Cash Flow Statement (Part - 1) | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Page No. 5.89
Question:1
Identify the transactions as belonging to (i) Operating Activities, (ii) Investing Activities, (iii) Financing Activities and iv Cash and Cash Equivalents:
(a) Cash Sale of Goods
(b) Cash Received against Revenue from Services rendered
(c) Cash Purchase of Goods
(d) Cash Paid against Services Taken
(e) Patents Purchased
(f) Marketable Securities
(g) Bank Overdraft
(h) Proceeds from Issue of Debentures
(i) Purchase of Shares
(j) Repayment of Long-term Loan
(k) Commission Received
(l) Redemption of Debentures
(m) Interest on Debentures
(n) Interest on Investments
(o) Income Tax Paid
(p) Income Tax Paid on Gain of Sale of Asset
(q) Cash Received from Debtors
(r) Cash Paid to Creditors.
Solution: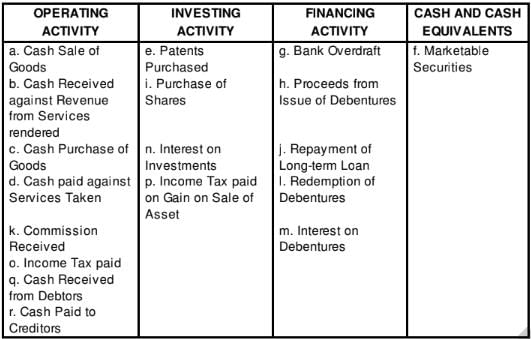
Page No. 5.90
Question:2
Classify the following transactions as Operating Activities for a financial company and a non-financial company:
(a) Purchase of Shares on a Stock Exchange.
(b) Dividend received on Shares.
(c) Dividend paid on Shares.
(d) Loans given.
(e) Loans taken.
(f) Interest paid on borrowings.
Solution:
A financial company deals with securities like shares, bonds, debentures, etc on a regular basis. These securities form part of their stock and hence purchase and sale of these securities will be categorised under Operating Activity. But, Dividend paid by them will be the part of Financing Activities.
However, for a non-financial company issue of shares, debentures, etc form part of financing activities as such issue will increase the capital employed in the business.
Page No. 5.90
Question:3
State which of the following would result in inflow/outflow or no flow of Cash and Cash Equivalents:
(a) Sale of Fixed Assets, Book Value 1,00,000 at a profit of 10,000.
(b) Sale of goods against cash.
(c) Purchase of machinery for cash.
(d) Purchase of Land and Building for 10,00,000. Consideration paid by issue of debentures.
(e) Issued fully paid Bonus Shares.
(f) Cash withdrawn from bank.
(g) Payment of Interim Dividend.
(h) Proposed Dividend.
Solution: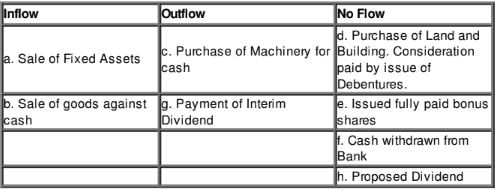
Question:3
State which of the following would result in inflow/outflow or no flow of Cash and Cash Equivalents:
(a) Sale of Fixed Assets, Book Value 1,00,000 at a profit of 10,000.
(b) Sale of goods against cash.
(c) Purchase of machinery for cash.
(d) Purchase of Land and Building for 10,00,000. Consideration paid by issue of debentures.
(e) Issued fully paid Bonus Shares.
(f) Cash withdrawn from bank.
(g) Payment of Interim Dividend.
(h) Proposed Dividend.
Solution: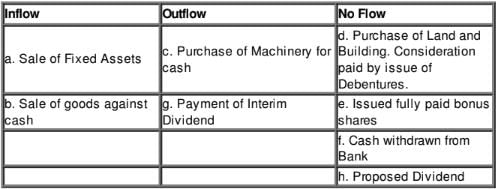
Question:4
For each of the following transactions, calculate the resulting Cash Flow and state the nature of Cash Flow, i.e., whether it is Operating, Investing or Financing:
(a) Acquired machinery for 2,50,000 paying 20% by cheque and executing a bond for the balance payable.
