IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous sol...
Start Learning for Free
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol–1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol–1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:
- a)d-d transit ion
- b)Transit ion in K+ ion
- c)Ligand to metal charge transfer
- d)Metal to ligand charge transfer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA)...
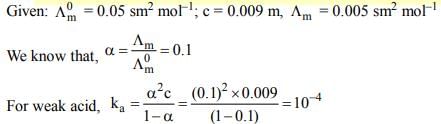
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
Most Upvoted Answer
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA)...
The molar conductivity of a solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. It is influenced by the concentration and degree of dissociation of the solute in the solution. In this case, we are given the molar conductivity of a weak acid (HA) at a certain concentration and temperature.
Given information:
- Molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of HA = 0.005 S m2 mol-1
- Limiting molar conductivity of HA = 0.05 S m2 mol-1 at 298 K
To determine the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of HA, we can use the equation:
Λm = Λ°m - (K / C)
Where:
Λm is the molar conductivity of the solution
Λ°m is the limiting molar conductivity
K is the ionic strength of the solution (in this case, the concentration of the acid)
C is the concentration of the acid
We can rearrange the equation to solve for K:
K = (Λ°m - Λm) * C
Using the given values, we can substitute them into the equation:
K = (0.05 - 0.005) * 0.009
Simplifying the expression:
K = 0.045 * 0.009
K = 0.000405
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is equal to K, so Ka = 0.000405.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - d-d transition.
Explanation:
- The molar conductivity of the solution is determined by the degree of dissociation of the acid. A higher degree of dissociation results in a higher molar conductivity.
- The limiting molar conductivity is the maximum value that the molar conductivity can reach when the concentration of the acid approaches zero. It represents the fully dissociated state.
- By subtracting the molar conductivity of the solution from the limiting molar conductivity and multiplying it by the concentration, we can determine the value of the ionic strength (K).
- The ionic strength is directly proportional to the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
- The correct answer is option 'A' because the acid dissociation constant (Ka) is related to the ionic strength of the solution, which is determined by the molar conductivity.
Given information:
- Molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of HA = 0.005 S m2 mol-1
- Limiting molar conductivity of HA = 0.05 S m2 mol-1 at 298 K
To determine the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of HA, we can use the equation:
Λm = Λ°m - (K / C)
Where:
Λm is the molar conductivity of the solution
Λ°m is the limiting molar conductivity
K is the ionic strength of the solution (in this case, the concentration of the acid)
C is the concentration of the acid
We can rearrange the equation to solve for K:
K = (Λ°m - Λm) * C
Using the given values, we can substitute them into the equation:
K = (0.05 - 0.005) * 0.009
Simplifying the expression:
K = 0.045 * 0.009
K = 0.000405
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is equal to K, so Ka = 0.000405.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - d-d transition.
Explanation:
- The molar conductivity of the solution is determined by the degree of dissociation of the acid. A higher degree of dissociation results in a higher molar conductivity.
- The limiting molar conductivity is the maximum value that the molar conductivity can reach when the concentration of the acid approaches zero. It represents the fully dissociated state.
- By subtracting the molar conductivity of the solution from the limiting molar conductivity and multiplying it by the concentration, we can determine the value of the ionic strength (K).
- The ionic strength is directly proportional to the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
- The correct answer is option 'A' because the acid dissociation constant (Ka) is related to the ionic strength of the solution, which is determined by the molar conductivity.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 S m2 mol1 aned the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 S m2 mol1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociat ion constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is:a)d-d transit ionb)Transit ion in K+ ionc)Ligand to metal charge transferd)Metal to ligand charge transferCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















