JEE Exam > JEE Questions > 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the e...
Start Learning for Free
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.?
Verified Answer
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6...
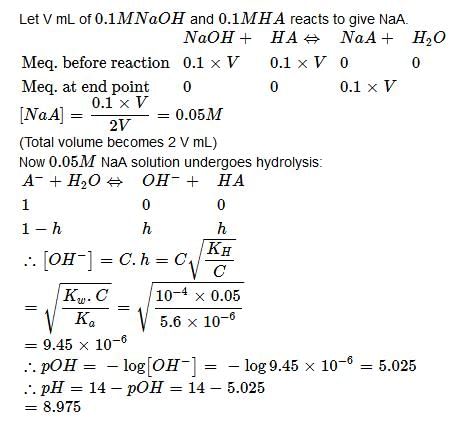
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6...
Introduction:
In this titration, we are adding a 0.1 M solution of a strong base, NaOH, to a 0.1 M solution of a weak acid, HA. The acid has a dissociation constant, Ka, of 5.6×10^-6, which means it only partially ionizes in water. We are interested in finding the pH of the resulting solution at the end point of the titration.
Understanding the titration:
During the titration, NaOH reacts with HA to form water and the corresponding salt, NaA. The reaction can be represented as follows:
HA + NaOH → NaA + H2O
Equilibrium equation:
Since HA is a weak acid, it undergoes partial ionization in water. The equilibrium equation for the dissociation of HA can be written as:
HA ⇌ H+ + A-
Hydrolysis of the salt:
After the addition of NaOH, the resulting solution contains the salt NaA. This salt can undergo hydrolysis in water, leading to the formation of the weak acid HA and hydroxide ions. The hydrolysis reaction can be represented as follows:
NaA + H2O ⇌ HA + OH-
pH at the end point:
At the end point of the titration, all of the HA has reacted with the NaOH. This means that the concentration of A- ions in the solution is equal to the initial concentration of HA. Since the degree of hydrolysis is less than 1, the extent of hydrolysis is small and we can consider the concentration of HA to be equal to the concentration of H+ ions.
Calculating the pH:
To calculate the pH at the end point, we need to determine the concentration of H+ ions. We can do this by using the equilibrium constant, Ka, for the dissociation of HA. The expression for Ka is:
Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA]
Since [HA] = [H+], we can substitute [HA] for [H+] in the equation:
Ka = [H+][A-] / [H+]
Rearranging the equation, we get:
[H+]^2 = Ka
Taking the square root of both sides, we find:
[H+] = √Ka
Substituting the value of Ka (5.6×10^-6), we can calculate the concentration of H+ ions, which is the same as the pH of the solution at the end point.
Conclusion:
In this titration, the resulting solution at the end point will have a pH equal to the square root of the dissociation constant (Ka) of the weak acid HA. It is important to note that the degree of hydrolysis is less than 1, indicating that the weak acid does not completely dissociate in water.
In this titration, we are adding a 0.1 M solution of a strong base, NaOH, to a 0.1 M solution of a weak acid, HA. The acid has a dissociation constant, Ka, of 5.6×10^-6, which means it only partially ionizes in water. We are interested in finding the pH of the resulting solution at the end point of the titration.
Understanding the titration:
During the titration, NaOH reacts with HA to form water and the corresponding salt, NaA. The reaction can be represented as follows:
HA + NaOH → NaA + H2O
Equilibrium equation:
Since HA is a weak acid, it undergoes partial ionization in water. The equilibrium equation for the dissociation of HA can be written as:
HA ⇌ H+ + A-
Hydrolysis of the salt:
After the addition of NaOH, the resulting solution contains the salt NaA. This salt can undergo hydrolysis in water, leading to the formation of the weak acid HA and hydroxide ions. The hydrolysis reaction can be represented as follows:
NaA + H2O ⇌ HA + OH-
pH at the end point:
At the end point of the titration, all of the HA has reacted with the NaOH. This means that the concentration of A- ions in the solution is equal to the initial concentration of HA. Since the degree of hydrolysis is less than 1, the extent of hydrolysis is small and we can consider the concentration of HA to be equal to the concentration of H+ ions.
Calculating the pH:
To calculate the pH at the end point, we need to determine the concentration of H+ ions. We can do this by using the equilibrium constant, Ka, for the dissociation of HA. The expression for Ka is:
Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA]
Since [HA] = [H+], we can substitute [HA] for [H+] in the equation:
Ka = [H+][A-] / [H+]
Rearranging the equation, we get:
[H+]^2 = Ka
Taking the square root of both sides, we find:
[H+] = √Ka
Substituting the value of Ka (5.6×10^-6), we can calculate the concentration of H+ ions, which is the same as the pH of the solution at the end point.
Conclusion:
In this titration, the resulting solution at the end point will have a pH equal to the square root of the dissociation constant (Ka) of the weak acid HA. It is important to note that the degree of hydrolysis is less than 1, indicating that the weak acid does not completely dissociate in water.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.?.
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.?.
Solutions for 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.?, a detailed solution for 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? has been provided alongside types of 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice 0.1 M NaOH is titrated with 0.1MHA till the end point. Ka of HA is 5.6×10^-6 and degree of hydrolysis is less compared to 1. The pH of the resulting solution at the end point is.? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















