Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 1...
Start Learning for Free
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.
Passage
In octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g. The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.
Q.
The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field is
- a)-1.6 Δo
- b)-2.0 Δo
- c)-2.4 Δo
- d)-1.8 Δo
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains ...
The total crystal field stabilisation energy is given by CFSE(octahedral) = 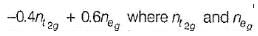 are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.
are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.
For d7 in strong field,
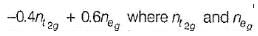 are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.
are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.For d7 in strong field,
CFSE = -0.4 x 6 + 0.6 x 1 = -2.4 + 0.6 = -1.8Δo
Most Upvoted Answer
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains ...
CFSE for d7 configuration in octahedral complexes with strong ligand field is -1.8 o.
Explanation:
CFSE (Crystal Field Stabilization Energy) is the energy difference between the two sets of d-orbitals (eg and t2g) in octahedral complexes. The magnitude of CFSE depends on the nature of ligands.
In octahedral complexes, the d-orbitals split into two sets due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals. The eg set consists of two orbitals of higher energy, while the t2g set consists of three orbitals of lower energy.
For a d7 configuration, there are 7 electrons in the d-orbitals. In a strong ligand field, the electrons will preferentially occupy the lower energy t2g orbitals due to the strong interaction with the ligands. This leads to a lower energy state, resulting in a negative CFSE.
The magnitude of CFSE for a d7 configuration in a strong ligand field is -1.8 o. This value indicates the stabilization energy gained by the system due to the splitting of d-orbitals and the arrangement of electrons in the t2g set.
The negative value of CFSE indicates that the energy of the system is lowered due to the interaction between the ligands and the d-orbitals. This stabilization energy is a result of the electrostatic interactions between the ligands and the metal cation.
In summary, the CFSE for a d7 configuration in octahedral complexes with a strong ligand field is -1.8 o. This negative value signifies the lowering of energy and stabilization of the system due to the splitting of d-orbitals and the arrangement of electrons in the t2g set.
Explanation:
CFSE (Crystal Field Stabilization Energy) is the energy difference between the two sets of d-orbitals (eg and t2g) in octahedral complexes. The magnitude of CFSE depends on the nature of ligands.
In octahedral complexes, the d-orbitals split into two sets due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals. The eg set consists of two orbitals of higher energy, while the t2g set consists of three orbitals of lower energy.
For a d7 configuration, there are 7 electrons in the d-orbitals. In a strong ligand field, the electrons will preferentially occupy the lower energy t2g orbitals due to the strong interaction with the ligands. This leads to a lower energy state, resulting in a negative CFSE.
The magnitude of CFSE for a d7 configuration in a strong ligand field is -1.8 o. This value indicates the stabilization energy gained by the system due to the splitting of d-orbitals and the arrangement of electrons in the t2g set.
The negative value of CFSE indicates that the energy of the system is lowered due to the interaction between the ligands and the d-orbitals. This stabilization energy is a result of the electrostatic interactions between the ligands and the metal cation.
In summary, the CFSE for a d7 configuration in octahedral complexes with a strong ligand field is -1.8 o. This negative value signifies the lowering of energy and stabilization of the system due to the splitting of d-orbitals and the arrangement of electrons in the t2g set.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.PassageIn octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g.The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.Q.The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field isa)-1.6 Δob)-2.0 Δoc)-2.4 Δod)-1.8 ΔoCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















