Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 5
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Changes |

|
| Rusting of Iron |

|
| Difference between Physical and Chemical Changes |

|
Introduction
We will learn about physical and chemical changes. Understanding these changes helps us see how materials around us react and interact in our daily lives. We see different types of changes; everyday in our surroundings. Growth of tree, rising of sun, setting of sun, different shape and size of moon, burning of coal, paper, wood, etc. are the examples of changes around us.
Before knowing the scientific meaning of changes, it is necessary to understand some terms, i.e. physical properties, chemical properties, reversible and irreversible.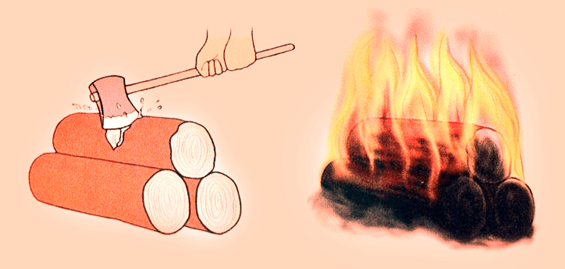 Physical and chemical changes respectively
Physical and chemical changes respectively
Important Terminologies:
Physical Properties: Shape, Size and State of substance are known as physical properties. For example; when a sheet of paper is folded, its shape changes and this is an example of change in physical property.
Chemical Properties: The internal properties of a substance are known as chemical properties. For example; curd is the product of milk but the internal properties of milk and curd are completely different.
Reversible: Things or processes which can be reversed are called reversible. For example; a folded sheet of paper can be unfolded and hence folding a sheet of paper is reversible.
Irreversible: Things or processes which cannot be reversed are called irreversible. For example; when milk turns into curd; it cannot be changed back to milk and hence is an irreversible change.
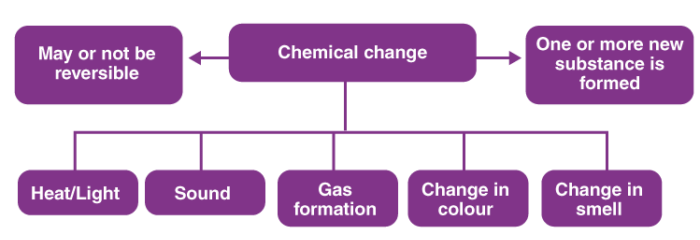
Types of Changes
(a) Physical Change:
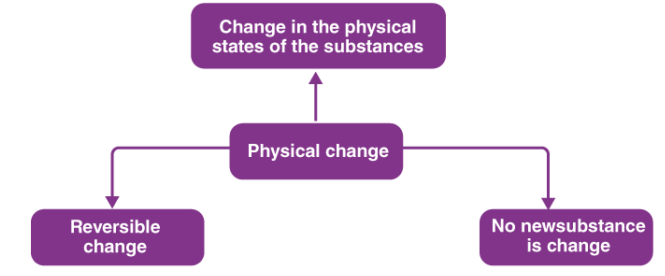 Physical Change
Physical Change
Change in which only physical properties of a substance change and no new substance is formed is called Physical Change.
Most of the physical changes are reversible, this means we can get the substance back even after the change.
Examples:
Folding of a paper sheet: A paper can be folded or unfolded and hence it is an example of physical change. Moreover, no new substance is formed in this process, so it is a physical change.
Tearing of paper sheet: Even after being torn in very small pieces; each piece is a piece of paper. Since no new substance is formed in this process, so it is a physical change.
