Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCO...
Start Learning for Free
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?
Most Upvoted Answer
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?
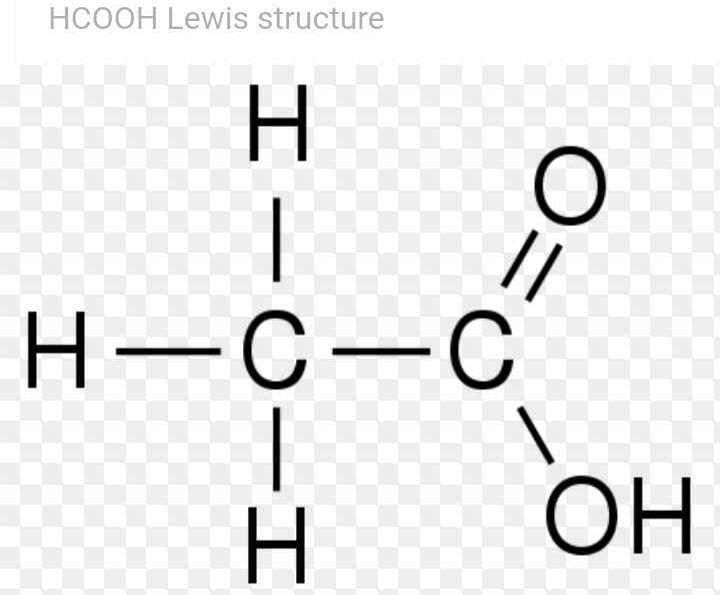
Community Answer
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?
Lewis Dot Structure for HCOOH
To draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH, we need to follow a set of rules. The Lewis dot structure is a visual representation of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule, using dots to represent the electrons. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to draw the Lewis dot structure for HCOOH:
Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
1. Start by determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. HCOOH consists of carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms.
2. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, oxygen has 6, and hydrogen has 1 each. In HCOOH, we have 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 2 hydrogen atoms.
3. The total number of valence electrons can be calculated by adding up the valence electrons of each atom: (4 for carbon) + (2 × 6 for oxygen) + (2 × 1 for hydrogen) = 14 valence electrons.
Place Atoms in the Structure
1. In HCOOH, carbon is the central atom because it can form multiple bonds. Hydrogen and oxygen will be placed around the carbon atom.
2. Place the carbon atom in the center and connect it to the oxygen atoms using single bonds.
3. The hydrogen atoms will be attached to the oxygen atoms.
Distribute Remaining Electrons
1. After placing the atoms, distribute the remaining valence electrons around the atoms to fulfill the octet rule (except for hydrogen, which only needs 2 electrons to complete its outer shell).
2. Start by adding lone pairs of electrons to the oxygen atoms until they have a total of 8 electrons.
3. Distribute the remaining electrons on the central carbon atom and make sure all atoms have their octet satisfied.
Check for Octet and Formal Charges
1. After distributing the electrons, check if all atoms have a complete octet (except for hydrogen, which only needs 2 electrons).
2. If there are any atoms that do not have an octet, move a lone pair from a neighboring atom to form a double bond.
3. Also, check for formal charges to ensure overall charge neutrality. Make sure the formal charges on each atom sum up to zero.
The Lewis dot structure for HCOOH will have the carbon atom in the center, bonded to both oxygen atoms with single bonds, and with hydrogen atoms attached to the oxygen atoms. The remaining valence electrons will be distributed as lone pairs and shared electrons to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
To draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH, we need to follow a set of rules. The Lewis dot structure is a visual representation of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule, using dots to represent the electrons. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to draw the Lewis dot structure for HCOOH:
Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
1. Start by determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. HCOOH consists of carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms.
2. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, oxygen has 6, and hydrogen has 1 each. In HCOOH, we have 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 2 hydrogen atoms.
3. The total number of valence electrons can be calculated by adding up the valence electrons of each atom: (4 for carbon) + (2 × 6 for oxygen) + (2 × 1 for hydrogen) = 14 valence electrons.
Place Atoms in the Structure
1. In HCOOH, carbon is the central atom because it can form multiple bonds. Hydrogen and oxygen will be placed around the carbon atom.
2. Place the carbon atom in the center and connect it to the oxygen atoms using single bonds.
3. The hydrogen atoms will be attached to the oxygen atoms.
Distribute Remaining Electrons
1. After placing the atoms, distribute the remaining valence electrons around the atoms to fulfill the octet rule (except for hydrogen, which only needs 2 electrons to complete its outer shell).
2. Start by adding lone pairs of electrons to the oxygen atoms until they have a total of 8 electrons.
3. Distribute the remaining electrons on the central carbon atom and make sure all atoms have their octet satisfied.
Check for Octet and Formal Charges
1. After distributing the electrons, check if all atoms have a complete octet (except for hydrogen, which only needs 2 electrons).
2. If there are any atoms that do not have an octet, move a lone pair from a neighboring atom to form a double bond.
3. Also, check for formal charges to ensure overall charge neutrality. Make sure the formal charges on each atom sum up to zero.
The Lewis dot structure for HCOOH will have the carbon atom in the center, bonded to both oxygen atoms with single bonds, and with hydrogen atoms attached to the oxygen atoms. The remaining valence electrons will be distributed as lone pairs and shared electrons to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?
Question Description
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?.
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?.
Solutions for Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH?, a detailed solution for Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? has been provided alongside types of Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Draw lewis dot structure for the molecule HCOOH? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























