Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to g...
Start Learning for Free
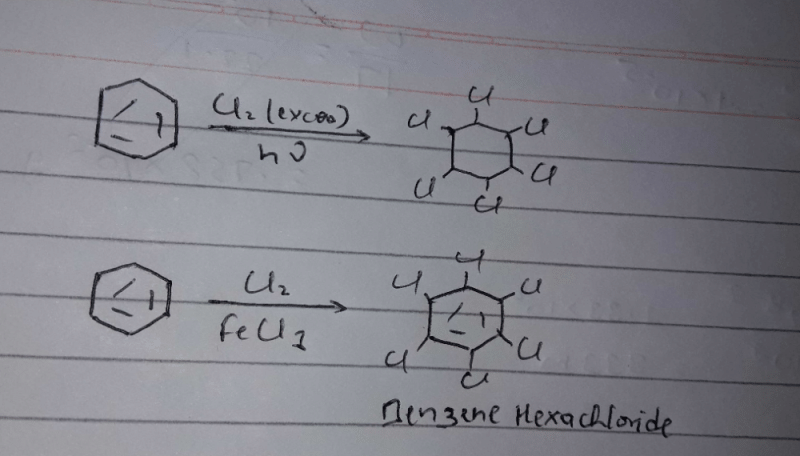
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final product
- a)C6H5Cl
- b)C6H6Cl6
- c)CCl4
- d)c6Cl6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5...
The reaction occurs as follows:
C6H6 + Cl2 ---------> C6H6Cl6
This is a free radical reaction, in presence of sunlight Cl2 undergoes homolytic fission to give 2 Cl radicals which add to the benzene ring.
Most Upvoted Answer
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5...
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5...
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final product C6H6Cl6.
Explanation:
When benzene (C6H6) reacts with chlorine (Cl2) in the presence of sunlight, it undergoes a substitution reaction known as chlorination. This reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Here is the step-by-step mechanism of the reaction:
1. Initiation:
- In the presence of sunlight, chlorine molecules (Cl2) dissociate homolytically to form chlorine radicals (Cl•).
2. Propagation:
- The chlorine radical (Cl•) attacks the benzene molecule (C6H6), forming a sigma complex.
- The sigma complex is an intermediate in which one of the carbon-hydrogen bonds in benzene is replaced by a carbon-chlorine bond.
- The sigma complex is resonance-stabilized, resulting in the delocalization of the positive charge on the carbon atom.
3. Termination:
- The sigma complex undergoes deprotonation, resulting in the formation of a chlorobenzene molecule (C6H5Cl) and a hydrogen chloride molecule (HCl).
- The chlorine radical (Cl•) generated in the previous step can initiate further chlorination reactions by attacking other benzene molecules, leading to the formation of additional chlorobenzene molecules.
Overall, the reaction proceeds through multiple substitution steps until all six hydrogen atoms in benzene are replaced by chlorine atoms. As a result, the final product obtained is hexachlorobenzene (C6H6Cl6).
The correct answer is option B: C6H6Cl6, which represents hexachlorobenzene.
Explanation:
When benzene (C6H6) reacts with chlorine (Cl2) in the presence of sunlight, it undergoes a substitution reaction known as chlorination. This reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Here is the step-by-step mechanism of the reaction:
1. Initiation:
- In the presence of sunlight, chlorine molecules (Cl2) dissociate homolytically to form chlorine radicals (Cl•).
2. Propagation:
- The chlorine radical (Cl•) attacks the benzene molecule (C6H6), forming a sigma complex.
- The sigma complex is an intermediate in which one of the carbon-hydrogen bonds in benzene is replaced by a carbon-chlorine bond.
- The sigma complex is resonance-stabilized, resulting in the delocalization of the positive charge on the carbon atom.
3. Termination:
- The sigma complex undergoes deprotonation, resulting in the formation of a chlorobenzene molecule (C6H5Cl) and a hydrogen chloride molecule (HCl).
- The chlorine radical (Cl•) generated in the previous step can initiate further chlorination reactions by attacking other benzene molecules, leading to the formation of additional chlorobenzene molecules.
Overall, the reaction proceeds through multiple substitution steps until all six hydrogen atoms in benzene are replaced by chlorine atoms. As a result, the final product obtained is hexachlorobenzene (C6H6Cl6).
The correct answer is option B: C6H6Cl6, which represents hexachlorobenzene.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Benzene reacts with chlorine in sunlight to give a final producta)C6H5Clb)C6H6Cl6c)CCl4d)c6Cl6Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