Melting of wax: In melting, only the state of the wax changes; from solid to liquid. Solid wax can be obtained from molten wax. This i: In melting, only the state of the wax changes; from solid to liquid. Solid wax can be obtained from molten wax. This is an example of physical and reversible change.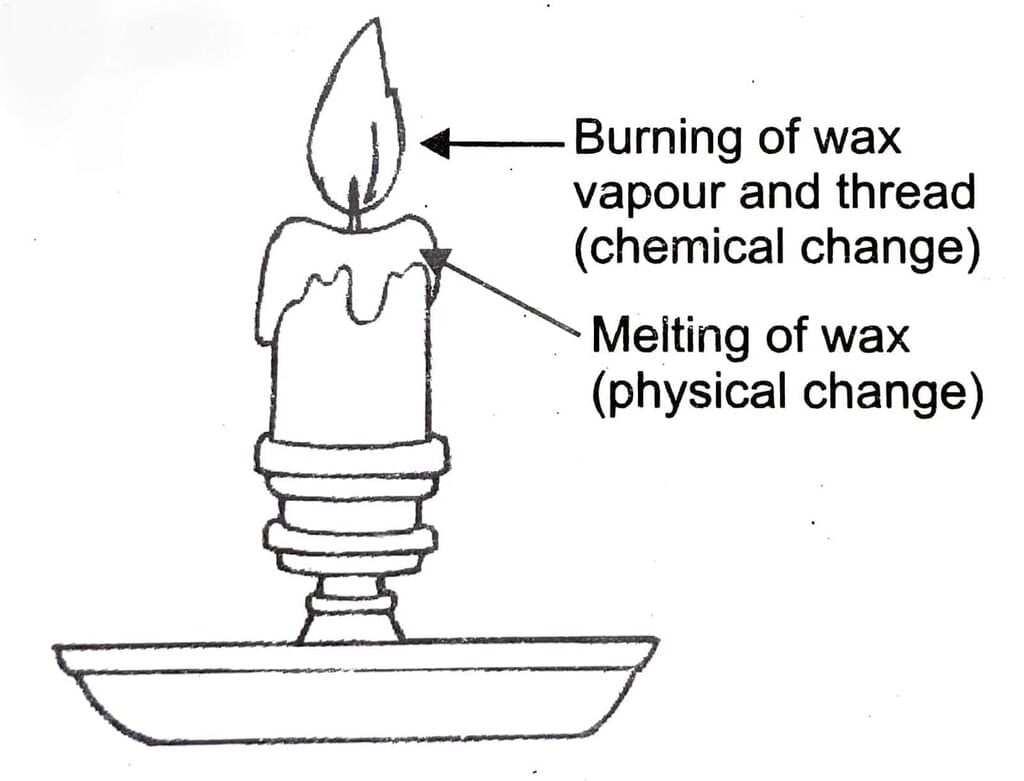 Melting of wax
Melting of wax
Melting of ice into water: In melting, only the state of water changes. Water can be changed to ice and vice-versa. This is an example of physical and reversible change.
Freezing of water: After freezing, water changes into ice. In this change; there is only the change in the state of water. Water can be obtained back from ice; by melting.
Change of water into vapour (Vaporisation): Vapour is another state of water. Water can be obtained after condensation of vapour. This is a physical and reversible change.
Change of vapour into water (Condensation): This is also a physical and reversible change as water can be changed into vapour again by the process of vaporization.
