Gupta Architecture
- The inception of the Gupta Empire in the 4th century A.D. is often regarded as the "Golden Period of Indian Architecture." During this time, temple construction flourished, particularly under the patronage of later Gupta rulers who embraced Hinduism.
- While the initial Gupta kings adhered to Buddhism and preserved Buddhist architectural traditions, the later Gupta rulers, who were predominantly Hindus, significantly promoted the construction of temples.
- The Gupta monarchs, particularly in the later phases, identified as Brahmanical rulers. Despite this, they exhibited remarkable tolerance for all other religions.
- In terms of religious practices, Vishnu was venerated in the northern and central regions of India, Shiva in the southern areas, and Shakti in the eastern part of India, as well as on the Malabar coast in the southwest.
Question for Nitin Singhania Summary Art & Architecture: The Gupta Period
Try yourself:
During the Gupta Empire, which region of India venerated Shiva as a religious practice?Explanation
- The Gupta Empire, known as the "Golden Period of Indian Architecture," had different regions in India where specific deities were venerated.
- According to historical records, Shiva was venerated as a religious practice in the southern regions of India during the Gupta Empire.
- The northern and central regions of India venerated Vishnu, while Shakti was venerated in the eastern part of India and on the Malabar coast in the southwest.
- Therefore, during the Gupta Empire, Shiva was predominantly venerated in southern India.
Report a problem
Cave Architecture
- The architectural evolution of caves remained consistent during the Gupta period, with the incorporation of mural paintings on cave walls emerging as an additional element. Notably, the Ajanta and Ellora caves showcase some of the finest examples of mural art.
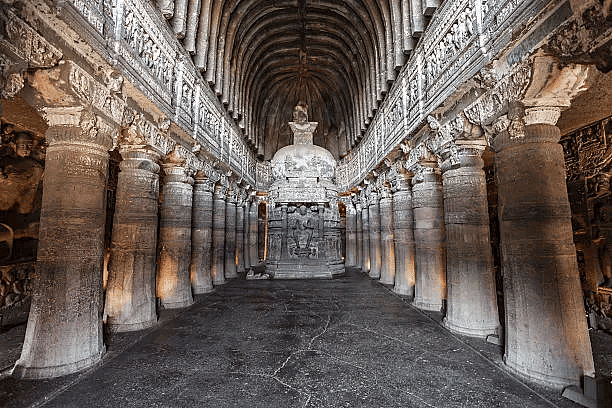
Ajanta caves
- Ajanta, situated near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, amidst the Sahyadri ranges on the Waghora River, consists of 29 caves. Among these, 25 served as Viharas (residence caves), and 4 were used as Chaitya (prayer halls). Constructed between 200 B.C. and 650 A.D., these caves were inscribed by Buddhist monks under the patronage of Vakataka rulers, including Harishena. The frescoes within these caves exhibited a high level of naturalism, utilizing colors derived from local plants and minerals. Notably, blue is absent in these paintings.
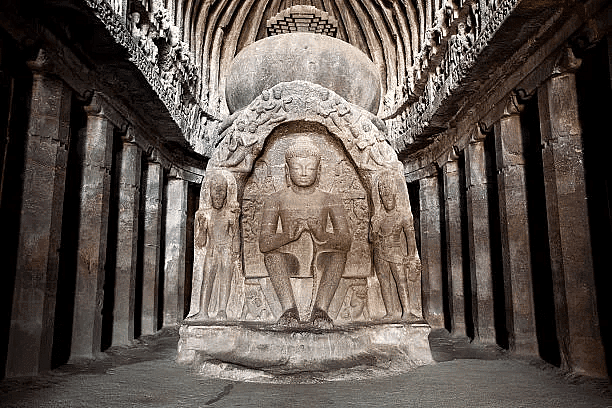
Ellora caves
- Ellora Caves, approximately 100 kilometers from Ajanta in Maharashtra's Sahyadri hills, comprises 34 caves, categorized into 17 Brahmanical, 12 Buddhist, and 5 Jain caves. Constructed by various guilds from Vidarbha, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu between the 5th and 11th centuries A.D., Ellora Caves exhibit a diverse range of topics and architectural styles.
