Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids ...
Start Learning for Free
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004]
(a) PhCOOH
(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH
(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH
(d) m – NO2C6H4COO
Which of the following order is correct ?
- a)a > b > c > d
- b)b > d > c > a
- c)b > d > a > c
- d)b > c > d > a
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(...
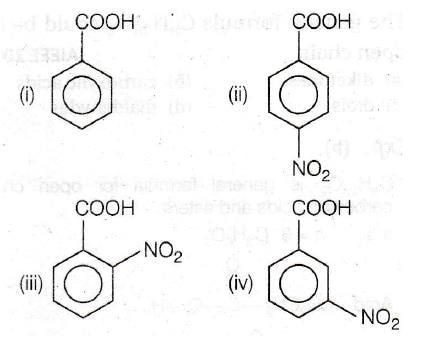
-NO2 group at any position shows electron withdrawing effect, thus acid strength is increased. But o -nitro benzoate ion is stabilised by intramolecular H-bonding like forces, hence its acid strength is maximum. Thus, the order of acid strength is (ii) > (iii) > (iv) > (i)
The effect is more pronounced at para position than meta.
The effect is more pronounced at para position than meta.
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(...
Explanation:
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids:
- The acidity of carboxylic acids is influenced by the stability of the carboxylate anion formed after the loss of a proton.
- Electron-withdrawing groups attached to the benzene ring stabilize the carboxylate anion, increasing acidity.
- The order of acidity among the given carboxylic acids can be determined based on the position of the nitro group (-NO2) on the benzene ring.
Order of Acidity:
- The meta position (m) nitro group is the most electron-withdrawing, making the m-NO2C6H4COOH the most acidic among the given options.
- The para position (p) nitro group is less electron-withdrawing than the meta position, making p-NO2C6H4COOH less acidic than m-NO2C6H4COOH.
- The ortho position (o) nitro group is the least electron-withdrawing among the three positions, making o-NO2C6H4COOH the least acidic among the given options.
- PhCOOH (benzoic acid) has no electron-withdrawing groups attached to the benzene ring, making it the least acidic among the given options.
Therefore, the correct order of acidity is:
d) b > c > a

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids : [AIEEE-2004](a) PhCOOH(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH(d) m – NO2C6H4COOWhich of the following order is correct ?a)a > b > c > db)b > d > c > ac)b > d > a > cd)b > c > d > aCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















