Animals: Feeding Habits Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Classification of Animals |

|
| Animals without Backbones: Insects |

|
| Animals With Backbones |

|
| Characteristics of Animals |

|
| Summary |

|
Animals are living things just like us. They eat food, move, grow, and have babies. Some animals live in the jungle, some on farms, and some with us as pets. Every animal is different and amazing, and they help us in many ways. Let’s explore the world of animals together.
Classification of Animals
Animals can be classified into two main categories:
- Animals without backbones: Some animals like amoeba, jellyfish, earthworms, roundworms, snails, insects, and starfish do not have backbones (spinal column).
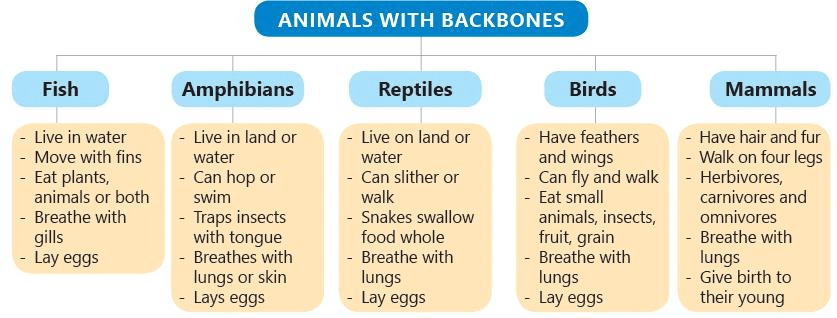
- Animals with backbone: Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are animals that have a backbone to support their body.
 Animals with backbone
Animals with backbone
Animals without Backbones: Insects
Most animals found on earth do not have a backbone. Insects are the largest group of animals. They do not have a backbone. All insects lay eggs.
- An insect's body has three main parts: the head, the middle part (thorax), and the last part (abdomen).
- Insects have two feelers (antennae) on their heads. These help them know what is around them. Insects can also smell and taste things very well.
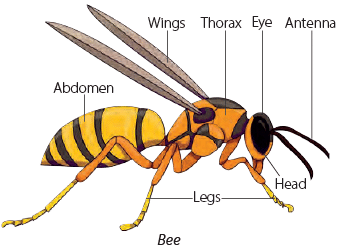
- Movement: Insects use their six legs to move. Some insects, like ants and cockroaches, can only crawl. Others, like butterflies and mosquitoes, have wings to fly. Grasshoppers have strong back legs to hop and wings to fly.