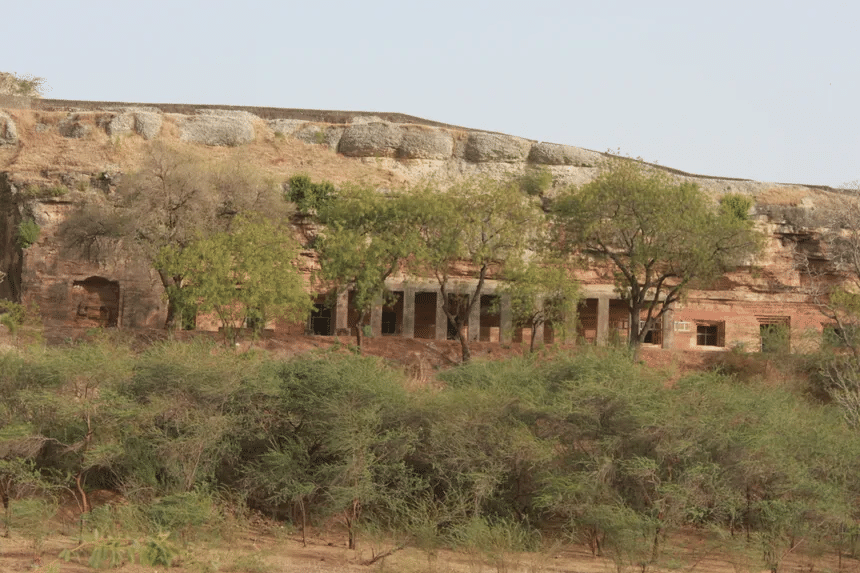

Bagh caves
- Other significant cave sites include the nine Buddhist caves along the Bagh river in Madhya Pradesh, which share architectural similarities with Ajanta, and the Buddhist caves in the Junagadh region of Gujarat, featuring Khapra Kodiya, Baba Pyare, and Uparkot.
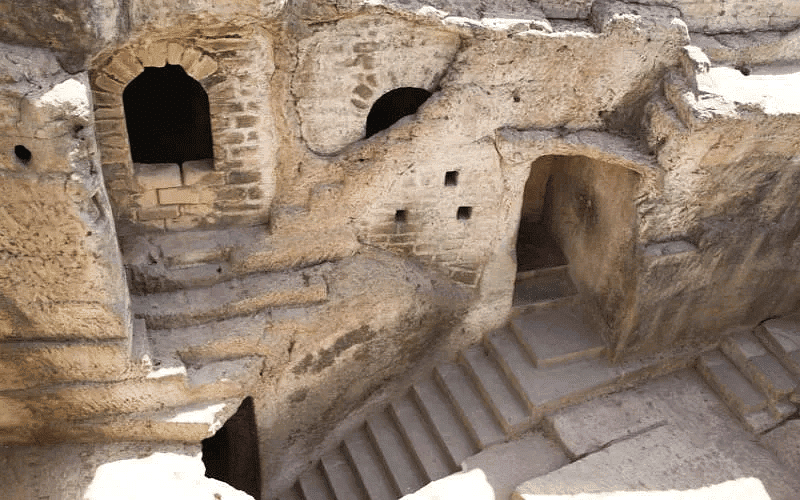

Junagadh caves
- In Nasik, the "Pandav Leni" consists of 24 Buddhist caves dating back to the first century A.D. and reflecting both Hinayana and Mahayana influences. The site displays Buddha idols and a well-engineered water management system.
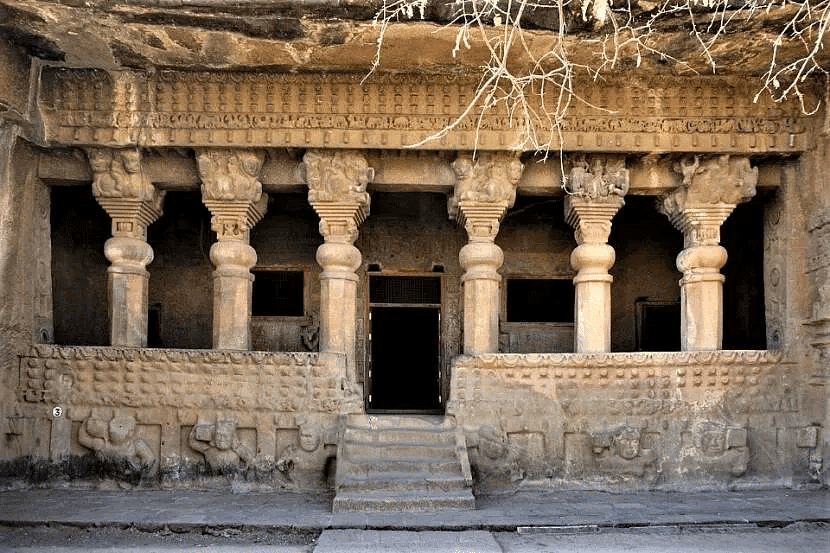
Nasik Caves
- Montperir Caves in Borivali, near Mumbai, originally constructed as a Brahmanical cave during the late Gupta dynasty, later transformed into a Christian cave. It contains sculptures of Natraja, Sada Shiva, and Ardhanarishwara.
