Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives: Nomenclature & Preparation | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are carbon compounds that have a special part called a carboxyl group (–COOH). This carboxyl group is made up of a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group, which is why it's called "carboxyl."
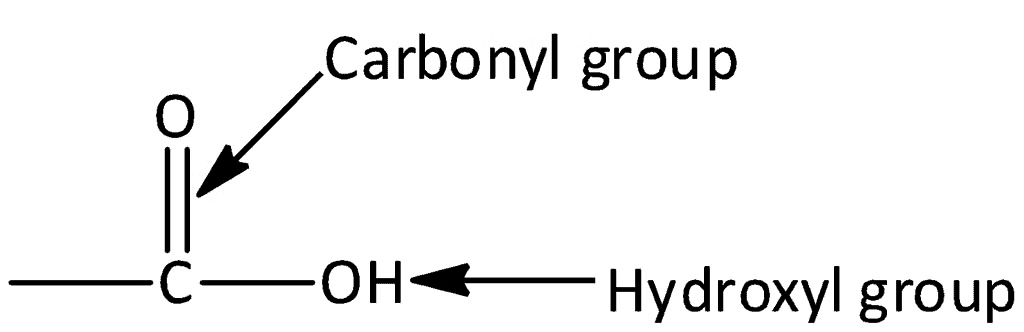 Representation of Carboxylic Acid
Representation of Carboxylic Acid
Classification of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids can be classified based on the number of carboxyl groups attached to the carbon chain:
1. Monocarboxylic Acids:
These acids have only one carboxyl group in their molecular structure. Example: Formic acid (HCOOH- obtained from red ants), acetic acid (CH3COOH-obtained from vinegar).
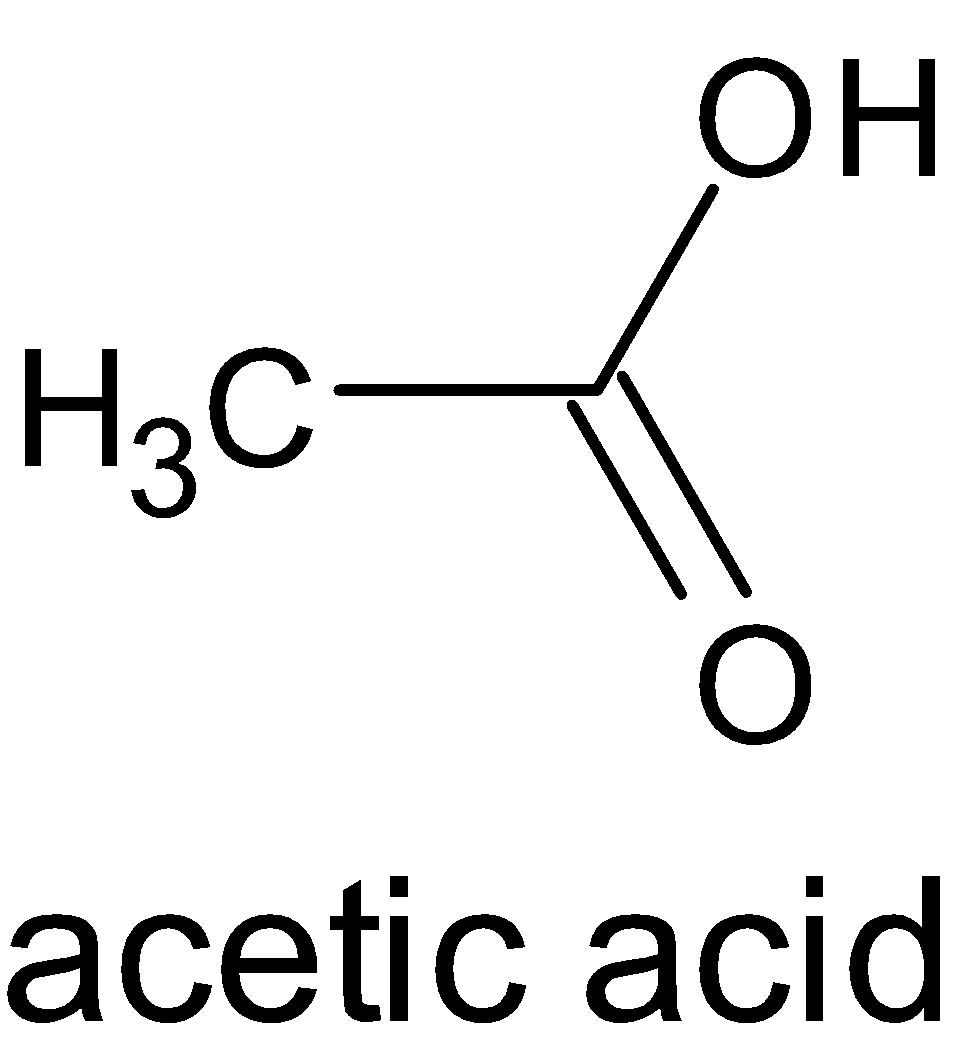 Example of Monocarboxylic Acid
Example of Monocarboxylic Acid
2. Dicarboxylic Acids:
These acids contain two carboxyl groups in their molecular structure. Example: Oxalic acid (H2C2O4), malonic acid (CH2(COOH)2).