(b) Paid 2,50,000 to acquire shares in Informa Tech Ltd. and received a dividend of 50,000 after acquisition.
(c) Sold machinery of original cost of 2,00,000 with an accumulated depreciation of 1,60,000 for 60,000.
Solution:
(a) Investing Activity: 50,000
(b) Investing Activity: 2,00,000
(c) Investing Activity: 60,000
Question:5
Following are the extracts from the Balance Sheet of MAH Ltd. as at 31st March, 2019: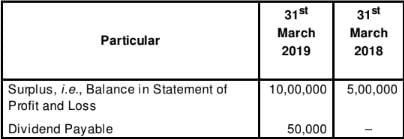
Additional Information: Proposed Dividend for the years ended 31st March, 2018 and 2019 are 4,00,000 and 5,00,000 respectively.
Prepare the Note to show Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Items.
Solution: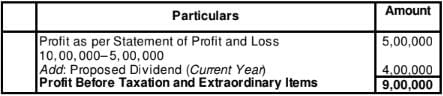
Page No. 5.91
Question:6
Following is the extract from the Balance Sheet of Zee Ltd.: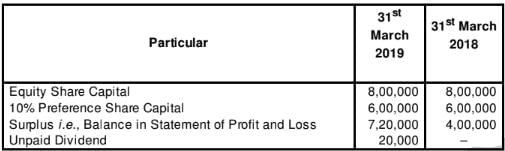
Additional Information:
(i) Proposed dividend on equity shares for the year 2017-18 and 2018-19 are
1,60,000 and 2,00,000 respectively.
(ii) An Interim Dividend of 40,000 on Equity Shares was paid. Calculate Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Items.
Solution:
Question:7
Calculate Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Items of Premier Sales Ltd. from its Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2019:
Notes to Accounts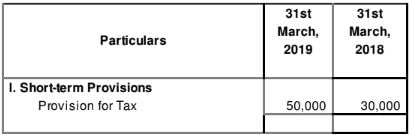
Additional Information:
(i) Proposed Dividend for the years ended 31st March, 2018 and 2019 are 50,000 and 75,000 respectively.
(ii) Interim Dividend paid during the year was 10,000.
Solution: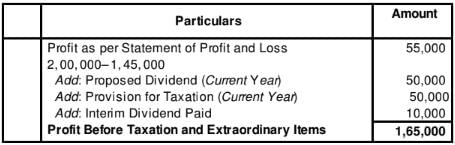
Question:8
From the following information, calculate Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Items:
Solution:
Cash Flow Statement
for the year ended...
Question:9
From the following information, calculate Operating Profit before Working Capital Changes:
Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Items 4,47,000
Depreciation on Machinery 84,000
Interest on Borrowings 16,800
Goodwill Amortised 18,600
Loss on Sale of Furniture 18,000
Premium on Redemption of Preference Shares 6,000
Gain Profit on Sale of Investments 12,000
Interest and Dividend Received on Investments 27,600
Solution:
Cash Flow Statement
for the year ended March 31, ....
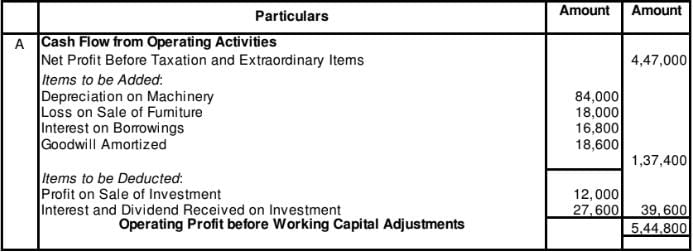
Note: Assuming Premium on Redemption of Preference Shares has been paid out of the Securities Premium Reserve Balance.
