Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Questions > In what ways indogenic forces are different f...
Start Learning for Free
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic
Verified Answer
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Ch...
Endogenic Force these are also known as hypogene process or force . In other words a force which originate within the earth crust .These are internal force.. Exogenic Force these are the forces of the external origin or in other words the force derive their energy from sources of external in relation to the earth..
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Ch...
Introduction:
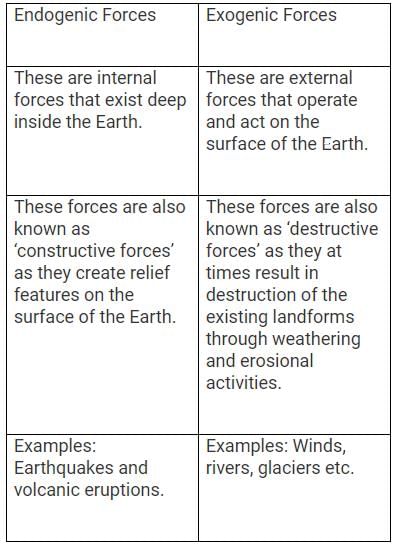
Indogenic forces and exogenic forces are two important processes that shape the Earth's surface. Indogenic forces are internal forces that originate from within the Earth, whereas exogenic forces are external forces that act on the Earth's surface. While both types of forces play a role in the formation of landforms, they differ in several ways.
Differences between Indogenic and Exogenic Forces:
1. Origin:
- Indogenic forces originate from within the Earth's interior, specifically from the movement of tectonic plates and volcanic activities.
- Exogenic forces, on the other hand, originate from external sources such as weathering, erosion, and deposition caused by wind, water, and ice.
2. Nature:
- Indogenic forces are characterized by large-scale, slow processes that occur over millions of years. These forces include plate tectonics, folding, faulting, and volcanic activities.
- Exogenic forces, in contrast, are relatively faster and act on a smaller scale. They involve processes like weathering, erosion, and deposition that occur due to external agents like water, wind, and ice.
3. Effects:
- Indogenic forces are responsible for the creation of major landforms such as mountains, plateaus, and rift valleys. They cause the upliftment and subsidence of the Earth's crust, leading to the formation of various geological features.
- Exogenic forces primarily shape the Earth's surface by wearing down existing landforms through weathering and erosion. They contribute to the formation of valleys, river channels, coastal features, and deposition of sediments.
4. Timeframe:
- Indogenic forces operate over long geological timescales, taking millions of years to create significant changes in the Earth's structure and landforms.
- Exogenic forces, although relatively faster, still require considerable time to modify the Earth's surface. Weathering, erosion, and deposition processes can occur over thousands to millions of years.
5. Agents:
- Indogenic forces do not require external agents and are driven by internal energy sources such as heat and pressure.
- Exogenic forces, on the other hand, are dependent on external agents such as water, wind, and ice to carry out processes like erosion, transportation, and deposition.
Conclusion:
In summary, indogenic forces and exogenic forces are distinct in their origin, nature, effects, timeframe, and agents. Indogenic forces arise from within the Earth and are responsible for large-scale geological changes, while exogenic forces operate on the Earth's surface and shape landforms through weathering, erosion, and deposition processes. Understanding the differences between these forces helps in comprehending the dynamic processes that shape our planet's landscape.
Indogenic forces and exogenic forces are two important processes that shape the Earth's surface. Indogenic forces are internal forces that originate from within the Earth, whereas exogenic forces are external forces that act on the Earth's surface. While both types of forces play a role in the formation of landforms, they differ in several ways.
Differences between Indogenic and Exogenic Forces:
1. Origin:
- Indogenic forces originate from within the Earth's interior, specifically from the movement of tectonic plates and volcanic activities.
- Exogenic forces, on the other hand, originate from external sources such as weathering, erosion, and deposition caused by wind, water, and ice.
2. Nature:
- Indogenic forces are characterized by large-scale, slow processes that occur over millions of years. These forces include plate tectonics, folding, faulting, and volcanic activities.
- Exogenic forces, in contrast, are relatively faster and act on a smaller scale. They involve processes like weathering, erosion, and deposition that occur due to external agents like water, wind, and ice.
3. Effects:
- Indogenic forces are responsible for the creation of major landforms such as mountains, plateaus, and rift valleys. They cause the upliftment and subsidence of the Earth's crust, leading to the formation of various geological features.
- Exogenic forces primarily shape the Earth's surface by wearing down existing landforms through weathering and erosion. They contribute to the formation of valleys, river channels, coastal features, and deposition of sediments.
4. Timeframe:
- Indogenic forces operate over long geological timescales, taking millions of years to create significant changes in the Earth's structure and landforms.
- Exogenic forces, although relatively faster, still require considerable time to modify the Earth's surface. Weathering, erosion, and deposition processes can occur over thousands to millions of years.
5. Agents:
- Indogenic forces do not require external agents and are driven by internal energy sources such as heat and pressure.
- Exogenic forces, on the other hand, are dependent on external agents such as water, wind, and ice to carry out processes like erosion, transportation, and deposition.
Conclusion:
In summary, indogenic forces and exogenic forces are distinct in their origin, nature, effects, timeframe, and agents. Indogenic forces arise from within the Earth and are responsible for large-scale geological changes, while exogenic forces operate on the Earth's surface and shape landforms through weathering, erosion, and deposition processes. Understanding the differences between these forces helps in comprehending the dynamic processes that shape our planet's landscape.
Community Answer
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Ch...
Attention Class 6 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 6 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 6.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Similar Class 6 Doubts
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST
Question Description
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST.
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST.
Solutions for In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 6.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST, a detailed solution for In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST has been provided alongside types of In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In what ways indogenic forces are different from exogenic Related: Chapter Overvies - Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth, Class 6, SST tests, examples and also practice Class 6 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