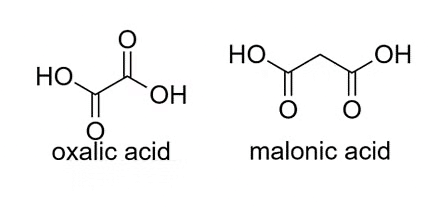 Examples of Dicarboxylic Acids
Examples of Dicarboxylic Acids
3. Tricarboxylic Acids:
These acids have three carboxyl groups in their molecular structure. Example: Citric Acid
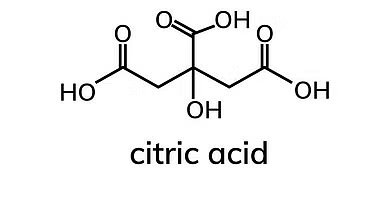 Example of Tricarboxylic Acids
Example of Tricarboxylic Acids
Structure of Carboxyl Group
In carboxylic acids, the bonds connected to the carboxyl carbon are arranged in a flat plane and are spread out at an angle of approximately 120°. The carboxyl carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of a possible resonance structure, as indicated in the resonance illustration below.
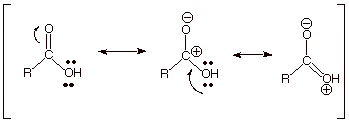 Resonance Structures of Carboxylic Acids
Resonance Structures of Carboxylic Acids
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are usually called by simple names, like acetic acid (CH3COOH). In IUPAC naming, they get a different name by changing the ending to "oic acid."
Here are the rules:
- Replace the "e" at the end of the alkane name with "oic acid."
- If there's only one carboxyl group, the carbon with it is always numbered as one. For example, CH3COOH becomes ethanoic acid.
- If there's more than one carboxyl group, count all the carbon atoms and use Greek numeral prefixes like "di-", "tri-", etc. to show how many carboxyl groups there are.
- Put together the alkyl chain name, numeral prefixes, and "oic acid" to name the carboxylic acid. Use Arabic numerals to show where the carboxyl groups are.
- If a carboxyl group is a substituent on a carbon chain, you can call it "carboxylic acid" or "carboxy." For example, 2-furoic acid can be called 2-carboxyfuran.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Closely related to the carboxylic acids and to each other are several chemical families known as functional derivatives of carboxylic acids: acid chloride, anhydrides, amides, and esters.
These derivatives are compounds in which the -OH of a carboxyl group has been replaced by–Cl, -OOCR, -NR2, or –OR.
