Cell, Types of Cell and Organisms | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cytology |

|
| Cell |

|
| Why is the Cell a Basic Unit of Life? |

|
| Discovery of Cell |

|
| Cell Theory |

|
| Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes |

|
| Types of Organisms on Basis of Number of Cells |

|
Cytology
Cytology is the branch of biology that deals with the study of cells and their structures.
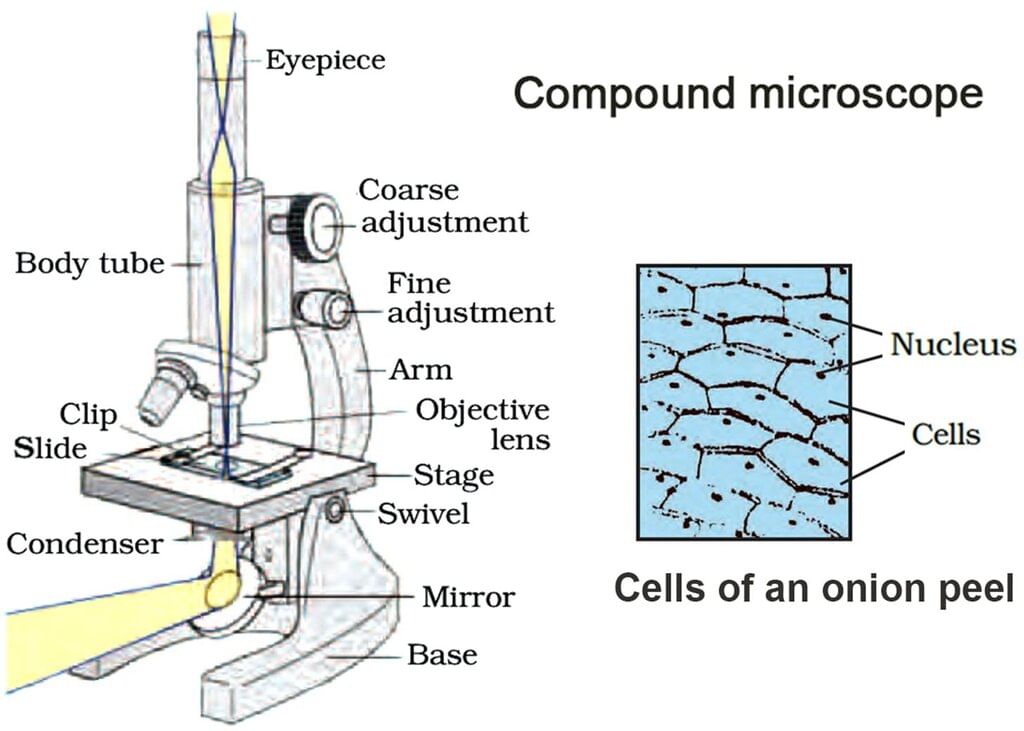
Cell
- The cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
- It is a mass of protoplasm enclosed within a plasma membrane.
- It performs all life processes like respiration, digestion, and excretion.
- Cells are capable of self-reproduction and carry genetic information.
Why is the Cell a Basic Unit of Life?
- All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- All life processes occur inside cells.
- Different cells perform different functions in multicellular organisms.
Discovery of Cell
1. Robert Hooke (1665): An English man and first curator of Royal Society of London.
- Observed a thin transverse section of the bark of a tree under a self-designed microscope.
- He noticed honey-comb-like compartments.
- He coined the term cell.
- He wrote a book - Micrographia.
- He observed dead cells.
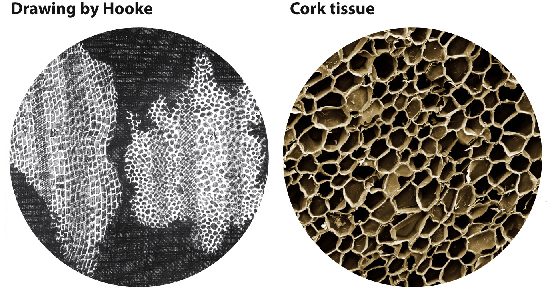 Image drawn by Hooke and the Cork Tissue
Image drawn by Hooke and the Cork Tissue
2. Antony Van Leeuwenhoek (1674): was the first to observe living cells like Bacteria (from tartar of teeth), Erythrocytes (fish), Sperms, and Protozoans (Vorticella).
3. N. Grew (1682): Proposed cell concept which states that a cell is the unit of structure of organisms.
4. Rudolf Virchow (1858): Proposed that new cells formed from the pre-existing cells.
5. Knoll & Ruska (1931): Designed the electron microscope which was employed to study the ultrastructure of a cell and various cell organelles.
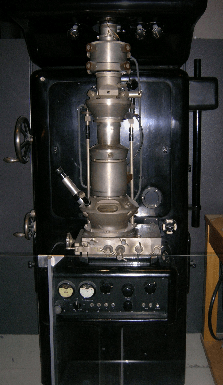 Microscope designed by Knoll and Ruska
Microscope designed by Knoll and Ruska
| Scientist | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Robert Hooke (1665) | Observed dead cork cells using a simple microscope; coined the term cell. |
