Carboxylic Acids: Physical & Chemical Properties | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Physical properties of Carboxylic Acids
Odor
Carboxylic acids containing up to nine carbon atoms exhibit colorless liquid states at room temperature, accompanied by unpleasant odors. In contrast, their higher counterparts exist as solid, wax-like substances, characterized by their lack of noticeable scent owing to reduced volatility.
Boiling point
Carboxylic acids, when compared to aldehydes, ketones, and similar-sized alcohols, have higher boiling points, meaning they need more heat to turn from a liquid to a gas.
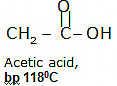
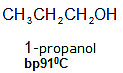
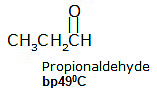
The high boiling points of carboxylic acids are the result of the formation of a stable hydrogen-bonded dimer.
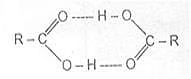 Hydrogen-bonded Acid Dimer
Hydrogen-bonded Acid Dimer
Solubility
Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water and the lower molecular–weight carboxylic acids (up to 4 carbon atoms) are miscible with water.
Acid derivatives (esters, acid chlorides, anhydride, nitriles, and amides) are soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols, ethers, chlorinated alkanes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Chemical Reactions
Reaction involving cleavage of O-H bond
Acidity of carboxylic acids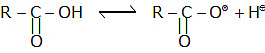
Ex.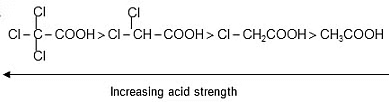
Ex. HCOOH > CH3COOH > CH3-CH2-COOH
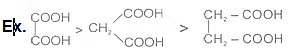
Ex. Relative acid strength is:-
RCOOH > HOH > ROH > HC = CH > NH3 > RH
Note: The acidity of acids is compared by comparing the stability of the conjugate base.
- Carboxylic acids, like alcohols, release hydrogen when they interact with metals that easily give up electrons.
- They also create salts with alkaline substances, similar to what happens with phenols.
- However, unlike phenols, they react with weaker bases like carbonates and bicarbonates, leading to the release of carbon dioxide. This particular reaction is employed to identify the presence of carboxyl groups in organic compounds.
Action with blue litmus: All carboxylic acids turn blue litmus red.
Reaction with metals :
2 CH3 COOH + 2Na → 2CH3COONa(Sodium acetate) + H2
2CH3 COOH + Zn → (CH3COO)2 Zn(Zinc acetate) + H2
Reaction with alkalies :
CH3 COOH + NaOH → CH3 COONa + H2O
Reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates :
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3 COONa + CO2 + H2O
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
The reaction of carboxylic acid with aqueous sodium carbonate solution produces brisk effervescence. However, most phenols do not produce effervescence. Therefore, the reaction may be used to distinguish between carboxylic acids and phenols.
Reaction with Grignard's reagent :

Note: A stronger acid displaces a weaker acid from the salt of the weaker acid.
Ex. CH3COOH (Stronger acid) + CH3ONa → CH3 COONa + CH3 —OH (WeakerAcid)
Ex. CH3COOH (stronger acid) + NaHCO3 → CH3 COONa + H2 CO3 (Weaker acid) → H2O + CO2
Reaction involving cleavage of C–OH bond
Formation of acid chlorides:
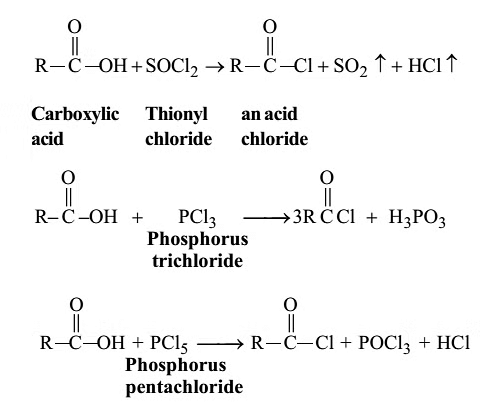
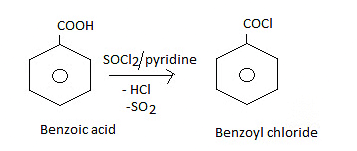
Fisher Esterification:
Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol to form esters through a condensation reaction known as esterification.
