Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > what is uniform circular motion definition
Start Learning for Free
what is uniform circular motion definition
Verified Answer
what is uniform circular motion definition
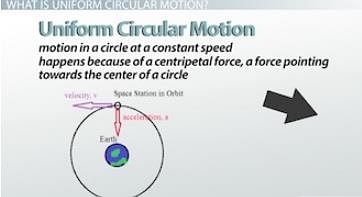
Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at a constant speed. This happens because of a centripetal force, a force pointing towards the center of a circle. Mathematically, an object in uniform circular motion has a net force towards the center of the circle, an acceleration vector towards the center of the circle, and a velocity tangent to the circle, as shown in this diagram:
uniform circular motion diagram
An interesting thing about circular motion is that it shows very clearly why it's important to know the difference between scalars and vectors. Speed is a scalar, whereas velocity is a vector - velocity has to include a direction, not just a number. The speed of an object in uniform circular motion is constant because after all, that's what makes it uniform. But the velocity is always changing. A satellite or car or bird moving in a circular motion is constantly changing direction, so their velocity is constantly changing. This shows why an object can have an acceleration even at a constant speed.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is uniform circular motion definition
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION :- The circular motion of an object is called uniform circular motion.
Community Answer
what is uniform circular motion definition
Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. It is characterized by the object's continuous motion along a circular trajectory, where the object covers equal distances in equal time intervals. This motion is commonly observed in various natural phenomena, such as the motion of planets around the sun, the rotation of a bicycle wheel, or the swinging of a pendulum.
Key Characteristics of Uniform Circular Motion:
1. Constant Speed: The object moves at a fixed speed throughout the circular path. This means that the magnitude of its velocity remains constant, although the direction continuously changes.
2. Centripetal Acceleration: Despite the constant speed, the object undergoes acceleration towards the center of the circle. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration and is always perpendicular to the object's velocity.
3. Centripetal Force: The centripetal acceleration is caused by a force called the centripetal force. It acts towards the center of the circular path, keeping the object in its curved trajectory. The centripetal force is responsible for continuously changing the object's direction.
4. Radial and Tangential Components: The velocity of the object in uniform circular motion can be divided into two components: the radial component, which points towards the center of the circle, and the tangential component, which is perpendicular to the radial component and lies along the circular path.
5. Period and Frequency: The period of uniform circular motion is the time taken for the object to complete one full revolution around the circle. It is inversely proportional to the frequency, which represents the number of revolutions completed per unit of time.
6. Angular Velocity: The object's angular velocity is a measure of how quickly it rotates around the circle. It is defined as the angle covered per unit of time and is directly related to the object's linear velocity.
Applications of Uniform Circular Motion:
Uniform circular motion finds applications in various fields, including:
1. Physics and Engineering: It is essential in understanding and analyzing the motion of objects in circular orbits, such as satellites or planets. It also plays a significant role in designing and optimizing machinery, such as engines, turbines, and rotating equipment.
2. Transportation: The principles of uniform circular motion are utilized in designing and maneuvering vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. The concept is particularly important in understanding cornering, banking, and turning forces.
3. Amusement Parks: Many amusement park rides, such as Ferris wheels, carousels, and roller coasters, rely on uniform circular motion to provide thrilling experiences for riders.
4. Sports: Activities like ice skating, figure skating, and gymnastics involve circular motions that rely on the principles of uniform circular motion.
In conclusion, uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. It exhibits distinct characteristics such as a constant speed, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, and radial and tangential components. Understanding uniform circular motion is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, transportation, amusement parks, and sports.
Uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. It is characterized by the object's continuous motion along a circular trajectory, where the object covers equal distances in equal time intervals. This motion is commonly observed in various natural phenomena, such as the motion of planets around the sun, the rotation of a bicycle wheel, or the swinging of a pendulum.
Key Characteristics of Uniform Circular Motion:
1. Constant Speed: The object moves at a fixed speed throughout the circular path. This means that the magnitude of its velocity remains constant, although the direction continuously changes.
2. Centripetal Acceleration: Despite the constant speed, the object undergoes acceleration towards the center of the circle. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration and is always perpendicular to the object's velocity.
3. Centripetal Force: The centripetal acceleration is caused by a force called the centripetal force. It acts towards the center of the circular path, keeping the object in its curved trajectory. The centripetal force is responsible for continuously changing the object's direction.
4. Radial and Tangential Components: The velocity of the object in uniform circular motion can be divided into two components: the radial component, which points towards the center of the circle, and the tangential component, which is perpendicular to the radial component and lies along the circular path.
5. Period and Frequency: The period of uniform circular motion is the time taken for the object to complete one full revolution around the circle. It is inversely proportional to the frequency, which represents the number of revolutions completed per unit of time.
6. Angular Velocity: The object's angular velocity is a measure of how quickly it rotates around the circle. It is defined as the angle covered per unit of time and is directly related to the object's linear velocity.
Applications of Uniform Circular Motion:
Uniform circular motion finds applications in various fields, including:
1. Physics and Engineering: It is essential in understanding and analyzing the motion of objects in circular orbits, such as satellites or planets. It also plays a significant role in designing and optimizing machinery, such as engines, turbines, and rotating equipment.
2. Transportation: The principles of uniform circular motion are utilized in designing and maneuvering vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. The concept is particularly important in understanding cornering, banking, and turning forces.
3. Amusement Parks: Many amusement park rides, such as Ferris wheels, carousels, and roller coasters, rely on uniform circular motion to provide thrilling experiences for riders.
4. Sports: Activities like ice skating, figure skating, and gymnastics involve circular motions that rely on the principles of uniform circular motion.
In conclusion, uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. It exhibits distinct characteristics such as a constant speed, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, and radial and tangential components. Understanding uniform circular motion is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, transportation, amusement parks, and sports.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
what is uniform circular motion definition
Question Description
what is uniform circular motion definition for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is uniform circular motion definition covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is uniform circular motion definition .
what is uniform circular motion definition for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is uniform circular motion definition covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is uniform circular motion definition .
Solutions for what is uniform circular motion definition in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is uniform circular motion definition defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is uniform circular motion definition , a detailed solution for what is uniform circular motion definition has been provided alongside types of what is uniform circular motion definition theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is uniform circular motion definition tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