Question:10
From the following Balance Sheet of Double Tree Ltd. as at 31st March, 2019 and additional information, calculate Operating Profit before Working Capital Changes: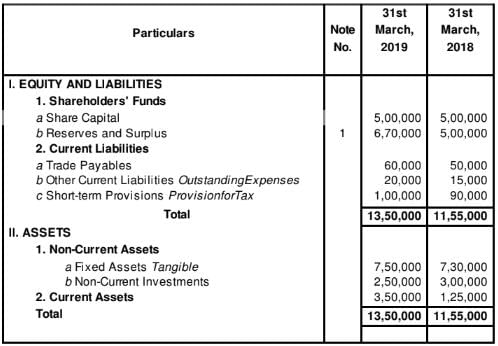
Notes to Accounts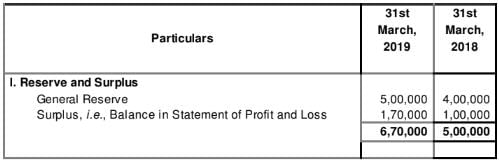
Additional Information: Depreciation for the year was 75,000.
Solution:
Computation of Operating Profit before Working Capital Changes
for the year ended March 31, 2019
Question:11
Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following details:
Solution:
Question:12
Compute Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following information:
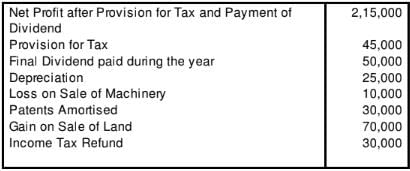
Solution:
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
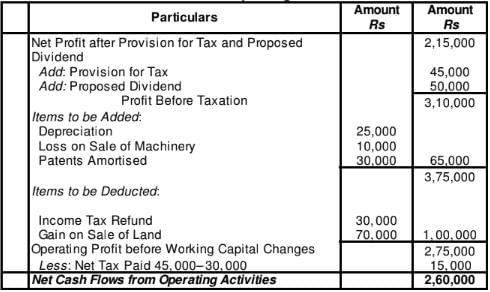
Question:13
Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following:
(i) Profit form the year is 7,00,000 after considering the following items: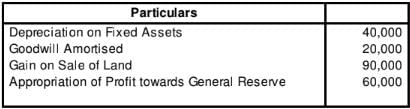
(ii) Following is the position of Current Assets and Current Liabiliites
Solution:
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Question:14
Grand Hospitality Ltd., reported Net Profit after Tax of 6,40,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2019. The relevant extract from Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2019 is: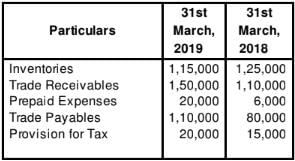
Depreciation charged on Plant and Machinery 55,000, insurance claim received 50,000, gain profit on sale of investment 20,000 appeared in the Statement of Profit and Loss for the year ended 31st March, 2019. Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities.
Solution: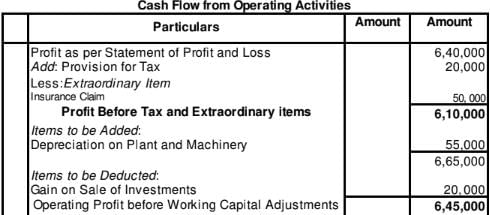
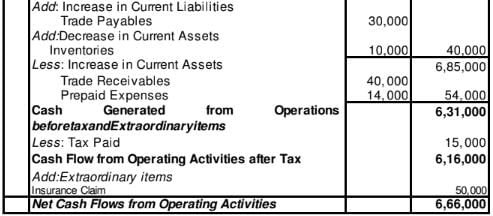
Question:15
Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following information.
Solution:
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Question:16
Following information is related to ABC Ltd.:
STATEMMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
for the year ended 31st March, 2019

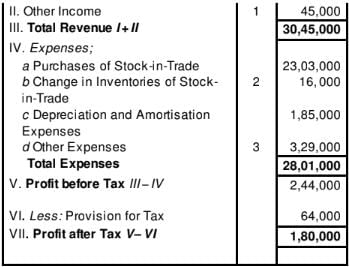
Notes to Accounts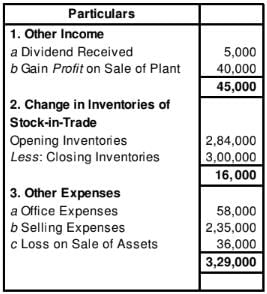
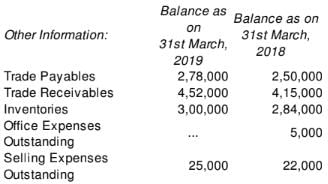
Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities.