- Feeding: Some insects, like butterflies, have a special mouth that looks like a long straw. They use it to suck juice from flowers, just like we drink with a straw.
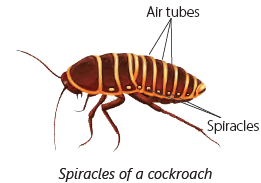
- Breathing: Insects breathe through small holes on their bodies called spiracles. Air goes in through these holes and moves through tiny tubes inside their body.
Animals With Backbones
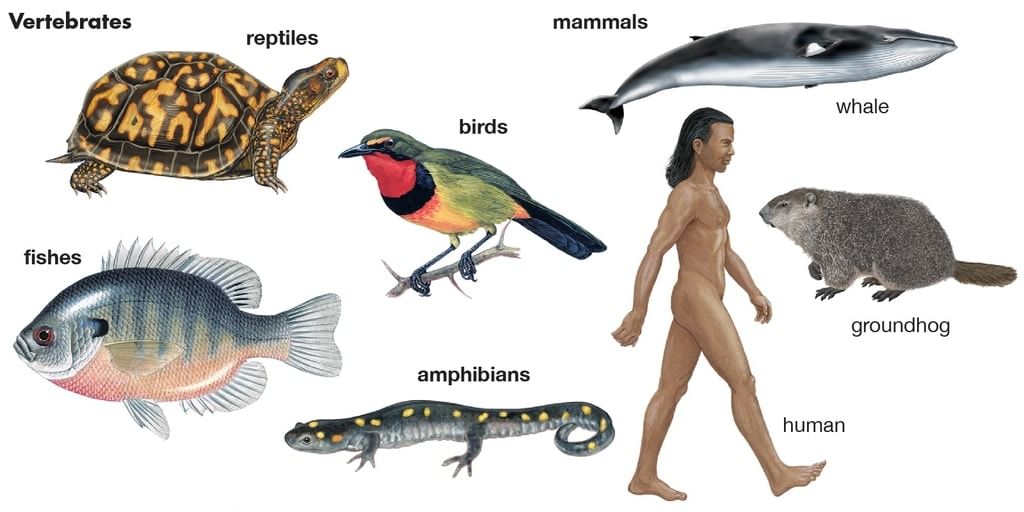
- Fish: Fish have scales on their bodies. They live in both rivers and seas. There are many types of fish, making them the second-largest group of animals.
- Amphibians: Amphibians have wet skin and can live on both land and in water. Examples are frogs, toads, and salamanders.
- Reptiles: Reptiles have scales on their bodies. This group includes snakes, crocodiles, lizards, and tortoises. Some reptiles live only on land, while others live in both land and water.
- Birds: Birds have feathers and wings. They are the third-largest group of animals. Some examples are sparrows, parrots, pigeons, eagles, and owls.
- Mammals: Mammals have hair or fur on their bodies. They give birth to babies instead of laying eggs. Examples include cows, tigers, lions, elephants, and humans. Mammals are the fourth-largest group of animals with backbones.
Characteristics of Animals
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Animals: Feeding Habits
|
Download as PDF |
1. Movement of Animals
Animals have unique features that set them apart from other living beings. One of the main characteristics is their ability to move from one place to another. Let's explore how different types of animals move:
(i) Fish
Fish are made for living in water. They use their fins and tail to swim. The fins help them turn and stay balanced, while the tail helps them move forward.
Amphibians, like frogs, are special because they can live in both water and on land. They have webbed feet to help them swim in water. On land, they use their strong back legs to jump and move. This makes them different from other animals.
(iii) ReptilesReptiles like lizards and crocodiles use their legs to move. But snakes do not have legs. They use their strong muscles and smooth scales to slide on the ground. Their muscles tighten and loosen, helping them move forward.

Birds can fly because they have wings. Their wings and feathers help them move easily in the air. Birds have hollow bones, which makes them weigh less and fly better. Their feet are also important. Ducks have webbed feet to swim, while some birds, like penguins, kiwis, and ostriches, cannot fly. They use their feet to walk or run instead.
(v) MammalsMost mammals have four legs. The front legs are called forelimbs, and the back legs are called hindlimbs. Mammals move in different ways, like running, hopping, or walking. Some, like whales and dolphins, live in water but are still mammals because they have things in common with land mammals.
Humans are also mammals. They stand upright and use their feet to balance. Their legs help them walk, and their hands, with four fingers and a thumb, help them hold things and do different tasks.

2. Animals that Eat Plants or Other Animals
(i) Fish- Herbivores: Some fish mainly eat plants.
- Carnivores: Other fish eat only animals, such as smaller fish and worms.
- Omnivores: Some fish eat both plants and animals.
- Fish may also feed on dead plants and animal remains.
- Amphibians like frogs catch and eat small insects using their long, sticky tongues.
- Large snakes hunt and eat big animals such as deer and pigs.
- Smaller snakes eat insects, mice, birds, eggs, frogs, and small mammals.
- Snakes do not chew their food; they swallow it whole.
- Reptiles like lizards and chameleons catch insects using their long, sticky tongues.

- Carnivorous birds: Eagles eat the flesh of animals.
- Herbivorous birds: Sparrows eat fruit, seeds, and grains.
- Birds do not have teeth; they use their beaks to eat.
- They use their claws to catch food and for safety.
- Different birds have different types of claws and beaks that help them eat their food.

- Herbivores: Animals like cows, horses, deer, rabbits, and giraffes eat only plants.
- Carnivores: Animals like tigers, lions, wolves, and snakes eat the flesh of other animals.
- Omnivores: Animals like bears, crows, and humans eat both plants and animal flesh.