| Leeuwenhoek (1674) | First to observe living cells (bacteria, protozoa, sperm, etc.). |
| Robert Brown (1831) | Discovered the nucleus in cells. |
| Purkinje (1839) | Coined the term protoplasm for cell contents. |
| Schleiden and Schwann | Proposed Cell Theory – all plants and animals are made of cells. |
| Rudolf Virchow (1855) | Added: "All cells arise from pre-existing cells." |
| Knoll & Ruska (1931) | Invented the electron microscope, revealing detailed cell structures. |
Cell Theory
Classical Cell Theory (1838-1839):
Proposed by Schleiden and Schwann.
All living organisms are made of cells.
Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
Modern Cell Theory:
All living beings are composed of cells.
Cells arise only from pre-existing cells.
Cells perform all essential life activities.
Cells contain hereditary material (DNA).
All cells are basically similar in structure and function.
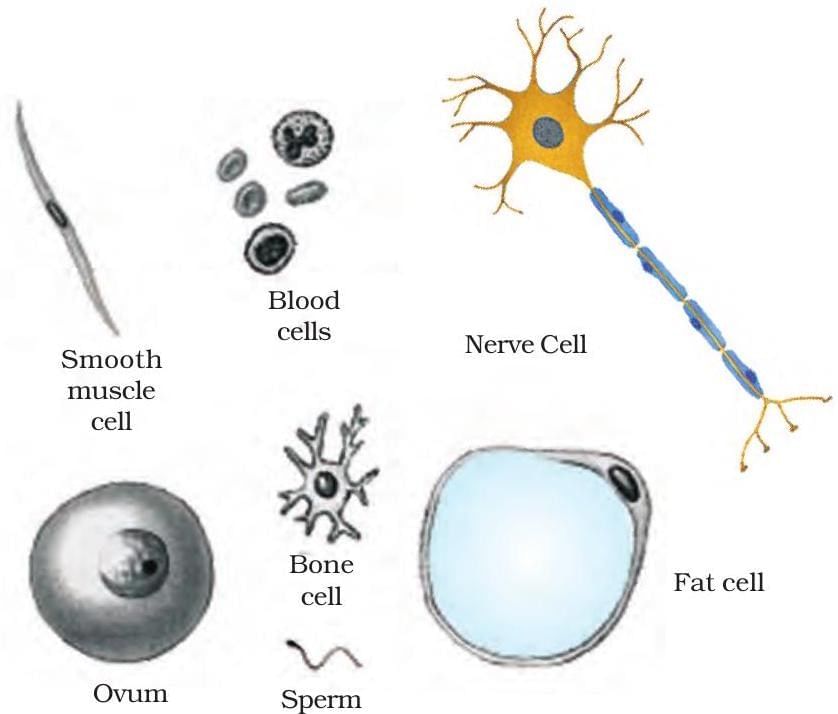
Size and Shape of Cell
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Size in Humans | Ranges from 20 to 30 µm. |
| Largest Cell | Ostrich egg (15 cm in diameter), Ovum/Egg cell (In Human Body) |
| Smallest Cell | Mycoplasma (0.1 µm to 0.5 µm), Sperm (In Human Body) |
| Longest Cell | Nerve cell (up to 1 meter). |
| Shape Depends On | Function (e.g., muscle cells are spindle-shaped, RBCs are disc-shaped). |
Units of Measurement Used in Cell Biology
- Millimetre (mm) = 10⁻³ m
- Micrometre (µm) = 10⁻⁶ m
- Nanometre (nm) = 10⁻⁹ m
- 1 µm = 10⁻³ mm
- 1 nm = 10⁻³ µm
- Angstrom (Å) = 10⁻¹ nm = 10⁻⁷ mm
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nuclear membrane, so the nuclear region is poorly defined and is called a nucleoid. They also lack most membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles. In photosynthetic prokaryotic bacteria, chlorophyll is present in membranous vesicles, not in plastids.
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane. Their cells also contain membrane-bound organelles, such as plastids in plant cells, where chlorophyll is stored for photosynthesis.
