Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Which cell organelle is the carrier of power ...
Start Learning for Free
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria?
Verified Answer
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondr...
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are rod-shaped organelles that can be considered the power generators of the cell, converting oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the chemical energy "currency" of the cell that powers the cell's metabolic activities. This process is called aerobic respiration and is the reason animals breathe oxygen. Without mitochondria (singular, mitochondrion), higher animals would likely not exist because their cells would only be able to obtain energy from anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen), a process much less efficient than aerobic respiration. In fact, mitochondria enable cells to produce 15 times more ATP than they could otherwise, and complex animals, like humans, need large amounts of energy in order to survive.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondr...
The cell organelle that serves as the carrier of power synthesized by mitochondria is the Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP is often referred to as the "molecular currency" of the cell as it provides the necessary energy for various cellular processes.
Mitochondria and ATP Production:
1. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell and play a crucial role in cellular respiration.
2. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients, such as glucose, into usable energy in the form of ATP.
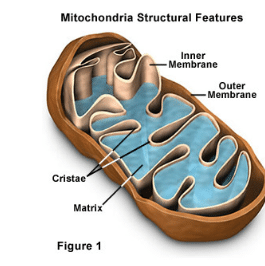
3. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that is highly folded, forming structures called cristae.
4. These cristae increase the surface area available for ATP production.
5. Within the mitochondria, there are various enzymes and proteins involved in the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis.
ATP Structure and Function:
1. ATP is composed of three main components: a sugar molecule called ribose, a nitrogenous base called adenine, and three phosphate groups.
2. The energy stored in ATP is primarily in the phosphate bonds.
3. When one phosphate group is cleaved from ATP, it forms Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) and releases energy.
4. The energy released is used by the cell to perform various functions such as muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules.
Role of ATP in Cellular Processes:
1. ATP is required for mechanical work, such as muscle contraction and movement of flagella and cilia.
2. It is involved in active transport processes, where molecules are transported against their concentration gradient.
3. ATP provides the energy required for biosynthetic reactions, including the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other macromolecules.
4. It plays a crucial role in signal transduction pathways, allowing cells to respond to external signals.
5. ATP is also involved in the maintenance of cell membrane potential and electrical signaling within the nervous system.
Conclusion:
The carrier of power synthesized by mitochondria is ATP. Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration, and ATP serves as the primary energy currency within the cell. ATP provides energy for various cellular processes, including mechanical work, active transport, biosynthesis, and signal transduction.
Mitochondria and ATP Production:
1. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell and play a crucial role in cellular respiration.
2. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients, such as glucose, into usable energy in the form of ATP.
3. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that is highly folded, forming structures called cristae.
4. These cristae increase the surface area available for ATP production.
5. Within the mitochondria, there are various enzymes and proteins involved in the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis.
ATP Structure and Function:
1. ATP is composed of three main components: a sugar molecule called ribose, a nitrogenous base called adenine, and three phosphate groups.
2. The energy stored in ATP is primarily in the phosphate bonds.
3. When one phosphate group is cleaved from ATP, it forms Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) and releases energy.
4. The energy released is used by the cell to perform various functions such as muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules.
Role of ATP in Cellular Processes:
1. ATP is required for mechanical work, such as muscle contraction and movement of flagella and cilia.
2. It is involved in active transport processes, where molecules are transported against their concentration gradient.
3. ATP provides the energy required for biosynthetic reactions, including the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other macromolecules.
4. It plays a crucial role in signal transduction pathways, allowing cells to respond to external signals.
5. ATP is also involved in the maintenance of cell membrane potential and electrical signaling within the nervous system.
Conclusion:
The carrier of power synthesized by mitochondria is ATP. Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration, and ATP serves as the primary energy currency within the cell. ATP provides energy for various cellular processes, including mechanical work, active transport, biosynthesis, and signal transduction.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria?
Question Description
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria?.
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria?.
Solutions for Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria?, a detailed solution for Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? has been provided alongside types of Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which cell organelle is the carrier of power synthesised by mitochondria? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