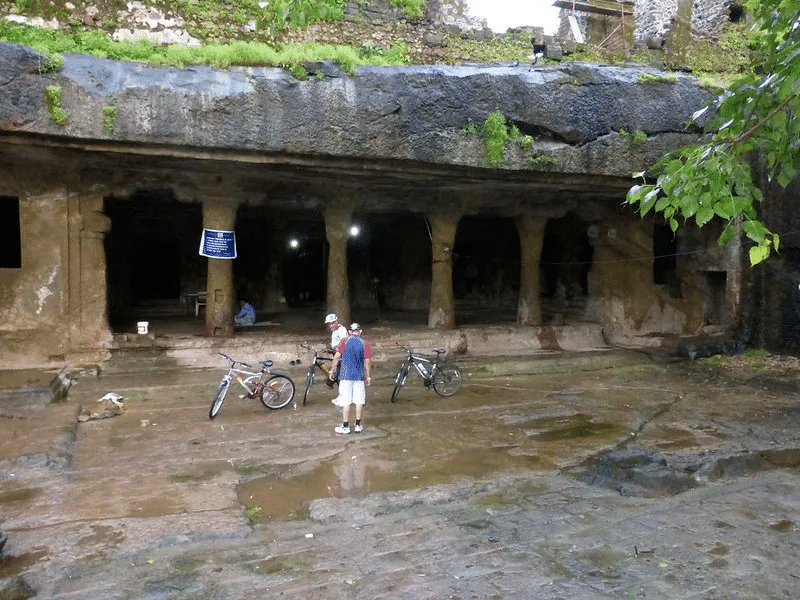

Mandapeshwar Caves
- The Udayagiri Caves in Madhya Pradesh's Vidisha district, built under the patronage of Chandragupta II in the early fifth century AD, is renowned for numerous sculptures on the hill walls, including the notable Varaha sculpture depicting Vishnu's Boar incarnation.
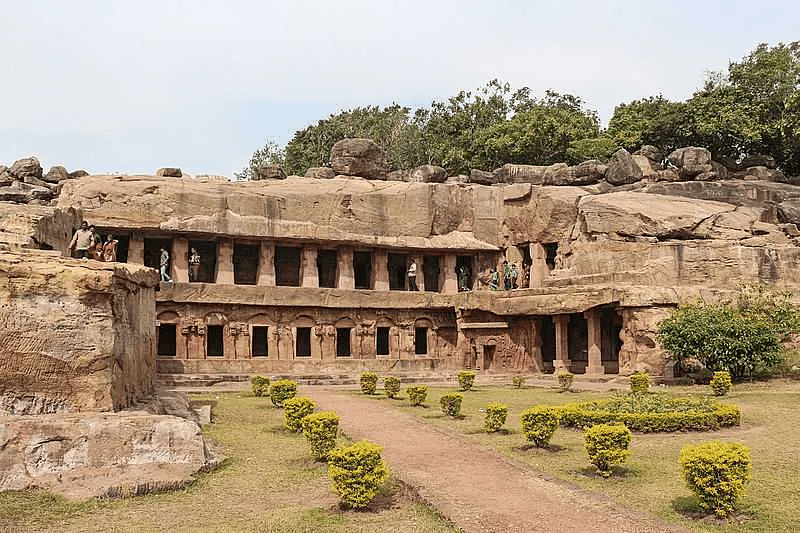

Udaygiri Caves
Question for Nitin Singhania Summary Art & Architecture: The Gupta Period
Try yourself:
Which caves are known for their mural paintings during the Gupta period?Explanation
- The Ajanta caves are known for their mural paintings during the Gupta period.
- These caves, located near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, were constructed between 200 B.C. and 650 A.D.
- Buddhist monks inscribed the caves under the patronage of Vakataka rulers, including Harishena.
- The frescoes within the Ajanta caves exhibited a high level of naturalism, utilizing colors derived from local plants and minerals.
- Notably, the color blue is absent in these paintings.
- Therefore, option A, the Ajanta caves, is the correct answer.
