Aquifer and Aquitards | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Aquifers and Aquitards: An Overview |

|
| Types of Aquifers and Aquitards |

|
| Groundwater Recharge and Discharge |

|
| Aquifer and Aquitard Mapping and Modeling |

|
Aquifers and Aquitards: An Overview
Aquifers and aquitards are critical components of the hydrological cycle, playing a crucial role in groundwater availability and management.
- Aquifers are geological formations that are both porous and permeable, allowing them to store and transmit significant amounts of water. These formations can consist of materials such as sand, gravel, and fractured rock and can occur at various depths below the Earth's surface. Aquifers are vital sources of water for many communities, with their characteristics influencing both the quantity and quality of water available.
- Aquitards, in contrast, are geological formations with low permeability that restrict water flow. They are typically composed of fine-grained materials like clay or shale, acting as barriers that prevent or slow the movement of water between aquifers or between groundwater and surface water.
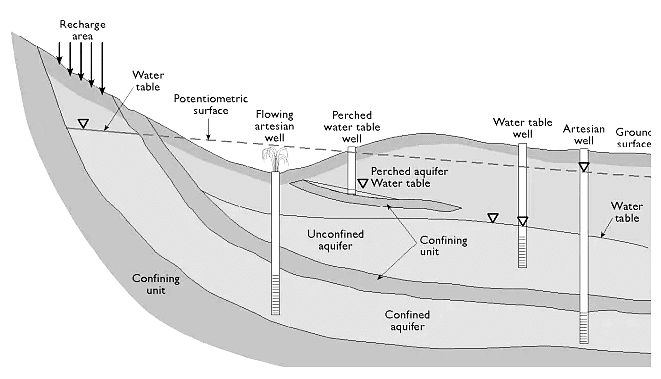
Types of Aquifers and Aquitards
Aquifers can be classified based on their characteristics and the source and movement of water:
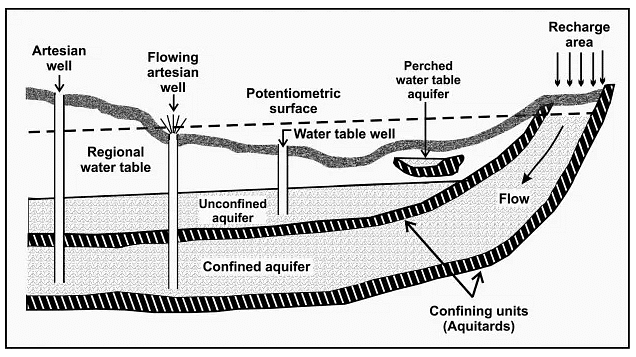
- Unconfined Aquifers: These are open to the surface and directly receive water from surface infiltration.
- Confined Aquifers: These are bounded above and below by impermeable layers (aquitards) and are recharged from distant areas where the confining layer is absent.
- Artesian Aquifers: A type of confined aquifer where water is under pressure and can rise above the top of the aquifer without pumping.
Aquitards can also be classified based on their permeability and thickness, including:
- Clay Layers: Fine-grained and typically very low permeability.
- Shale: Composed of compacted silt and clay particles, with low permeability.
- Silt: Fine-grained but can be more permeable than clay or shale.
Aquifer Properties
Understanding the properties of aquifers is essential for groundwater management:
- Porosity: The volume of void space in the soil or rock material, expressed as a percentage. High porosity indicates a greater capacity to hold water.
- Permeability: The ability of a material to transmit water, often measured as hydraulic conductivity.
- Transmissivity: The rate at which water can be transmitted through the entire thickness of the aquifer.
- Storage Coefficient: The volume of water an aquifer releases from storage per unit decline in hydraulic head.
- Specific Yield: The ratio of the volume of water that can be drained by gravity to the total volume of the aquifer.
Aquitard Properties: Their low permeability and thickness determine the extent to which they can impede groundwater movement.
Aquifer Testing
Aquifer testing, or pumping tests, evaluate the hydraulic properties of an aquifer. The process involves pumping water from a well at a constant rate and measuring the response of water levels in the well and surrounding aquifer. This data helps calculate hydraulic parameters such as conductivity, transmissivity, and storativity.
Groundwater Flow Equations
Groundwater flow equations describe groundwater movement in aquifers based on fluid mechanics and mass conservation principles:
- Darcy's Law: States that groundwater flow rate is proportional to the hydraulic gradient and the aquifer's hydraulic conductivity.
- Continuity Equation: Expresses mass conservation for groundwater, stating that the rate of change of groundwater storage in an aquifer equals the difference between recharge and discharge rates.
Flow Nets
Flow nets are graphical representations of two-dimensional, steady-state groundwater flow. They consist of flow lines (showing groundwater flow direction) and equipotential lines (lines of equal hydraulic head), which intersect at right angles. Flow nets help visualize and analyze groundwater flow patterns.
Well Hydraulics
Well hydraulics involves studying groundwater flow around wells and optimizing well design and operation. Factors include aquifer properties, pumping rate, well geometry, and boundary conditions. Pumping tests estimate parameters like transmissivity and storativity, aiding in well management.
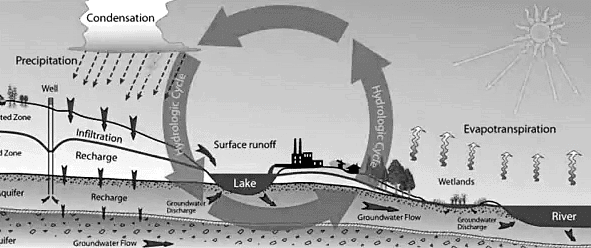
Groundwater Recharge and Discharge
- Recharge: Water enters the groundwater system through precipitation, surface water infiltration, or artificial methods like recharge wells.
- Discharge: Water exits the groundwater system through springs, seeps, or wells, maintaining surface water flow during dry periods and supporting ecosystems.
Groundwater Contamination
Groundwater contamination occurs when harmful substances enter the groundwater system, making it unfit for use. Contaminants can be natural or man-made, with sources including leaking storage tanks, industrial waste, and agricultural practices. Remediation technologies range from pump-and-treat systems to in-situ treatments.
Groundwater Management
Effective groundwater management optimizes the use of groundwater resources while protecting them from depletion and contamination. Key objectives include:
- Identifying and Quantifying Resources: Mapping aquifers and assessing water quantity and quality.
- Managing Use: Regulating extraction and allocating resources.
- Protecting Quality: Monitoring and controlling contamination sources.
- Restoring Degraded Aquifers: Remediating over-pumped or contaminated aquifers.
 |
Download the notes
Aquifer and Aquitards
|
Download as PDF |
Aquifer and Aquitard Mapping and Modeling
Mapping and modeling involve creating spatial representations of aquifers and aquitards using geological, geophysical, and hydrogeological methods. This helps identify contamination sources, assess land-use impacts, and optimize groundwater extraction rates.
Conclusion
Aquifers and aquitards are fundamental to the hydrological cycle and groundwater management. Understanding their properties, behavior, and interactions is crucial for sustainable water resource management and environmental protection. Effective groundwater management strategies ensure the long-term availability and quality of this vital resource.
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Aquifer and Aquitards - Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the difference between an aquifer and an aquitard? |  |
| 2. How is groundwater recharge and discharge related to aquifers and aquitards? |  |
| 3. How are aquifers and aquitards mapped and modeled? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of aquifers and aquitards? |  |
| 5. How do aquifers and aquitards impact groundwater availability and quality? |  |