3. Animals Breathe through Lungs, Gills, or Air Holes
- Fish use special organs called gills to breathe underwater. Amphibians breathe with their lungs when on land, and they can also absorb oxygen through their skin when in water.
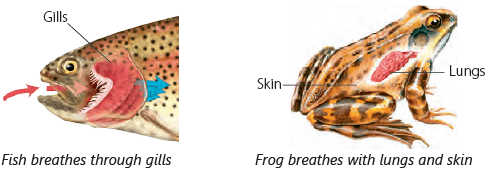
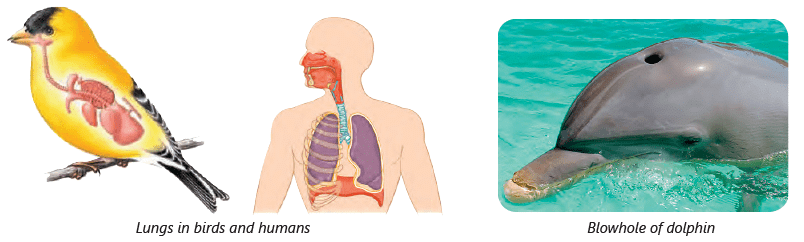
- Reptiles and birds breathe using their lungs.
Whales and dolphins live in the water, but they're not fish! They're mammals, just like us. That means they need to come up to the top of the water to breathe air. They have a special hole on top of their heads called a blowhole, which helps them in breathing.
4. Animals have Sense Organs
- Sense organs are the connection between animals and the outside world.
- Fish have different types of eyesight as well as senses of taste. They can also feel movements in the water, which helps them find food and stay away from danger.
- Frogs have large eyes that allow them to see to the sides and behind without turning their heads. They can also feel movements through the water.
- Snakes have limited eyesight and use their tongues to smell their surroundings.
- Birds have much better eyesight than humans, which helps them find food easily and be aware of dangers.

- Humans have five sense organs: eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Eyes allow us to see, while ears help us hear and maintain balance. Noses are used for breathing and smelling.
Our tongue helps us taste yummy food! It also helps us talk. It has tiny bumps called taste buds that let us know if something is sweet, sour, salty, or bitter. Our skin helps us feel things too, like if something is hot or cold or if it hurts.

5. Animals Reproduce by Laying Eggs or Giving Birth to Young Ones
- Fish reproduce by laying eggs in water. They lay thousands of eggs because some eggs and baby fishes that hatch out of them are eaten by other fishes.
- Amphibians also lay their eggs in water. The eggs hatch to give birth to baby frogs called tadpoles. These live in water till they grow into frogs. They have gills that help them breathe in water.
- Reptiles reproduce by laying their eggs on land. When the eggs hatch, the mother picks the babies in her mouth and carries them to the water.
 Birds give birth by laying eggs in their nest. The mother bird lays eggs and keeps them warm until the young ones hatch.
Birds give birth by laying eggs in their nest. The mother bird lays eggs and keeps them warm until the young ones hatch. 
- Mammals do not lay eggs. They give birth to their young ones. The mother produces milk to feed her babies. They guard their babies and keep them clean. They look after them until they are old enough to look after themselves.
- The duck-billed platypus and spiny anteater are the only two mammals that lay eggs. Their young ones hatch from eggs.


Summary
- Animals are classified into two main groups: those with backbones (vertebrates) and those without backbones (invertebrates).
- Insects, while the largest group of animals, are different from vertebrates and invertebrates. They can fly, hop, or crawl; breathe through small openings in their bodies called spiracles; and lay eggs.
- Vertebrates include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, all of which have backbones.
- Animals move in different ways:
- Fish swim through water.
- Frogs can both swim and hop.
- Snakes move by slithering on the ground.
- Birds fly through the air.
- Mammals often walk on four legs.
- Animals can be classified by what they eat: herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plants and animals. They have different ways of catching and eating their food.
- Fish breathe underwater using gills. Amphibians breathe through their lungs and skin, and some have gills when they are young. Reptiles, birds, and mammals breathe using their lungs. Dolphins have a special body part called a blowhole that helps them to breathe air at the top of the water.
- Animals use various body parts to sense their environment. Some have antennae to feel things around them, while others can sense movements in water. Most animals have sense organs like eyes, ears, noses, tongues, and skin to help them understand what is happening around them.
- Animals reproduce by either laying eggs or giving birth to live young.
- Different animals have different eating habits and special body parts that help them stay safe in different places.
|
19 videos|97 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Animals: Feeding Habits Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What are the main characteristics of animals without backbones, specifically insects? |  |
| 2. How do animals with backbones differ from those without backbones? |  |
| 3. What are the different feeding habits of animals? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to classify animals into groups like invertebrates and vertebrates? |  |
| 5. What role do insects play in the ecosystem? |  |

