Stretching of a rubber band: In this change, only the size of the rubber band changes. The rubber band comes back in its original shape and size, once it is released. This is a physical and reversible change.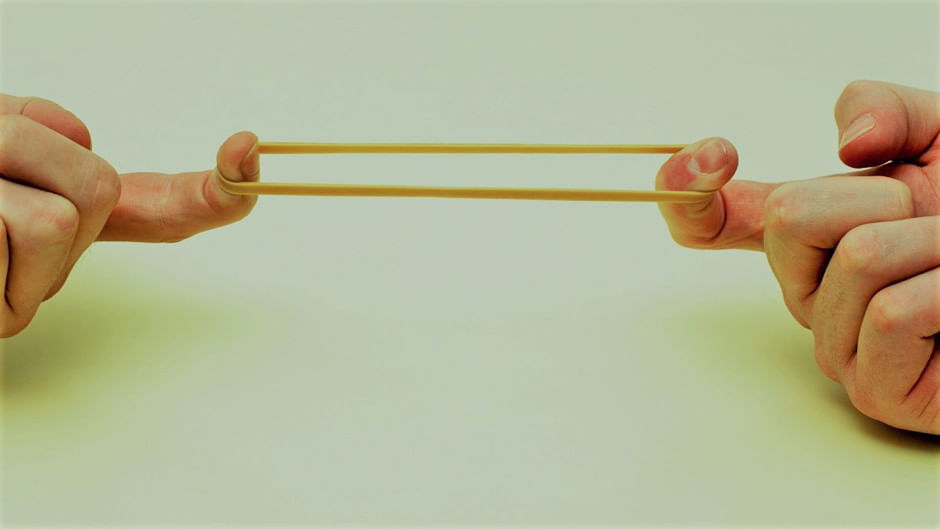 Stretching of a rubber band
Stretching of a rubber band
(b) Chemical Changes:
 Chemical Change
Chemical Change
Chemical change is a phenomenon that changes the internal structure of a substance to form a new substance.
Most of the chemical changes are irreversible.
Examples:
Burning of paper, wood, fuel or anything: When something is burnt, many new substances are formed; especially carbon dioxide is formed in most of the cases. Once something is burnt, the ash or carbon dioxide cannot be turned into the original substance. Hence, when something is burnt, many new substances are formed; especially carbon dioxide is formed in most of the cases.
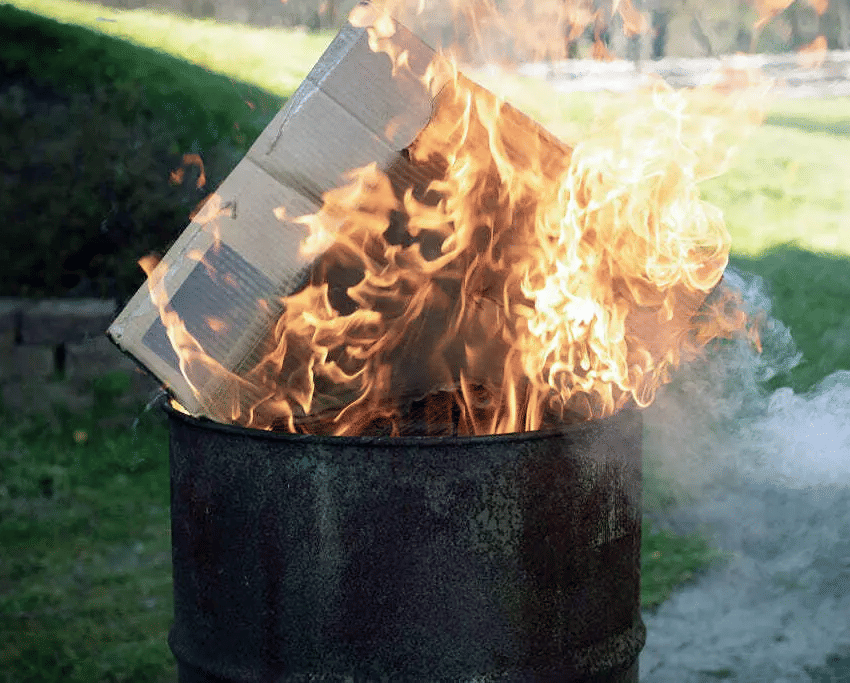 Burning of paper
Burning of paper
Melting of wax and burning of wax are different kinds of change. Burning of wax is chemical change while melting of wax is a physical change. Burning of wax is irreversible while melting of wax is reversible.
Reaction between vinegar and Baking Soda: Vinegar is an acid (Acetic acid). The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate.
