A is completely saturated, it must contain more than one chiral carbon atoms in order to show both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Also, C on ozonolysis gives D (C5H10O) as one product, other product must be CH3SHO. Hence, C must be 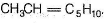
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.
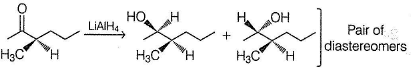
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B(C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2Ogives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q.If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will givea)a pure enantiomerb)a racemic mixturec)a pair of diastereomersd)an achiral alcoholCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