Solution:
Question:17
Compute Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following: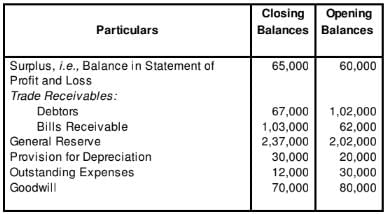
An asset costing 40,000 having book value of 28,000 was sold for 36,000.
Solution:
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
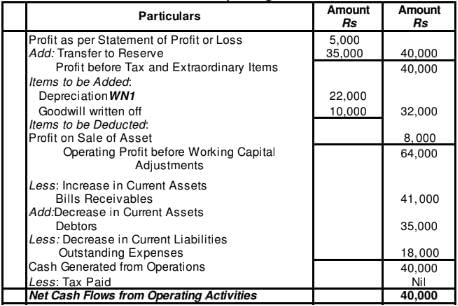
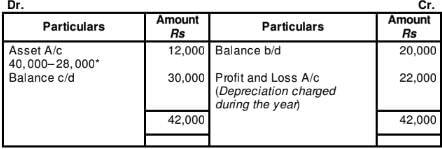
Working Note1:
Provision for Depreciation Account
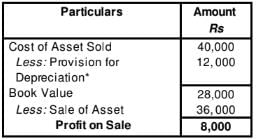
Question:18 Charles Ltd. earned a profit of 1,00,000 after charging depreciation of 20,000 on assets and a transfer to General Reserve of 30,000. Goodwill amortised was 7,000, and gain on sale of machinery was 3,000. Other information available is changes in the value of Current Assets and Current Liabilities: trade receivables showed an increase of 3,000; trade payables an increase of 6,000; Prepaid expenses an increase of 200; and outstanding expenses a decrease of 2,000. Ascertain Cash Flow from Operating Activities.
Solution:
Cash Flow Statement
Question:19
Compute Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following:
(i) Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2019 is 10,000 after providing for depreciation of 2,000.
(ii) Current Assets and Current Liabilities of the business for the year ended 31st March, 2018 and 2019 are as follows: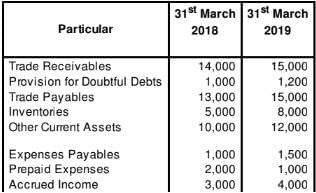

Solution:
Cash Flow Statement
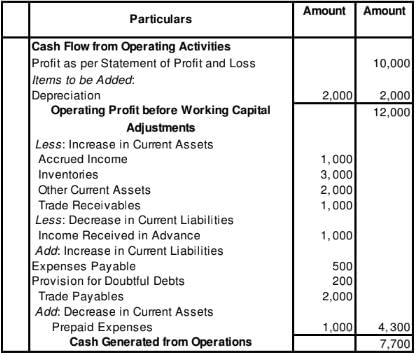
Question:20
Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities from the following information:
Notes to Accounts
Solution:
Cash Flow Statement
for the year ended March 31, 2019


Question:21
21 Mars Ltd. has Plant and Machinery whose written down value on 1st April, 2017 was 9,60,000 and on 31st March, 2018 was 10,50,000. Depreciation for the year was 35,000. In the beginning of the year, a part of plant was sold for 45,000 which had a written down value of 30,000. Calculate Cash Flow from Investing Activities.