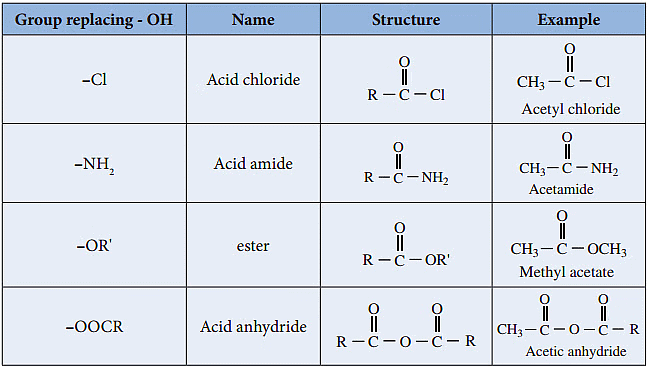 Carboxylic Acid DerivativesThey all contain the acyl group,
Carboxylic Acid DerivativesThey all contain the acyl group,
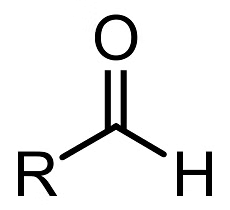 Acyl Group
Acyl Group
Acid halides
Methods of preparation of Acyl halides:
(i) RCOOH + PCl5 → RCOCl + POCl3 + HCl
(ii) 3RCOOH + PCl3 → 3RCOCl + H3PO3
(iii) RCOOH + SOCl2 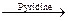 RCOCl +SO2 + HCl
RCOCl +SO2 + HCl
Ex. 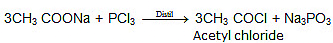
Ex. 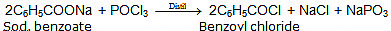
Chemical Reactions:
1. Reaction with carboxylic acids:
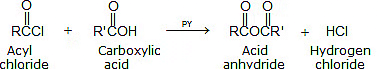
2. Reaction with alcohols:
Acyl chlorides react with alcohols to form esters. The reaction is typically carried out in the presence of pyridine.
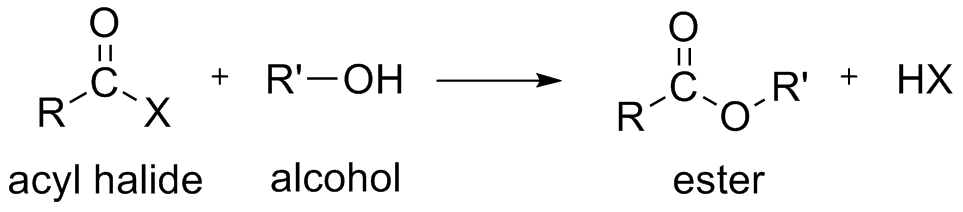 Reaction of Acid Chlorides with Alcohols
Reaction of Acid Chlorides with Alcohols
3) Hydrolysis:
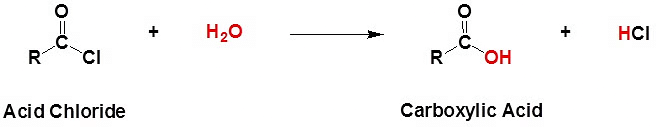 Hydrolysis of Acid Chloride