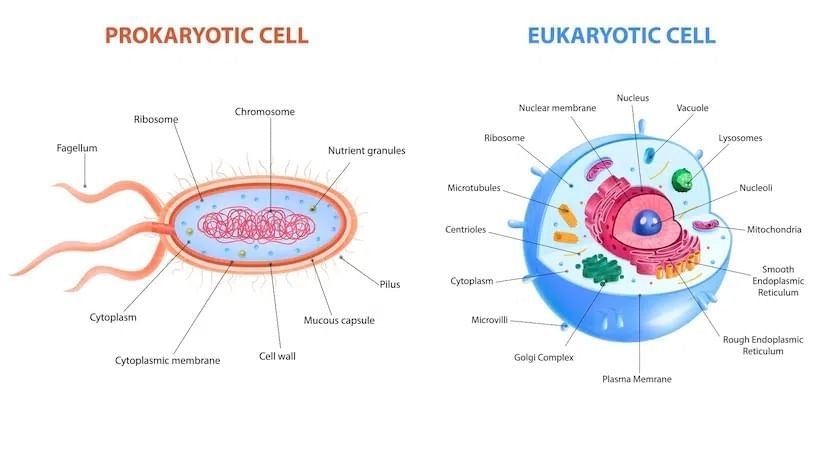
| Characteristics | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Type of Cell | Always unicellular | Unicellular and multi-cellular |
| Cell size | Ranges in size from 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm in diameter | Size ranges from 10 μm – 100 μm in diameter |
| Cell wall | Usually present; chemically complex | When present, chemically simple |
| Nucleus | Absent. Instead, they have a nucleoid region in the cell | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present. Smaller in size and spherical in shape | Present. Comparatively larger in size and linear in shape |
| DNA arrangement | Circular | Linear |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present, but cell organelles absent | Present, cell organelles present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Plasmids | Present | Very rarely found in eukaryotes |
| Ribosome | Small ribosomes | Large ribosomes |
| Lysosome | Lysosomes and centrosomes are absent | Lysosomes and centrosomes are present |
| Celldivision | Through binary fission | Through mitosis |
| Flagella | The flagella are smaller in size | The flagella are larger |
| Reproduction | Asexual | Both asexual and sexual |
| Example | Bacteria and Archaea | Plant and Animal cell |
Types of Organisms on Basis of Number of Cells
Based on the number of cells the organisms can be categorised as:
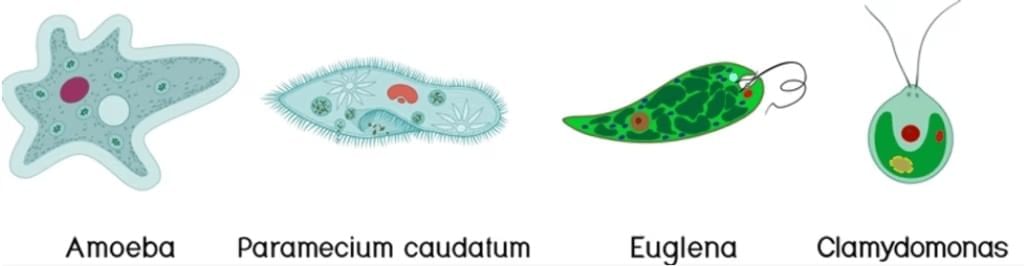
1. Unicellular organisms: Made of one cell (e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium, Chlamydomonas).
2. Multicellular organisms: Made of many cells (e.g., Plants, Animals).
Eutely: Fixed number of cells in an organism (e.g., rotifers, nematodes).
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Cell, Types of Cell and Organisms - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the basic unit of life known as? |  |
| 2. Who discovered the cell and when? |  |
| 3. What are the main criteria for defining a cell? |  |
| 4. What is the cell theory? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? |  |
















