Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Describe the structure of cardic muscle?
Start Learning for Free
Describe the structure of cardic muscle?
Most Upvoted Answer
Describe the structure of cardic muscle?
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells. These cells, unlike skeletal muscle cells, are typically unicellular and connect to one another through special intercalated discs. These specialized cell junction and the arrangement of muscle cells enables cardiac muscle to contract quickly and repeatedly, forcing blood throughout the body.
Cardiac Muscle Structure
Cardiac muscle exists only within the heart of animals. It is a specialized form of muscle evolved to continuously and repeatedly contract, providing circulation of blood throughout the body. The heart is a relatively simple organ. Through all the twists and turns and various chambers, there are only three layers. The outer layer, known as the epicardium or visceral pericardium, surround the cardiac muscle on the exterior. This helps protect it from contact with other organs. The parietal pericardium attaches to this outer layer creates a fluid-filled layer which helps lubricate the heart. The inner layer, or endocardium, separates the muscle from the blood it is pumping within the chambers of the heart. In between these two sheets lies the cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is sometimes referred to as myocardium. This can be seen in the image below.
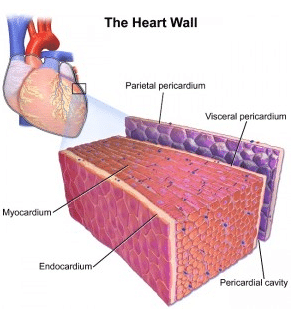
When we look a bit closer at cardiac muscle, we can see that it is arranged in sheets of cells, which are connected to each other in a lattice-work fashion. Where two cells meet a specialized junction called an intercalated disc locks the two cells into place. While this region looks like a dark disc under the microscope, it is actually the interlocking of hundreds of finger-like projections from each cell. These projections have small holes in them, gap junctions, which can pass the impulse to contract to connected cells. Interlaced between and around these cells are nerves and blood vessels, which carry signals and oxygen to the cardiac muscle.
Community Answer
Describe the structure of cardic muscle?
Cardiac muscle tissue is made up of many interlocking cardiac muscle cells, or fibers, that give the tissue its properties.,,, Each cardiac muscle fiber contains a single nucleus and is striated, or striped, because it appears to have light and dark bands when seen through a microscope...

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Question Description
Describe the structure of cardic muscle? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Describe the structure of cardic muscle? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describe the structure of cardic muscle?.
Describe the structure of cardic muscle? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Describe the structure of cardic muscle? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describe the structure of cardic muscle?.
Solutions for Describe the structure of cardic muscle? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Describe the structure of cardic muscle? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Describe the structure of cardic muscle?, a detailed solution for Describe the structure of cardic muscle? has been provided alongside types of Describe the structure of cardic muscle? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Describe the structure of cardic muscle? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