Hydrolysis of Acid Chloride
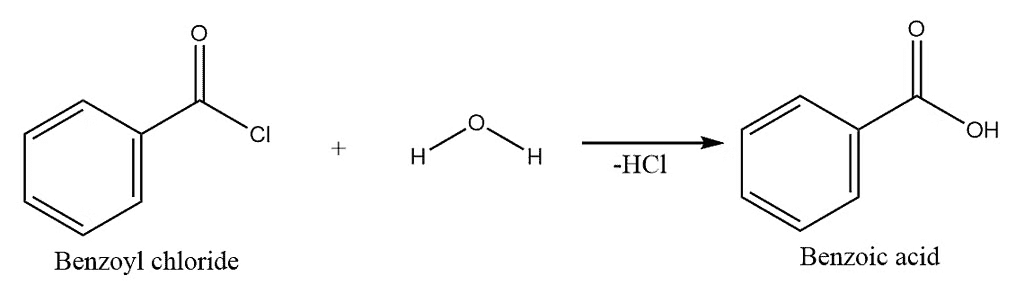 Hydrolysis of Benzoyl Chloride
Hydrolysis of Benzoyl Chloride
4) Reaction of acid halide with organometallic compounds:
(a) With Grignard's Reagent:
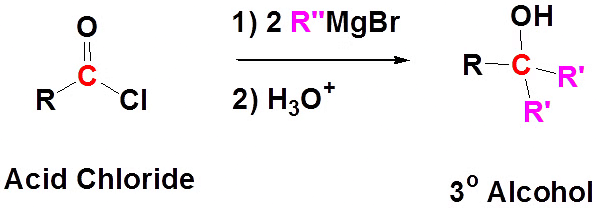 Reaction of Acid Chloride with Grignard Reagent
Reaction of Acid Chloride with Grignard Reagent
(b) Reaction with Gillman's Reagent:
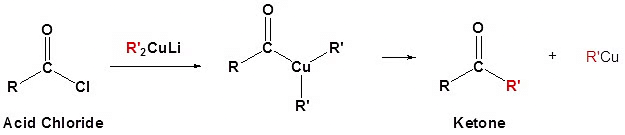
5) Reduction of acid halide:
(a) Reduction with LiAlH4/NaBH4:
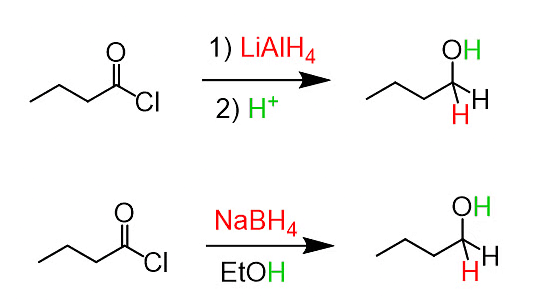 Reduction of Acid Halide with LiAlH4/NaBH4
Reduction of Acid Halide with LiAlH4/NaBH4
(b) Reduction with H2/Pd/BaSO4 (Rosenmund reduction):
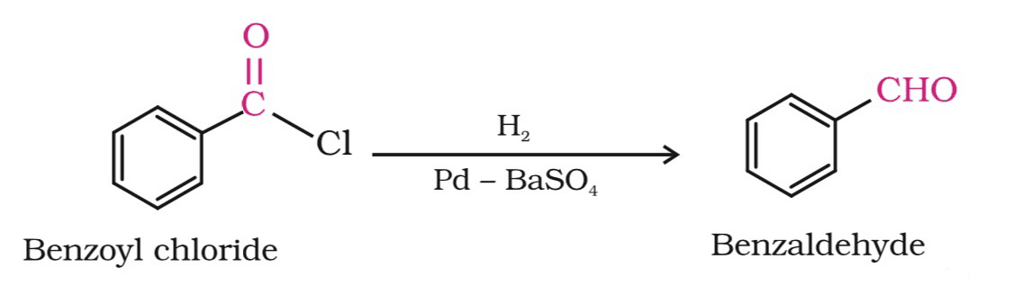 Rosenmund Reduction
Rosenmund Reduction
Summary of Reaction of Acid Chlorides: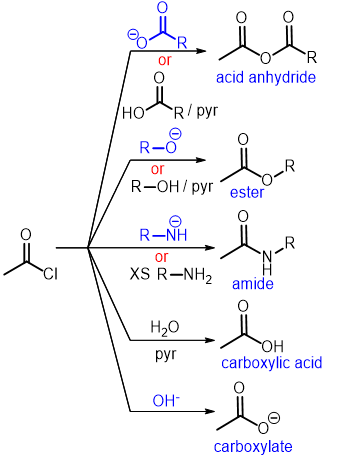 Summary of Reaction of Acid Chlorides
Summary of Reaction of Acid Chlorides
Acid amides:
Methods of preparation of acids amides:
