Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Structure of the Atom
Case I
Read the given passage and answer the questions based on the passage and related studied concepts.
Atom consists of electrons, protons and neutrons. J.J. Thomson proposed that electrons are embedded in a positive charge uniform sphere. Rutherford a-scattering experiment led to discovery of nucleus in the centre of atom which is positively charged and whole mass of atom is concentrated in the nucleus. Neil Bohr proposed that electrons are distributed in different shells in M, N... with discrete energy around the nucleus. If atomic shell is complete, atom will be stable and less reactive. Electrons are negatively charged, protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral. Valency is the combining capacity of an atom. Atomic number is equal to number of protons in an atom. The mass number of an atom is equal to sum of number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes have same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isobars have same mass number but different atomic numbers. Elements are defined by number of protons (atomic number) they possess.
Q1: Which of the following does not contain neutron?
(a) Al
(b) Na
(c) H
(d) Mg
Ans: Hydrogen (H) does not contain neutron.
Q2: What is the atomic number of Al3+, if it has 13 protons, 10 electrons, 14 neutrons?
(a) 13
(b) 10
(c) 14
(d) 27
Ans: (a)
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons it contains. In this case:
- The element has 13 protons.
- Therefore, the atomic number is 13.
It is important to note that the number of electrons and neutrons does not affect the atomic number.
Q3: Write electronic configuration of 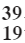 K.
K.
Ans: The electronic configuration of potassium (K) is:
- 2 electrons in the first shell
- 8 electrons in the second shell
- 8 electrons in the third shell
- 1 electron in the fourth shell
Thus, the complete configuration is 2, 8, 8, 1.
Q4: Isotopes differ in which sub-atomic particles?
Ans: Neutrons
Case II
Observe the Bar-chart shown for elements with atomic number 1 to 10. Answer the questions based on this graph and related studied concepts.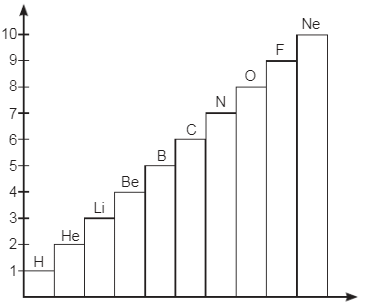 Q1: Name the element whose first shell is complete.
Q1: Name the element whose first shell is complete.
Ans: Helium is the element whose first shell is complete.
- It has two electrons in its outermost shell.
- This configuration makes it stable and non-reactive.
- Other elements typically aim for a full outer shell of eight electrons.
Q2: Name the element in which second shell has twice electrons than 1st shell.
Ans: The element where the second shell has twice the number of electrons compared to the first shell is carbon.
- First shell (K-shell): 2 electrons
- Second shell (L-shell): 4 electrons
This gives the electronic configuration of carbon as C(2, 4).
Q3: How does valence electrons vary from Li to Ne?
Ans: The number of valence electrons varies as you move from Lithium (Li) to Neon (Ne) in the periodic table:
- Li has 1 valence electron.
- Be has 2 valence electrons.
- B has 3 valence electrons.
- C has 4 valence electrons.
- N has 5 valence electrons.
- O has 6 valence electrons.
- F has 7 valence electrons.
- Ne has 8 valence electrons.
In summary, the number of valence electrons increases from Li to Ne, reaching a maximum of 8 in Ne.
Q4: Name the element which has 7 valence electrons.
Ans: Fluorine (F) has 7 valence electrons in its outermost shell.
- It is more stable for fluorine to gain one electron.
- This gives it a valency of 1.
|
84 videos|384 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Structure of the Atom
| 1. What are the main components of an atom? |  |
| 2. How do the number of protons determine the identity of an element? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of electron configuration in an atom? |  |
| 4. Can you explain isotopes and their importance? |  |
| 5. What role do electrons play in chemical bonding? |  |

















