Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m ha...
Start Learning for Free
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will be
- a)0.1
- b)0.2
- c)0.3
- d)0.4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and ...
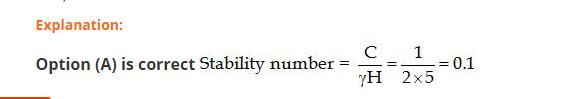
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and ...
Stability Number Calculation for Infinite Slope of Clay
Given data:
Depth of clay slope, h = 5m
Cohesion of clay, c = 1 t/m2
Unit weight of clay, γ = 2 t/m3
The stability number is defined as the ratio of the shear strength of the soil to the gravitational forces acting on the soil mass.
1. Calculation of Shear Strength of Clay
The shear strength of clay can be calculated using Mohr-Coulomb's theory. The shear strength equation is given by:
τ = c + σtanφ
Where,
τ = Shear strength
c = Cohesion of soil
σ = Effective stress
φ = Angle of internal friction
In this case, the angle of internal friction is not given. Therefore, it is assumed that the soil is in a fully saturated state and the angle of internal friction is equal to zero.
φ = 0
Thus, the equation for shear strength becomes:
τ = c
Substituting the values of c and γ, we get:
τ = 1 t/m2
2. Calculation of Gravitational Forces
The gravitational forces acting on the soil mass can be calculated using the following equation:
W = γAh
Where,
W = Weight of soil
A = Area of the slope
h = Height of the slope
γ = Unit weight of soil
Substituting the given values, we get:
W = 2 × 5 × A
3. Calculation of Stability Number
The stability number is given by the ratio of shear strength to the gravitational forces:
SN = τ / (W / A)
Substituting the values of τ and W, we get:
SN = 1 / (2 × 5)
Therefore, the stability number is:
SN = 0.1
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Given data:
Depth of clay slope, h = 5m
Cohesion of clay, c = 1 t/m2
Unit weight of clay, γ = 2 t/m3
The stability number is defined as the ratio of the shear strength of the soil to the gravitational forces acting on the soil mass.
1. Calculation of Shear Strength of Clay
The shear strength of clay can be calculated using Mohr-Coulomb's theory. The shear strength equation is given by:
τ = c + σtanφ
Where,
τ = Shear strength
c = Cohesion of soil
σ = Effective stress
φ = Angle of internal friction
In this case, the angle of internal friction is not given. Therefore, it is assumed that the soil is in a fully saturated state and the angle of internal friction is equal to zero.
φ = 0
Thus, the equation for shear strength becomes:
τ = c
Substituting the values of c and γ, we get:
τ = 1 t/m2
2. Calculation of Gravitational Forces
The gravitational forces acting on the soil mass can be calculated using the following equation:
W = γAh
Where,
W = Weight of soil
A = Area of the slope
h = Height of the slope
γ = Unit weight of soil
Substituting the given values, we get:
W = 2 × 5 × A
3. Calculation of Stability Number
The stability number is given by the ratio of shear strength to the gravitational forces:
SN = τ / (W / A)
Substituting the values of τ and W, we get:
SN = 1 / (2 × 5)
Therefore, the stability number is:
SN = 0.1
Hence, the correct answer is option A.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If an infinite slope of clay at a depth 5m has cohesion of 1 t/m2 and unit wt. of 2t/m3. Thenthe stability number will bea)0.1b)0.2c)0.3d)0.4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