1. By the reaction of Esters with Ammonia and Amines.
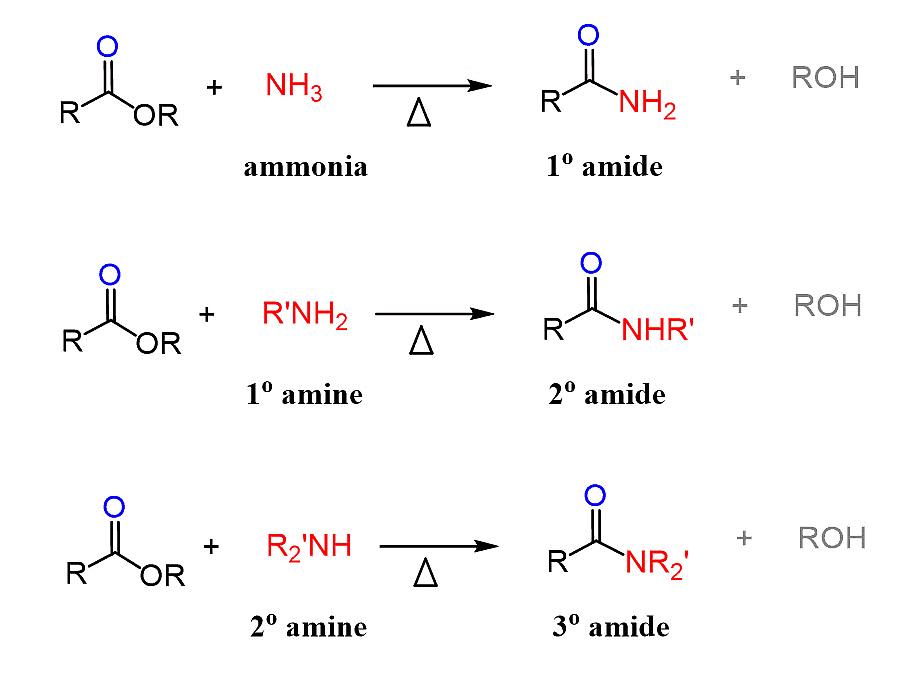 Reaction of Esters with Ammonia and Amines
Reaction of Esters with Ammonia and Amines
Ammonia is more nucleophilic than water, making it possible to carry out this reaction using aqueous ammonia.
Ex.
2. From acid halides:
RCOCl + 2NH3 → RCONH2 + NH4Cl
3. From anhydride:
(RCO)2O + 2NH3 → RCONH2 + RCOO NH4
4. From esters:
RCOOR + NH3 → RCONH2 + R’OH
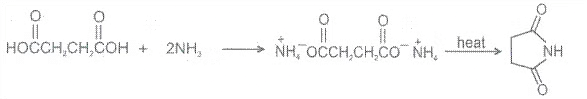
5. From ammonium salt of carboxylic acid:
RCOONH4  RCONH2 + H2O
RCONH2 + H2O
CH3 COONH4  CH3CONH2
CH3CONH2
6. From cyanides:
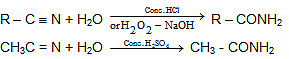
7.
Chemical Reactions:
1. Hoffmann rearrangement:
General reaction
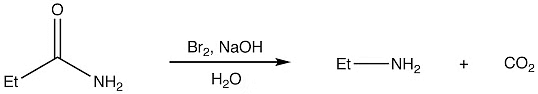 Hoffmann Rearrangement
Hoffmann Rearrangement
(2) Hydrolysis of amides:
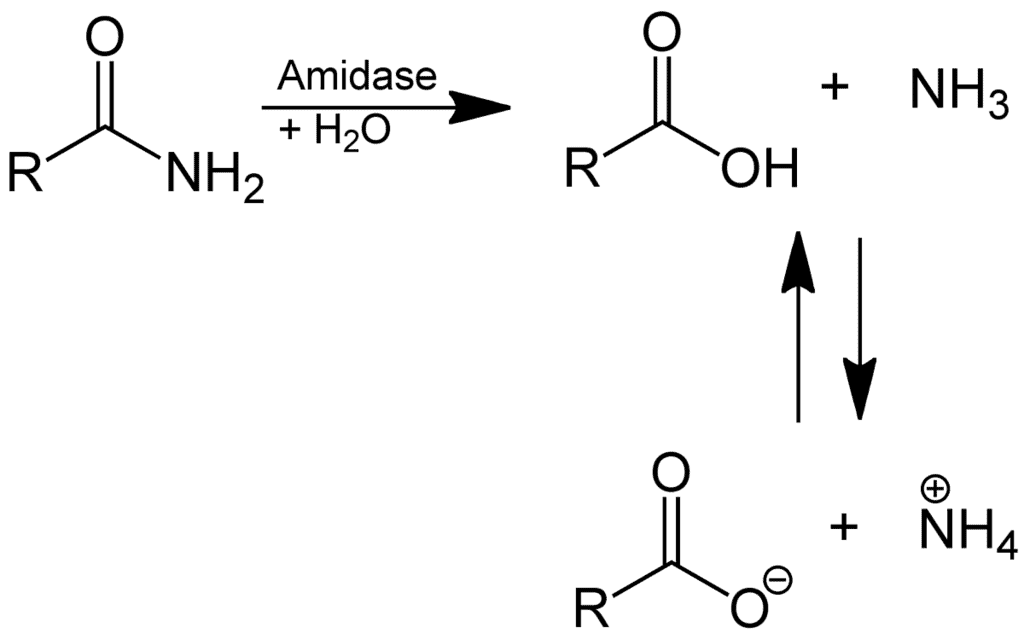 Hydrolysis of Amides
Hydrolysis of Amides
In acid, however, the amine is protonated, giving an ammonium ion, R2’ 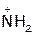

Summary of Reaction of Amide:
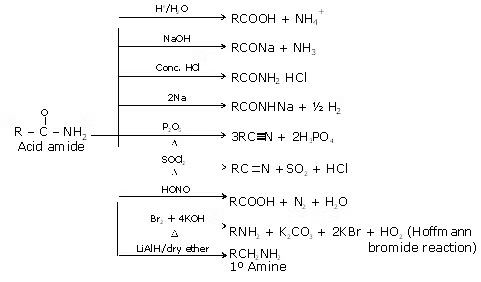 Summary of Reactions of Amides
Summary of Reactions of Amides
Esters
Methods of Preparation:
(i) CH3 COOH + C2H5OH  CH3COOC2 H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2 H5 + H2O
