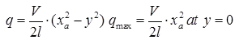Bond, Anchorage & Development Length | RCC & Prestressed Concrete - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
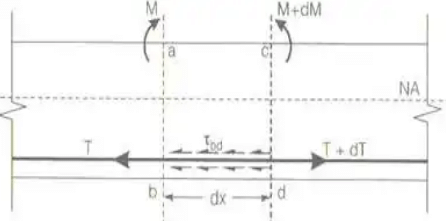
Bond stress(τbd) 
Where V = Shear force at any section
d = Effective depth of the section
∑ p = Sum of all perimeter of reinforcement
= n · π(ϕ)
n = Number of reinforcement
ϕ = diameter of reinforcement
Permissible bond stress
As per IS 456 : 2000
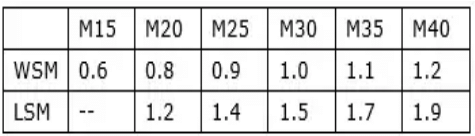
- This value of bond stress is for a plain bar in tension.
- For the deformed bar, the above value should be increased by 60%.
- For a bar in compression, the above value should be increased by 25%.
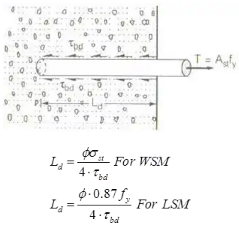
Development Length (Ld)
Shear stress
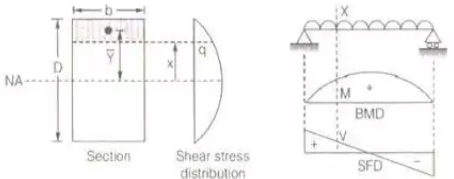
- For Homogeneous beam

 where, q = shear stress at any section
where, q = shear stress at any section
V = shear force at any section Moment of the area of the section above the point of consideration
Moment of the area of the section above the point of consideration
I = Moment of inertia of the section
= bD3 / 12 - For Reinforced concrete beam
 (i) Shear stress above NA
(i) Shear stress above NA
(ii) Shear stress below NA
q = V / bjd
Nominal shear stress, τv = V / bd
Design shear strength of concrete (τc) without shear reinforcement as per IS 456: 2000 (τc) depends on
(i) Grade of concrete
(ii) Percentage of steel, p = Ast / bd x 100
Where, Ast = Area of steel
b = Width of the Beam
d = Effective depth of the beam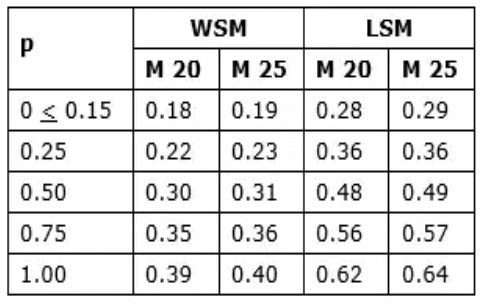
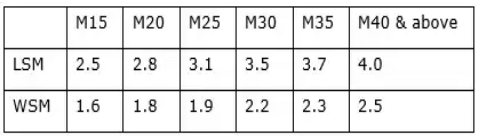
Maximum shear stress τc, max with shear reinforcement is
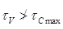
Minimum shear reinforcement (As per IS 456 : 2000)
ASV / bSV ≥ 0.4 / 0.87fy
This is valid for both WSM and LSM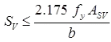
where, ASV = Area of shear reinforcement
SV = Spacing for shear reinforcement
Spacing of shear reinforcement
Maximum spacing is a minimum of (i), (ii) and (iii)
(i)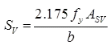
(ii) 300 mm
(iii) 0.75 → For vertical stirrups
d → For inclined stirrups
where, d = effective depth of the section
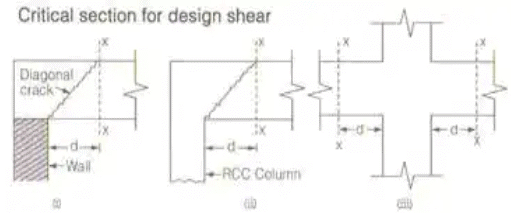
(a) Critical section X-X at d from the face of the support
(b) Critical section X-X at the face of the support
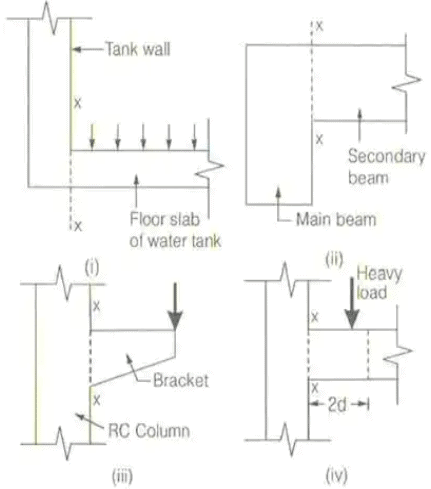
The above provisions are applicable for beams generally carrying uniformly distributed load or where the principal load is located beyond 2d from the face of the support.
Vertical stirrups
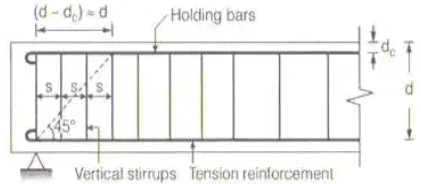
Shear force VS will be
Resisted by shear Reinforcement provided in 'd' length of the beam,

where, ASV = Cross-sectional area of stirrups
SV = Centre to centre spacing of stirrups
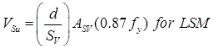
Inclined stirrups: or a series of bars bent up at different cross-section:
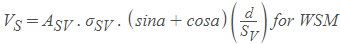

Bent up Bars
- Single or a group of bent up bars are provided at distance √2a = √2jd from support.
Generally, the bar should not be bent up beyond a distance l/4 from the support. Where l = length of the span.
|
13 videos|42 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Bond, Anchorage & Development Length - RCC & Prestressed Concrete - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is bond length in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How is bond length determined in civil engineering? |  |
| 3. What is anchorage length in civil engineering? |  |
| 4. How is anchorage length determined in civil engineering? |  |
| 5. What is development length in civil engineering? |  |

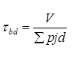
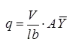
 where, q = shear stress at any section
where, q = shear stress at any section Moment of the area of the section above the point of consideration
Moment of the area of the section above the point of consideration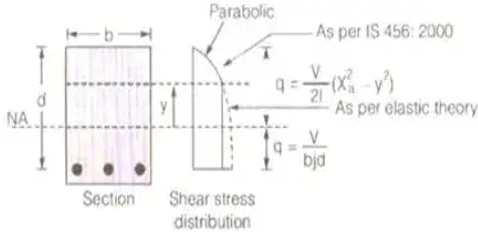 (i) Shear stress above NA
(i) Shear stress above NA