Solution:
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
for the year ended March 31, 2017
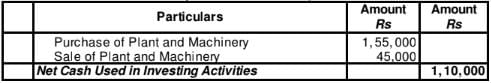
Working Notes:
Plant and Machinery Account
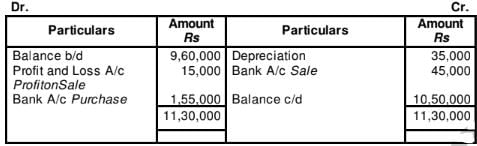
Question:22
From the following details. calculate Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Additional Information:
1. During the year, machine costing 90,000 with accumulated depreciation of 60,000 was sold for 50,000.
2. Patents written off were 50,000 while a part of patents were sold at a profit of 40,000.
Solution:
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Working Notes:
WN1: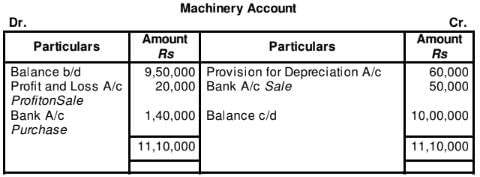
WN2:
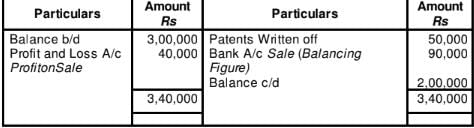
WN3:
Provision for Depreciation Account
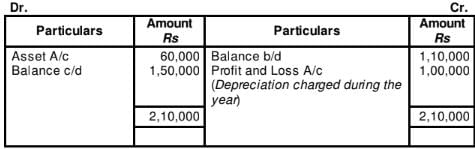
Question:23
Welprint Ltd. has given the following information:
Machinery as on 1st April, 2018 50,000
Machinery as on 31st March, 2019 60,000
Accumulated Depreciation on 1st April, 2018 25,000
Accumulated Depreciation on 31st march, 2019 15,000
During the year, a machine costing 25,000 accumulateddepreciationthereon
15, 000 was sold for 13,000.
Calculate Cash Flow from Investing Activities on the basis of the above information.
Solution: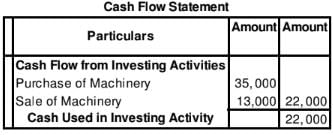
Working Notes:
Machinery Account
Accumulated Depreciation Account
Question:24
From the following details. Calculate Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Additional Information:
1. Half of the investment held in the beginning of the year were sold at 10% profit.
2. Depreciation on Land and Building was 50,000 for the year.
3. Interest received on investments 75,000.
Solution:
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
for the year ended March 31, 2019
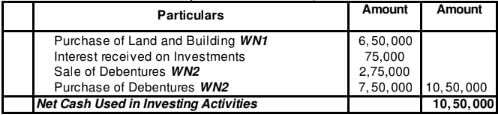
Working Notes:
WN1:
Land and Building Account
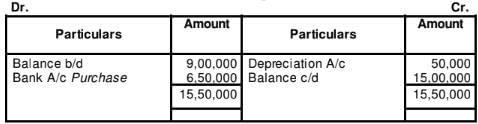
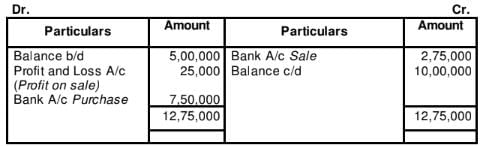
WN2:
Investment in Debentures Account
Question:25
From the following information, calculate Cash Flow from Investing Activities:
A building was purchased as investment out of surplus which was let out for commercial purposes. Rent Received 20,000.
Solution: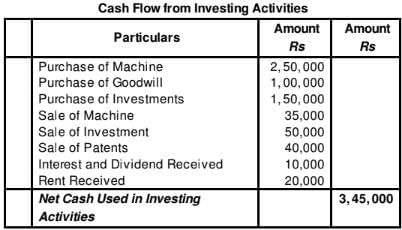
|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Cash Flow Statement (Part - 1) - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is a cash flow statement? |  |
| 2. Why is a cash flow statement important? |  |
| 3. How is a cash flow statement different from an income statement? |  |
| 4. What are the three main sections of a cash flow statement? |  |
| 5. How can a negative cash flow affect a company? |  |





















