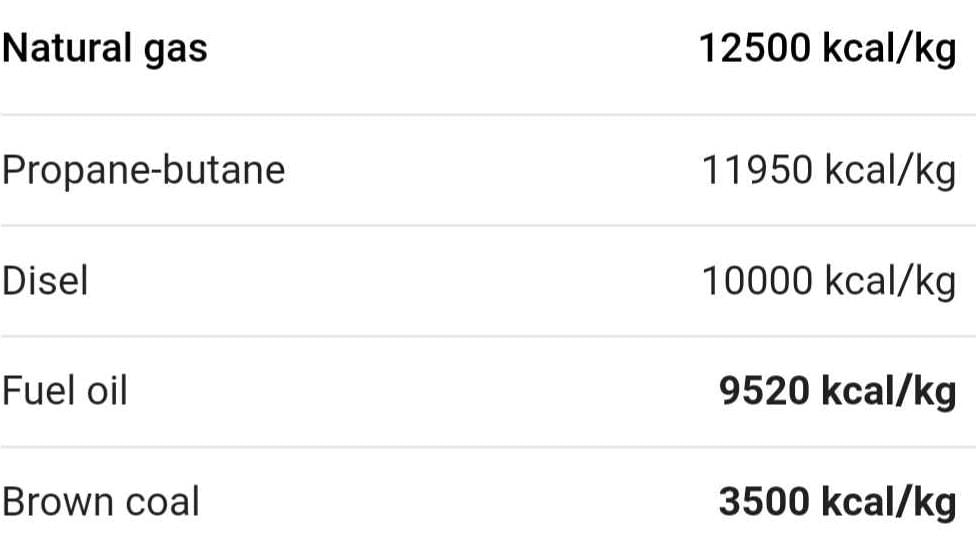
Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Questions > Calorific value of fuel
Start Learning for Free
Calorific value of fuel
Community Answer
Calorific value of fuel
Calorific Value of Fuel
The calorific value of a fuel refers to the amount of energy that can be obtained from burning a specific unit of that fuel. It is a measure of the fuel's energy content and is usually expressed in units of energy per unit mass or volume. The calorific value of a fuel is an important parameter in various applications, including energy production, engineering, and environmental studies.
Types of Calorific Value
There are two main types of calorific value: the gross calorific value (GCV) and the net calorific value (NCV).
1. Gross Calorific Value (GCV): The GCV of a fuel is the total amount of heat liberated when the fuel is completely burned and the products of combustion are cooled to a standard reference temperature. It includes the latent heat of vaporization of any water formed during combustion. GCV is also known as the higher heating value (HHV) or the gross heat of combustion.
2. Net Calorific Value (NCV): The NCV of a fuel is the amount of heat released when the fuel is burned, excluding the heat required to vaporize any water produced during combustion. NCV does not consider the latent heat of vaporization of water vapor. NCV is also known as the lower heating value (LHV) or the net heat of combustion.
Factors Affecting Calorific Value
The calorific value of a fuel can vary depending on several factors, including:
1. Composition: Different fuels have different chemical compositions, which directly affect their energy content. For example, hydrocarbon-based fuels generally have higher calorific values compared to non-hydrocarbon-based fuels.
2. Moisture Content: The presence of moisture in a fuel reduces its calorific value. This is because energy is required to vaporize the water during combustion, which decreases the overall energy released.
3. Ash Content: The presence of ash in a fuel can also lower its calorific value. Ash does not contribute to the energy released during combustion and can absorb heat, reducing the overall energy output.
Applications of Calorific Value
The calorific value of a fuel is crucial in several applications, including:
1. Energy Production: Calorific value is used to determine the energy content of fuels, which is essential in power generation, heating systems, and industrial processes. It helps in calculating the efficiency and performance of different energy sources.
2. Fuel Selection: Calorific value is considered when selecting a fuel for specific applications. Higher calorific value fuels are preferred as they provide more energy per unit mass or volume.
3. Environmental Analysis: Calorific value is used in environmental studies to assess the environmental impact of different fuels. It helps in evaluating the efficiency and emissions associated with fuel combustion.
In conclusion, the calorific value of a fuel is a measure of its energy content. It is categorized into gross calorific value (GCV) and net calorific value (NCV). The composition, moisture content, and ash content of a fuel affect its calorific value. Calorific value plays a crucial role in energy production, fuel selection, and environmental analysis.
The calorific value of a fuel refers to the amount of energy that can be obtained from burning a specific unit of that fuel. It is a measure of the fuel's energy content and is usually expressed in units of energy per unit mass or volume. The calorific value of a fuel is an important parameter in various applications, including energy production, engineering, and environmental studies.
Types of Calorific Value
There are two main types of calorific value: the gross calorific value (GCV) and the net calorific value (NCV).
1. Gross Calorific Value (GCV): The GCV of a fuel is the total amount of heat liberated when the fuel is completely burned and the products of combustion are cooled to a standard reference temperature. It includes the latent heat of vaporization of any water formed during combustion. GCV is also known as the higher heating value (HHV) or the gross heat of combustion.
2. Net Calorific Value (NCV): The NCV of a fuel is the amount of heat released when the fuel is burned, excluding the heat required to vaporize any water produced during combustion. NCV does not consider the latent heat of vaporization of water vapor. NCV is also known as the lower heating value (LHV) or the net heat of combustion.
Factors Affecting Calorific Value
The calorific value of a fuel can vary depending on several factors, including:
1. Composition: Different fuels have different chemical compositions, which directly affect their energy content. For example, hydrocarbon-based fuels generally have higher calorific values compared to non-hydrocarbon-based fuels.
2. Moisture Content: The presence of moisture in a fuel reduces its calorific value. This is because energy is required to vaporize the water during combustion, which decreases the overall energy released.
3. Ash Content: The presence of ash in a fuel can also lower its calorific value. Ash does not contribute to the energy released during combustion and can absorb heat, reducing the overall energy output.
Applications of Calorific Value
The calorific value of a fuel is crucial in several applications, including:
1. Energy Production: Calorific value is used to determine the energy content of fuels, which is essential in power generation, heating systems, and industrial processes. It helps in calculating the efficiency and performance of different energy sources.
2. Fuel Selection: Calorific value is considered when selecting a fuel for specific applications. Higher calorific value fuels are preferred as they provide more energy per unit mass or volume.
3. Environmental Analysis: Calorific value is used in environmental studies to assess the environmental impact of different fuels. It helps in evaluating the efficiency and emissions associated with fuel combustion.
In conclusion, the calorific value of a fuel is a measure of its energy content. It is categorized into gross calorific value (GCV) and net calorific value (NCV). The composition, moisture content, and ash content of a fuel affect its calorific value. Calorific value plays a crucial role in energy production, fuel selection, and environmental analysis.
Attention Class 8 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 8 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 8.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Similar Class 8 Doubts
Calorific value of fuel
Question Description
Calorific value of fuel for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Calorific value of fuel covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Calorific value of fuel.
Calorific value of fuel for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Calorific value of fuel covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Calorific value of fuel.
Solutions for Calorific value of fuel in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 8.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Calorific value of fuel defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Calorific value of fuel, a detailed solution for Calorific value of fuel has been provided alongside types of Calorific value of fuel theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Calorific value of fuel tests, examples and also practice Class 8 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.