Benzene: Resonance, Aromaticity, Preparation, & Properties | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Benzene
The parent member of the family of aromatic hydrocarbons is benzene (molecular formula:C6H6). It has hexagonal ring of six carbon atoms with three double bonds at alternate positions. It is resonance stabilized and the structure may be represented as given below.
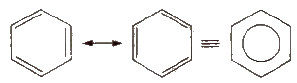
Resonance of Benzene
The oscillating double bonds in the benzene ring are explained with the help of resonance structures as per valence bond theory. All the carbon atoms in the benzene ring are sp2 hybridized. One of the two sp2 hybridized orbitals of one atom overlaps with the sp2 orbital of adjacent carbon atom forming six C-C sigma bonds. Other left sp2 hybridized orbitals combine with s orbital of hydrogen to form six C-H sigma bonds. Remaining unhybridized p orbitals of carbon atoms form π bonds with adjacent carbon atoms by lateral overlap.
This explains an equal possibility for the formation of C1 –C2, C3 – C4, C5 – C6 π bonds or C2 – C3, C4 – C5, C6-C1 π bonds. The hybrid structure is represented by inserting a circle in the ring as shown below in the figure. Hence, it explains the formation of two resonance structures proposed by Kekule.
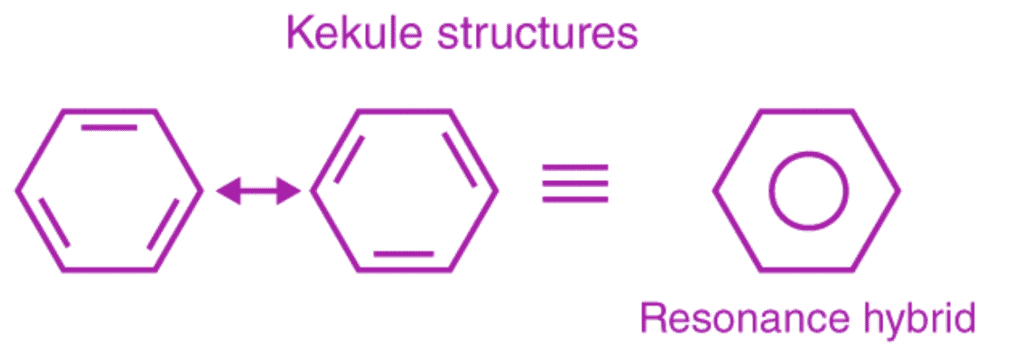
Aromaticity of benzene
Benzene is an aromatic compound, as the C-C bonds formed in the ring are not exactly single or double, rather they are of intermediate length. Aromatic compounds are divided into two categories: benzenoids (one containing benzene ring) and non-benzenoids (those not containing benzene ring), provided they follow Huckel rule. According to Huckel rule, for a ring to be aromatic it should have the following property:
- Planarity
- Complete delocalization of the π electrons in the ring
- Presence of (4n + 2) π electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2, . . .)
Methods of Preparation:
(i) Cyclic polymerization of ethyne
(ii) Decarboxylation of aromatic acids
(iii)
Physical Properties of Benzene:
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are non-polar molecules and are usually colourless liquids or solids with a characteristic aroma.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are immiscible with water but readily miscible with organic solvents.
- Aromatic compounds burn with sooty flame.
Chemical Reactions of Benzene:
- Benzene gives electrophilic substitution reactions.
- According to experimental evidences, electrophilic substitution reaction involve following three steps:
(a) Generation of electrophilie
(b) Formation of carbocation intermediate.
(c) Removal of proton from the carbocation intermediate.
(i) Nitration
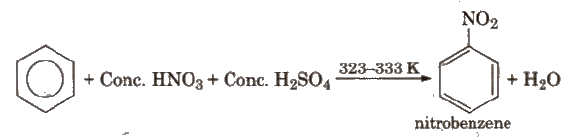
(ii) Halogenation
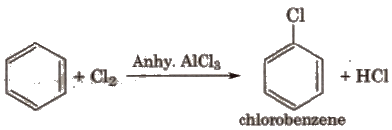
(iii) Sulphonation
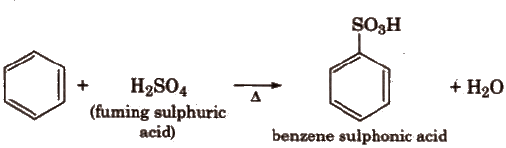
(iv) Friedel-Craft’s alkylation reaction
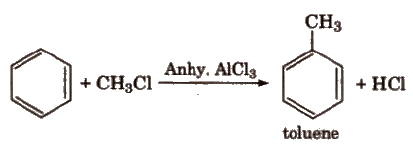
When Friedel-Craft alkylation is carried out with CH3Cl, the product obtained is C6H5CH3. In case the alkylation is carried out with higher alkyl halide, e.g., n-propyl chloride, then the electrophile n-propyl carbocation (CH3 – CH2 – +CH2) which is a primary carbocation rearranges to form more stable secondary carbocation (iso-propyl carbocation), and the main product formed will be iso-propyl benzene.
(v) Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction
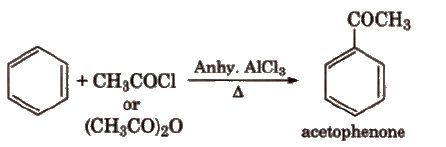
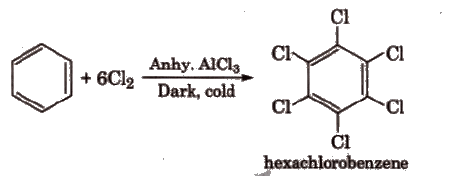
(vi) With Cl2: In excess of chlorine, benzene yields hexachlorobenzene [C6Cl6].
Benzene also undergoes addition reactions e.g.,
Combustion: 2C6H6 + 15O2 → 12CO2 + 6H2O
Reactions for Benzene:
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Benzene: Resonance, Aromaticity, Preparation, & Properties - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is resonance in benzene? |  |
| 2. What is aromaticity in benzene? |  |
| 3. How is benzene prepared? |  |
| 4. What are the properties of benzene? |  |
| 5. Is benzene harmful to humans? |  |

