Report a problem
Stupas
Stupa construction experienced a decline during the Gupta period, yet the Dhamek Stupa in Sarnath, near Varanasi, stands as a notable exception from this era.
Dhamek Stupa:
- Situated in Sarnath, the Dhamek Stupa is a sizable stupa.
- It is believed that after attaining enlightenment, the Buddha delivered his inaugural sermon to his first five disciples, led by Kaundinya, expounding the Eightfold Path leading to nirvana at the Dhamek Stupa.
 Dhamek Stupa
Dhamek Stupa
Sculptures
The emergence of the Sarnath School of Sculpture, located near Sarnath, is noteworthy. In Sarnath, numerous Buddha images feature simple, transparent drapery enveloping both shoulders, with a minimally adorned halo encircling the head. This contrasts with the Buddha images from Mathura, which preserve the folds of the drapery, and the halos around the head are intricately embellished. A notable example is the Sultanganj Buddha, standing at a height of 7.5 feet.
 Sultanganj Buddha
Sultanganj Buddha
Temple Architecture
- The origins of Indian temple architecture can be traced back to the Gupta dynasty, during which manuals were created to guide temple construction. Gupta temples were categorized into five types.
 Kankali Devi Temple
Kankali Devi Temple - Examples such as the Kankali Devi temple in Tigawa and the Vishnu Varaha temples in Eran represent square buildings with flat roofs and shallow pillared porches. During this period, the sanctum or cella (garbhagriha) of a temple with a single entrance and a porch (Mandapa) made its first appearance.
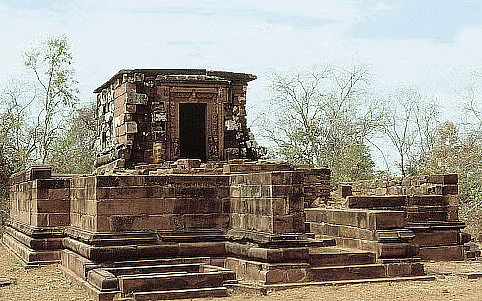 Shiva Temple
Shiva Temple - An evolved form included the addition of an ambulatory (pradakshina) surrounding the shrine, often on a second level. Examples include the Shiva temple in Bhumara and the ladkhan at Aihole, with the Parvati temple in Nachna Kuthara being another notable instance.
 Dashavatara Temple
Dashavatara Temple - Famous examples of the square temple with a low and squat tower (shikhara) above, pillared approach, and a high platform at the base include the Dashavatara temple in Deogarh Jhansi and the brick temple at Bhitargaon Kanpur. The most notable achievement of this stage was the introduction of the "Curvilinear tower" or "Shikhara."
 Kapoteswara Temple
Kapoteswara Temple - The third stage marked the triumph of temple construction in the "Nagara Style." Noteworthy examples include the Kapoteswara temple in Cezarla (Krishna district), which is a rectangular temple with an apsidal back and a barrel-vaulted roof.
 Maniyar Math Shrine In Rajgir
Maniyar Math Shrine In Rajgir - Circular temples with shallow rectangular projections on the four cardinal faces, as seen in the Maniyar Math shrine in Rajgir, Bihar, represent a unique form, with this monument being the sole example illustrating such a structure.
Conclusion
From 320 to 550 CE, the Gupta Empire held sway over northern, central, and southern India, leaving an indelible mark on the realms of arts, architecture, sciences, religion, and philosophy. The era witnessed significant achievements under the rule of Chandragupta I (320–335 CE), who spearheaded the rapid development of the Gupta Empire and emerged as its inaugural autonomous ruler. This period marked the conclusion of 500 centuries dominated by regional powers and the ensuing instability that followed the decline of the Mauryas. Instead, it ushered in an era of overall prosperity and expansion, spanning the next two and a half centuries and famously known as India's Golden Age.







 Ajanta caves
Ajanta caves Ellora caves
Ellora caves Bagh caves
Bagh caves Junagadh caves
Junagadh caves Nasik Caves
Nasik Caves Mandapeshwar Caves
Mandapeshwar Caves Udaygiri Caves
Udaygiri Caves Dhamek Stupa
Dhamek Stupa Sultanganj Buddha
Sultanganj Buddha Kankali Devi Temple
Kankali Devi Temple Shiva Temple
Shiva Temple Dashavatara Temple
Dashavatara Temple Kapoteswara Temple
Kapoteswara Temple Maniyar Math Shrine In Rajgir
Maniyar Math Shrine In Rajgir




















