Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Margi...
Start Learning for Free
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE?
Verified Answer
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product C...
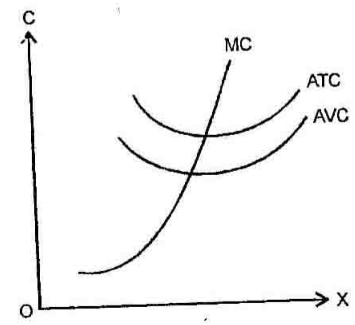
The short run cost curves AVC, AC and MC are U shaped because of the law of variable proportions. According to this law, in the initial sages of production, as the rm combines its Fixed and variable factors to begin with, to produce more and more of output, the productivity of the variable factors increases, and per unit costs falls. Then, they reach the stage of minimum costs at the level of optimum combination of fixed and variable factor. Thereafter, as the use of variable input increases given the fixed factor to increase the output, the productivity of variable factor fall, resulting in rise in per unit costs. This is shown in the following diagram:
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Similar Commerce Doubts
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce
Question Description
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce.
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce.
Solutions for WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce, a detailed solution for WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce has been provided alongside types of WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice WHY IS THE ATC CURVE U-SHAPE? Related: Marginal and Average Product Curves (With Diagram) - Commerce tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