When vinegar reacts with acetic acid, it gives carbon dioxide. A hissing sound is produced when baking soda is added to vinegar. This happens because of production of carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water (calcium hydroxide), it turns the lime water milky. This happens because of formation of calcium carbonate. Water is also formed; along with calcium carbonate. The reaction involved in this can be written as follows:
Burning of magnesium ribbon: Magnesium ribbon burns with dazzling light in air and forms magnesium oxide. The ash of magnesium oxide gives magnesium hydroxide when mixed with water. Solution of magnesium hydroxide turns blue litmus paper red; this shows its basic characteristic. Reaction involved in it can be written as follows:
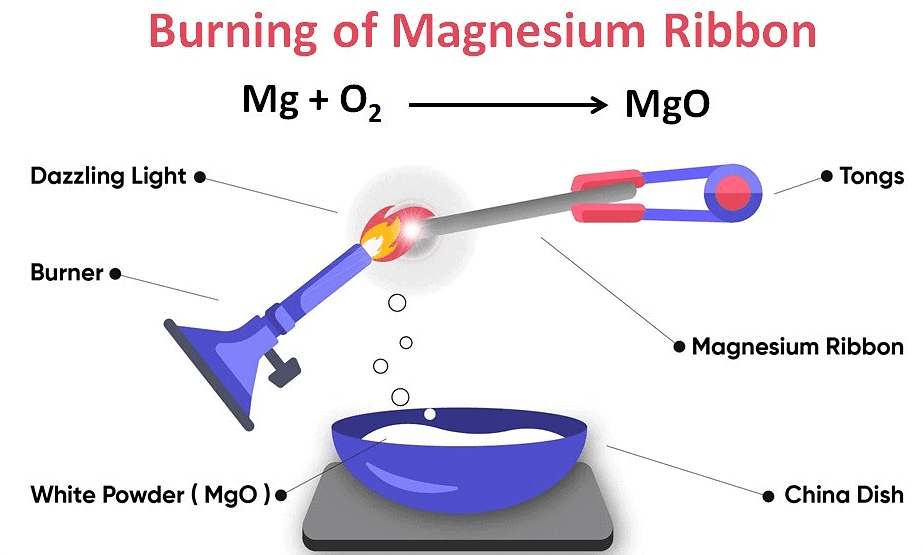 Burning of Magnesium Ribbon
Burning of Magnesium Ribbon
These are chemical changes as new substances are formed after change. Original substances cannot be retrieved by simple physical processes.
Reaction between solution of copper sulphate and iron: Copper sulphate solution is blue in colour. Copper sulphate is also known as blue vitriol. When an iron nail or shaving blade is left in copper sulphate solution; for some time; the colour of solution changes from blue to pale green. This happens because of the formation of iron sulphate.
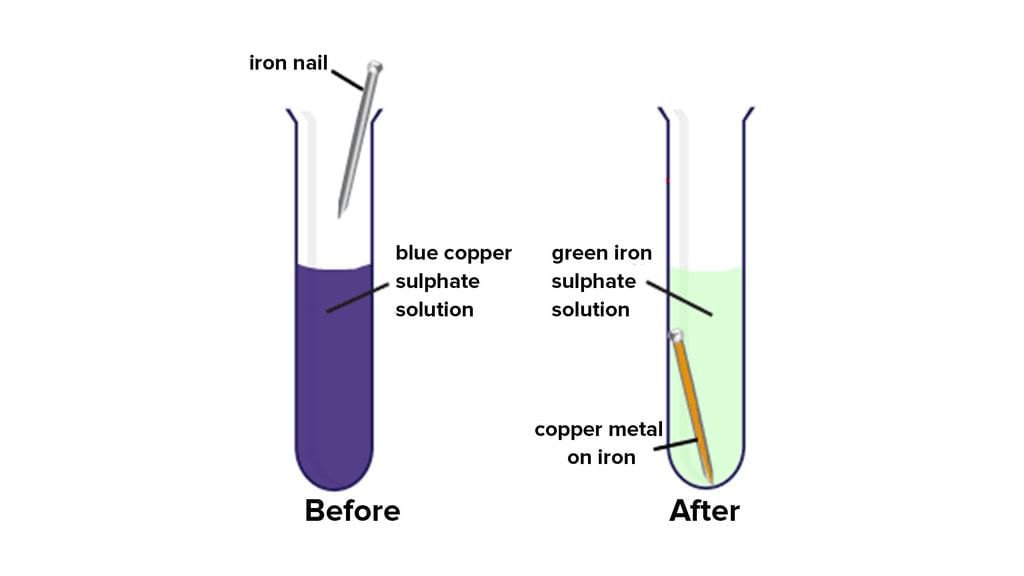 Change in colour of the copper sulphate solution due to reaction with iron
Change in colour of the copper sulphate solution due to reaction with iron
Additionally, a layer of brown copper gets deposited over the iron nail or blade. The reaction can be written as follows:
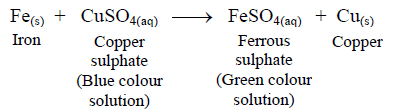
Rusting of Iron
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-548553969-56a134395f9b58b7d0bd00df.jpg) Rusting of Iron