Acetic acid
C6H5COOH + CH3OH  C6H5 COOCH3 + H2O
C6H5 COOCH3 + H2O
(ii) CH3COCl + C2H5OH  CH3COOC2H5 + HCl
CH3COOC2H5 + HCl
Alcohols react with acyl chlorides by nucleophilic acyl substitution to yield esters. These reactions are typically performed in the presence of a weak base such as pyridine.

Summary of Chemical reaction of esters:
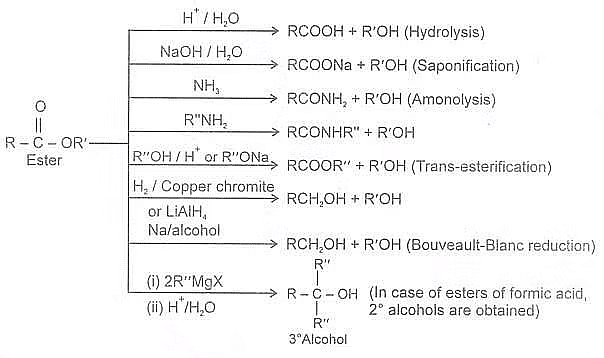 Summary of Reactions of Esters
Summary of Reactions of Esters
Acid anhydrides
Methods of Preparation of acid anhydrides:
1. From carboxylic acids
Ex.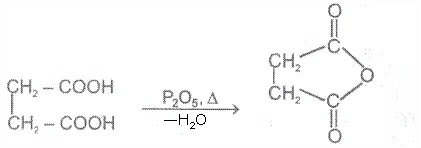
Ex. 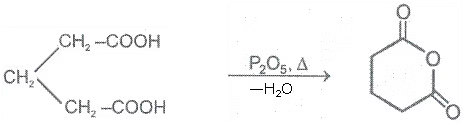
2. From acid and acid halide
Ex. CH3COOH + CH3COCl  CH3 CO.O.COCH3 + HCl
CH3 CO.O.COCH3 + HCl
Ex. CH3COCl + CH3COONa  CH3CO.O.COCH3 + NaCl
CH3CO.O.COCH3 + NaCl
Chemical Reaction:
1. Reaction with aromatic compounds (Friedel crafts acylation):
 Friedel Crafts Acylation
Friedel Crafts Acylation
2. Reaction with alcohols:
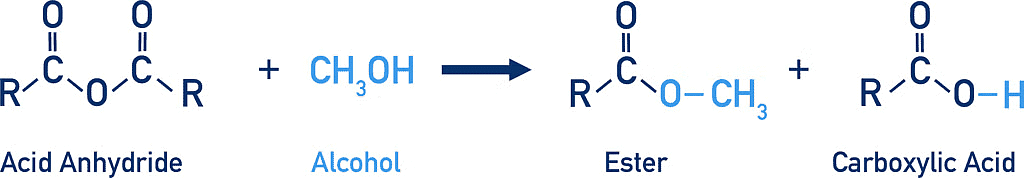 Reaction of Acid Anhydride with Alcohols
Reaction of Acid Anhydride with Alcohols
3. Reaction with Ammonia and Amines:
 Reaction of Acid Anhydride with Amines
Reaction of Acid Anhydride with Amines
4. Hydrolysis:
Acid anhydrides react with water to yield two carboxylic acids. Cyclic anhydrides yield dicarboxylic acids.

Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
- Primary alcohols and aldehydes can turn into carboxylic acids through an oxidation reaction using substances like potassium permanganate (KMnO4 in neutral, acidic, or alkaline media), chromium trioxide (CrO3– H2SO4– Jones reagent), and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7– in acidic media).
- When primary alcohols react with these oxidizing agents, they form aldehydes. Subsequently, another oxidation step transforms these aldehydes into carboxylic acids. Potassium dichromate, potassium permanganate, and chromium trioxide being strong oxidizers, can efficiently convert aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
On the other hand, milder oxidizing agents, such as manganese dioxide (MnO2) and Tollen’s reagent [Ag(NH3)2+ OH−], can only carry out one oxidation step, converting primary alcohols to aldehydes. As a result, these mild agents are used specifically for converting aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
 General Reaction Depicting Oxidation of Alcohols
General Reaction Depicting Oxidation of Alcohols
Oxidation of Aldehydes
Carboxylic acids can be produced using both typical strong oxidizing agents and gentler ones like Tollen’s reagent [Ag(NH3)2+OH−] and manganese dioxide (MnO2).
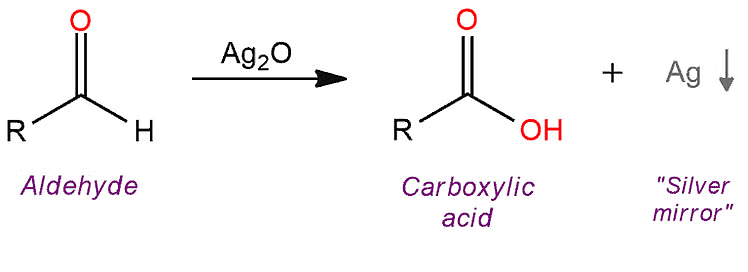 Oxidation of Aldehydes
Oxidation of Aldehydes
The above reaction serves as the silver mirror test. This test is based on the formation of a silver mirror on the inner surface of a test tube when Tollen's reagent [Ag(NH3)2+OH−] reacts with an aldehyde. The silver mirror formation is indicative of the presence of aldehydes, making it a valuable tool in qualitative analysis for identifying these functional groups in organic compounds.
Oxidation of Alkenes
- The oxidation of alkenes to carboxylic acids involves the introduction of oxygen to the carbon-carbon double bond in the alkene structure.
- This reaction is typically carried out using strong oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or ozone (O3).
- The double bond in the alkene is cleaved, and each carbon atom involved in the double bond is bonded to an oxygen atom, forming carboxylic acid functional groups. This process transforms the alkene into a carboxylic acid through oxidative cleavage of the double bond.
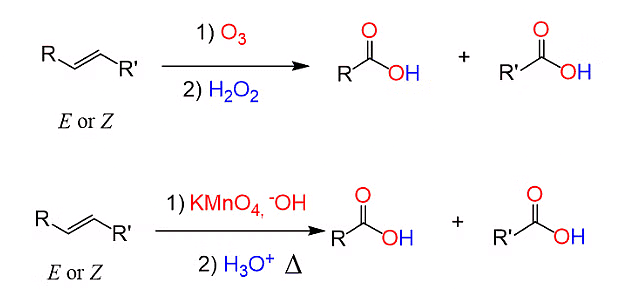 Oxidation of Alkenes
Oxidation of Alkenes
Carboxylation of Grignard Reagent
- The carboxylation of a Grignard reagent involves the reaction of a Grignard reagent (an organomagnesium compound) with carbon dioxide (CO2) to yield a carboxylic acid. This reaction is a useful method for synthesizing carboxylic acids.
