Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > What is meant by banking of road?
Start Learning for Free
What is meant by banking of road?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is meant by banking of road?
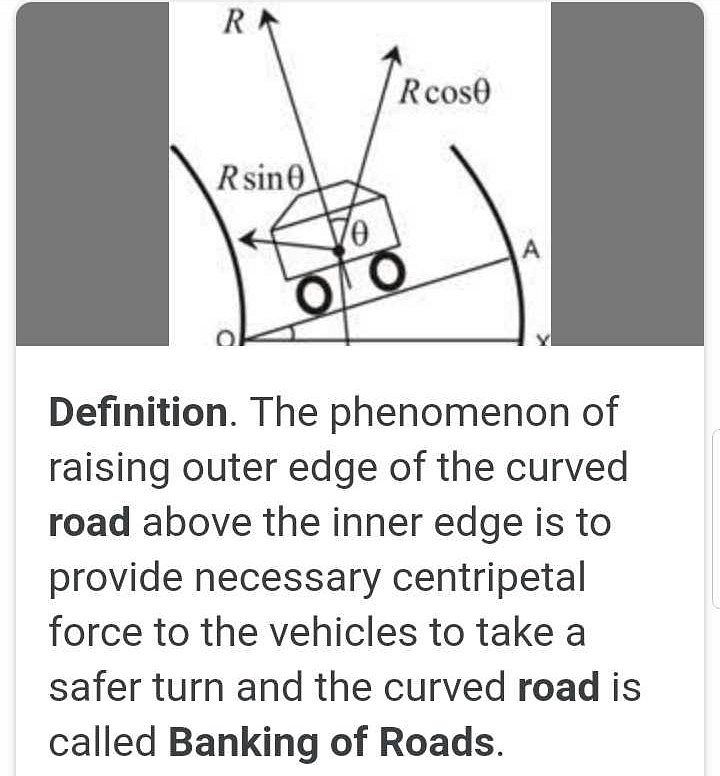
Community Answer
What is meant by banking of road?
Banking of Roads: Explained in Detail
Roads are an essential part of our transportation infrastructure, and their design plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of vehicular movement. One important aspect of road design is the concept of banking, also known as superelevation or cant.
Definition of Banking of Roads
Banking of roads refers to the process of raising the outer edge of a road higher than the inner edge on a curved section. This design technique allows vehicles to safely navigate curves at higher speeds by utilizing the force of friction between the tires and the road surface.
Key Concepts
To understand the concept of banking, it is important to consider the following key points:
1. Centripetal Force: When a vehicle moves in a curved path, it experiences a centripetal force that pulls it towards the center of the curve. This force is responsible for keeping the vehicle on the road and preventing it from skidding outwards.
2. Friction: Friction between the tires and the road surface provides the necessary centripetal force. It depends on the coefficient of friction, which is influenced by factors such as tire quality, road conditions, and weather.
3. Banking Angle: The banking angle is the angle at which the road is inclined from the horizontal plane. It is designed to provide the required centripetal force without relying solely on friction.
Advantages of Banking
Implementing banking on curved road sections offers several advantages:
1. Increased Safety: By providing the necessary centripetal force, banking reduces the risk of vehicles skidding or overturning while negotiating curves. This improves overall road safety.
2. Higher Speeds: Banking enables vehicles to safely navigate curves at higher speeds, as it reduces the lateral forces acting on them. This leads to smoother and more efficient traffic flow.
3. Reduced Wear and Tear: Properly designed banking minimizes the lateral forces exerted on the tires, which results in reduced wear and tear on both tires and road surfaces. This helps to prolong the lifespan of the road infrastructure.
Design Considerations
When designing the banking of a road, several factors need to be taken into account:
1. Radius of Curvature: The radius of curvature determines the magnitude of the required centripetal force. A smaller radius requires a steeper banking angle, while a larger radius can have a shallower angle.
2. Speed Limit: The desired speed limit for the road section influences the design of the banking angle. Higher speed limits generally require a greater banking angle to ensure safety.
3. Vehicle Types: The types of vehicles expected to use the road should be considered to determine the appropriate banking angle. Heavy vehicles, such as trucks, may require a different design compared to lighter vehicles.
Conclusion
Banking of roads is an important aspect of road design that aims to enhance safety and efficiency. By providing the necessary centripetal force, banking allows vehicles to navigate curves at higher speeds while minimizing the risk of skidding or overturning. Proper design considerations, such as the radius of curvature, speed limit, and types of vehicles, need to be taken into account to ensure
Roads are an essential part of our transportation infrastructure, and their design plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of vehicular movement. One important aspect of road design is the concept of banking, also known as superelevation or cant.
Definition of Banking of Roads
Banking of roads refers to the process of raising the outer edge of a road higher than the inner edge on a curved section. This design technique allows vehicles to safely navigate curves at higher speeds by utilizing the force of friction between the tires and the road surface.
Key Concepts
To understand the concept of banking, it is important to consider the following key points:
1. Centripetal Force: When a vehicle moves in a curved path, it experiences a centripetal force that pulls it towards the center of the curve. This force is responsible for keeping the vehicle on the road and preventing it from skidding outwards.
2. Friction: Friction between the tires and the road surface provides the necessary centripetal force. It depends on the coefficient of friction, which is influenced by factors such as tire quality, road conditions, and weather.
3. Banking Angle: The banking angle is the angle at which the road is inclined from the horizontal plane. It is designed to provide the required centripetal force without relying solely on friction.
Advantages of Banking
Implementing banking on curved road sections offers several advantages:
1. Increased Safety: By providing the necessary centripetal force, banking reduces the risk of vehicles skidding or overturning while negotiating curves. This improves overall road safety.
2. Higher Speeds: Banking enables vehicles to safely navigate curves at higher speeds, as it reduces the lateral forces acting on them. This leads to smoother and more efficient traffic flow.
3. Reduced Wear and Tear: Properly designed banking minimizes the lateral forces exerted on the tires, which results in reduced wear and tear on both tires and road surfaces. This helps to prolong the lifespan of the road infrastructure.
Design Considerations
When designing the banking of a road, several factors need to be taken into account:
1. Radius of Curvature: The radius of curvature determines the magnitude of the required centripetal force. A smaller radius requires a steeper banking angle, while a larger radius can have a shallower angle.
2. Speed Limit: The desired speed limit for the road section influences the design of the banking angle. Higher speed limits generally require a greater banking angle to ensure safety.
3. Vehicle Types: The types of vehicles expected to use the road should be considered to determine the appropriate banking angle. Heavy vehicles, such as trucks, may require a different design compared to lighter vehicles.
Conclusion
Banking of roads is an important aspect of road design that aims to enhance safety and efficiency. By providing the necessary centripetal force, banking allows vehicles to navigate curves at higher speeds while minimizing the risk of skidding or overturning. Proper design considerations, such as the radius of curvature, speed limit, and types of vehicles, need to be taken into account to ensure

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
What is meant by banking of road?
Question Description
What is meant by banking of road? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What is meant by banking of road? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is meant by banking of road?.
What is meant by banking of road? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What is meant by banking of road? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is meant by banking of road?.
Solutions for What is meant by banking of road? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is meant by banking of road? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is meant by banking of road?, a detailed solution for What is meant by banking of road? has been provided alongside types of What is meant by banking of road? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is meant by banking of road? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