Rusting of IronDeposition of a brown layer on iron is called rusting. In rusting, a new substance is formed. The chemical structures of iron and rust are completely different. Rust is iron oxide. Iron is a grey-black material while rust is reddish brown.
For rusting, the presence of both oxygen and water (or water vapour) is essential.
Thus, this is a chemical and irreversible change. Reaction in rusting can be written as follows:
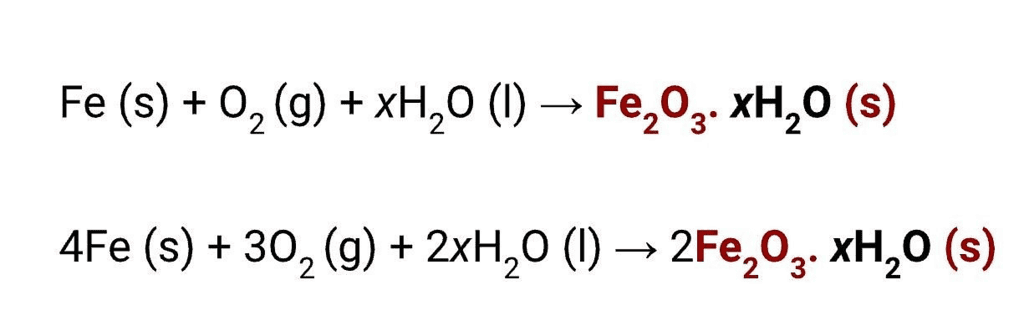 When articles made of iron come in contact with moisture present in air, they get rusted. Iron is converted into iron oxide, i.e. rust. The iron article becomes weak in due course as all the iron slowly turns into rust. This is corrosion of iron. Rusting gives a huge monetary loss to the people and nation.
When articles made of iron come in contact with moisture present in air, they get rusted. Iron is converted into iron oxide, i.e. rust. The iron article becomes weak in due course as all the iron slowly turns into rust. This is corrosion of iron. Rusting gives a huge monetary loss to the people and nation.
Prevention of rusting
For rusting, both water and oxygen should come in contact with iron. If anyone of these is prevented to come in contact with iron, rusting can be prevented.So, rusting is prevented using following methods:
1. Painting: articles such as; iron gates, grills, etc. are painted at regular intervals of time. Paint to prevent rusting2.Applying of layer of grease: Applying a layer of grease prevents the iron articles from coming in contact with moist air. This prevents rusting. That is why grease is applied over the chain of bicycle and also over many machine parts.
Paint to prevent rusting2.Applying of layer of grease: Applying a layer of grease prevents the iron articles from coming in contact with moist air. This prevents rusting. That is why grease is applied over the chain of bicycle and also over many machine parts.