- The general reaction is:
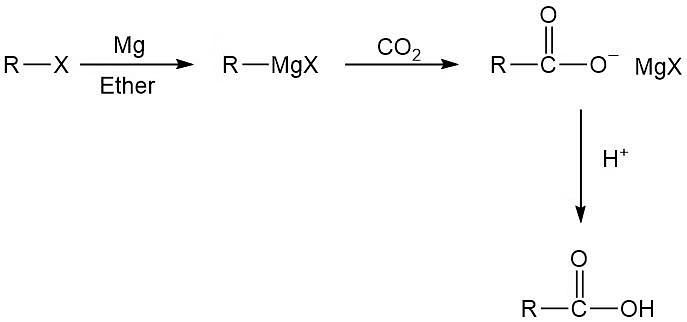 Carboxylation of Grignard's Reagent
Carboxylation of Grignard's Reagent
- The Grignard reagent, RMgX, acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of carbon dioxide. The intermediate formed undergoes further reactions, ultimately resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid.
- This method is valuable in organic synthesis for introducing carboxylic acid functional groups into organic compounds.
Hydrolysis of Acyl Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
Hydrolysis of acyl derivatives of carboxylic acids involves breaking these compounds with water, producing carboxylic acids or derivatives. It's a key process in chemical synthesis.
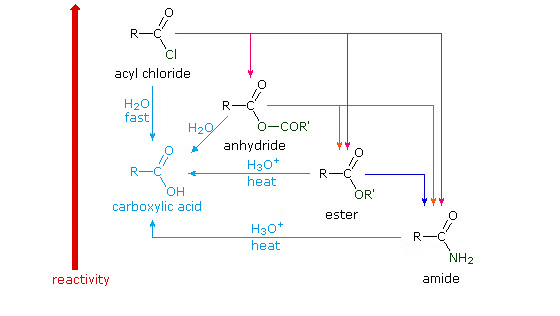 Hydrolysis of acyl derivatives of carboxylic acids
Hydrolysis of acyl derivatives of carboxylic acids
Cyanide Hydrolysis with Dilute Acids
- Cyanide hydrolysis with dilute acids involves the reaction of cyanide ions (CN-) with an acid, leading to the formation of carboxylic acids.
- This process, known as hydrolysis, results in the conversion of the highly toxic cyanide into less harmful carboxylic acids.
- The acidic conditions facilitate the nucleophilic attack of water molecules on the cyanide ion, breaking the carbon-nitrogen bond and forming carboxylic acid functional groups.
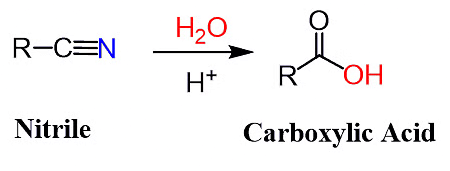 Cyanide hydrolysis with dilute acids
Cyanide hydrolysis with dilute acids
Oxidation of Alkyl Benzene
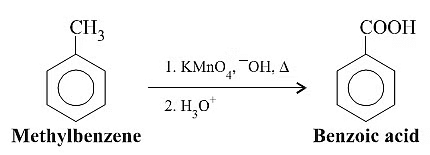 Oxidation of Alkyl Benzene
Oxidation of Alkyl Benzene
The position directly adjacent to an aromatic group is called the “benzylic” position.
The reaction only works if there is hydrogen attached to the carbon.
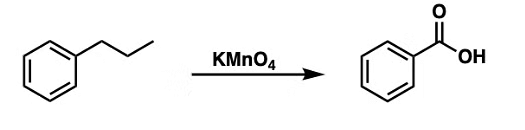
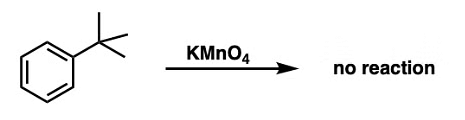
The order of benzoic acid formation by oxidation of alkyl benzene:
Methyl Benzene > 1o alkyl benzene > 2o alkyl benzene
|
366 videos|833 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives: Nomenclature & Preparation - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the structure of a carboxyl group in carboxylic acids? |  |
| 2. How are carboxylic acids named according to IUPAC nomenclature? |  |
| 3. What are some common methods for the preparation of carboxylic acids? |  |
| 4. How can carboxylic acids be distinguished from other functional groups in organic compounds? |  |
| 5. Can carboxylic acids be prepared from alkyl halides? |  |

