General Reaction:
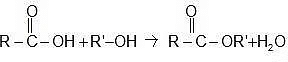
Specific Example:
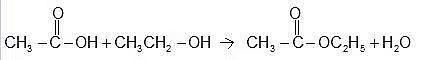
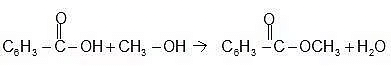
Mechanism:
Acid catalysed esterification:
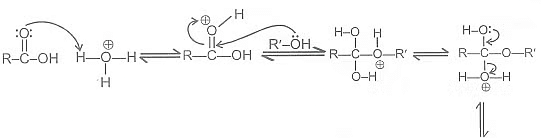
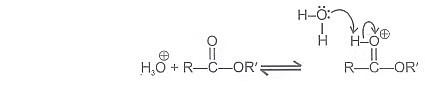
If we follow the forward path in this mechanism, we have the mechanism for the acid catalysed esterification for an acid. If however, we follow the reverse reactions, we have the mechanism for the acid catalysed hydrolysis of an ester. Acid catalysed ester hydrolysis gives:
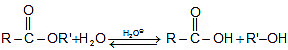
Formation of amides:
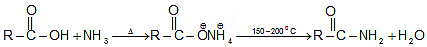
Formation of acid anhydride:
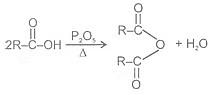
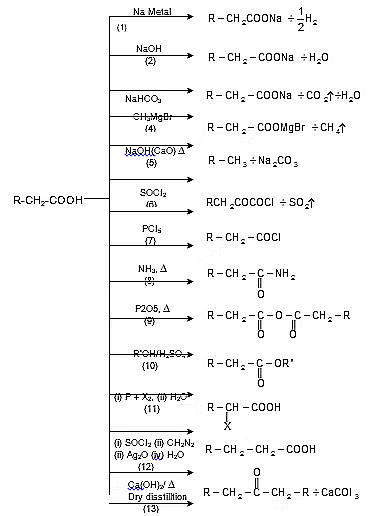
Reactions Involving -COOH Group:
Schmidt Reaction:
The carboxylic acids react with hydrazoic acid in the presence of H2SO4 to form a primary amine
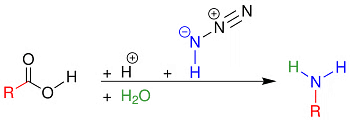 Schmidt Reaction
Schmidt Reaction
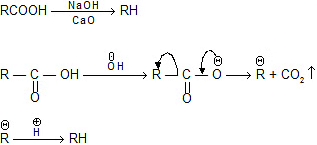
Soda-lime decarboxylation :
General reaction:
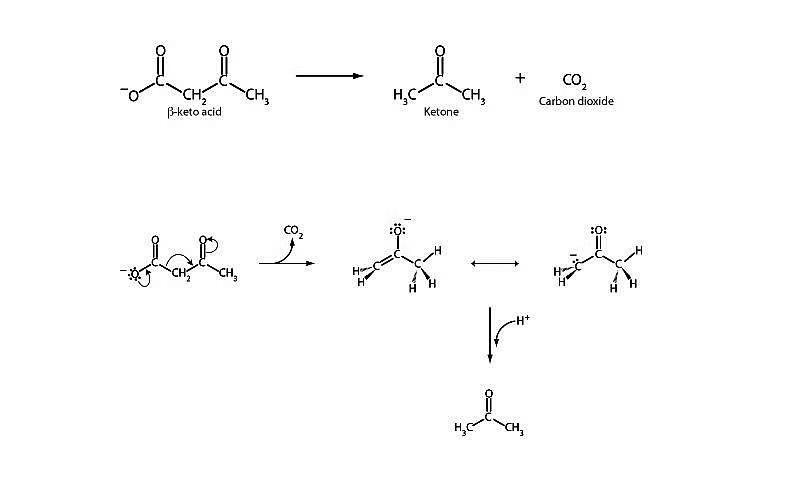
Decarboxylation of β- keto carboxylic acids :
Kolbe's electrolysis:
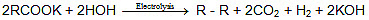
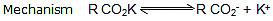
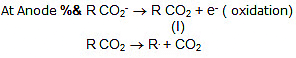
(II) R. + R. → R - R
If n is the number of carbon atoms in the salt of carboxylic acid, the alkane formed has 2(n-1) carbon atoms.

Hunsdiecker Reaction (Brome-decarboxylation):
R-COOAg + Br2 → R-Br + CO2 + AgBr
Mechanism:
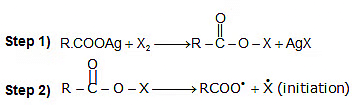
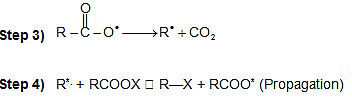
HVZ Reaction (Halogenation of aliphatic acids and Substituted acids):
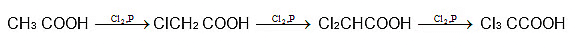
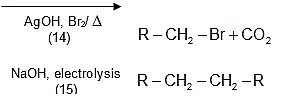
|
366 videos|833 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Carboxylic Acids: Physical & Chemical Properties - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the physical properties of carboxylic acids? |  |
| 2. How do carboxylic acids react with water? |  |
| 3. Can carboxylic acids undergo esterification? |  |
| 4. How do carboxylic acids react with bases? |  |
| 5. What are some common chemical reactions of carboxylic acids? |  |
