 Applying grease on the surface of iron tool3.Galvanisation: In the process of galvanization; a layer of non-reactive metal, such as zinc is deposited over iron articles. The layer of non-reactive metal prevents the iron articles from coming in contact with moisture. Water pipes which are made of iron are galvanized to prevent rusting.
Applying grease on the surface of iron tool3.Galvanisation: In the process of galvanization; a layer of non-reactive metal, such as zinc is deposited over iron articles. The layer of non-reactive metal prevents the iron articles from coming in contact with moisture. Water pipes which are made of iron are galvanized to prevent rusting.
4.Crystallisation: Common salt is obtained by the vapourisation of sea water, but crystals of common salt are very small. When a small crystal of common salt is left dipped in the saturated solution of common salt for some time, big crystal of common salt is obtained. Formation of big and pure crystal of a substance from the saturated solution is called crystallisation.
Difference between Physical and Chemical Changes
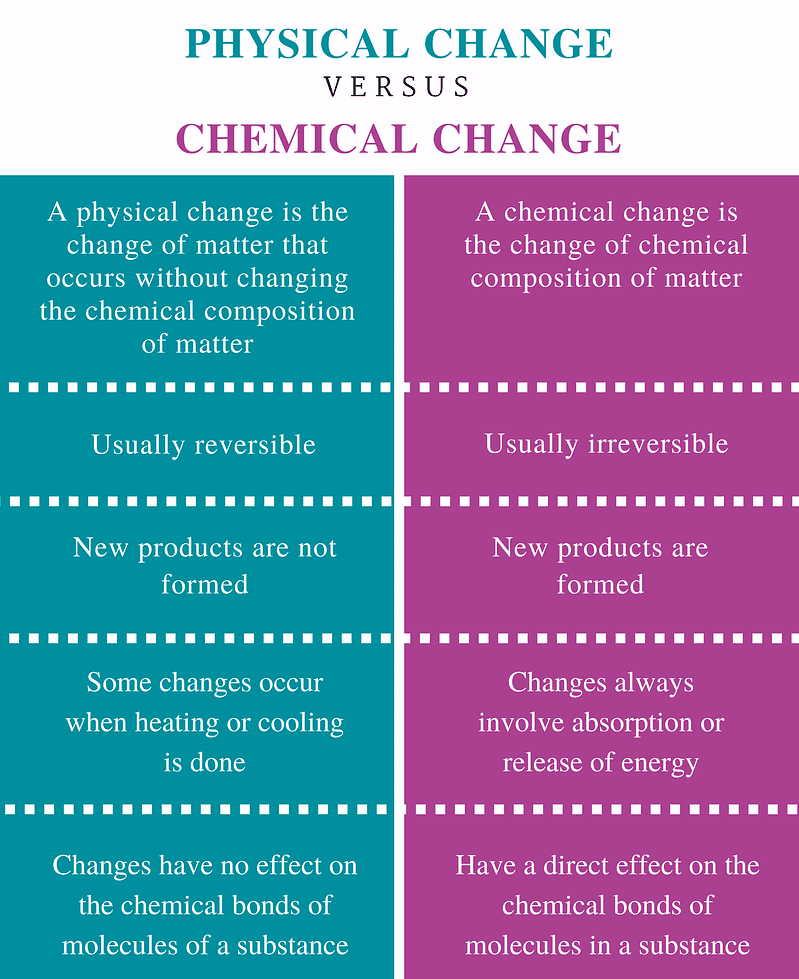 Physical Change vs Chemical Change
Physical Change vs Chemical Change
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 5
| 1. What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? |  |
| 2. What is an example of a physical change in the surroundings? |  |
| 3. How does rusting of iron occur and what type of change is it? |  |
| 4. Can rusting of iron be reversed back to iron? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand the types of changes in the surroundings? |  |
















