Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Biology Class 7 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Classification of Animals
Classification of Animals Chapter Notes | Biology Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Earth is home to countless animal species, thriving in diverse habitats and environments. These creatures vary widely in shape and size, from tiny ants to massive elephants, whales, and sharks. Despite their unique traits, animals share common characteristics. For instance, they are heterotrophic, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on plants or other animals for nutrition. Most animals exhibit locomotion, moving from place to place in search of food or shelter. Based on the presence or absence of a backbone, animals are broadly divided into two groups:
- Invertebrates
- Vertebrates
Invertebrates (Animals without Backbone)
Invertebrates lack a backbone and are divided into eight major phyla based on their characteristics.
Porifera (Pore-bearing Animals)
- Mostly found in marine environments, with a few in freshwater.
- Fixed to objects or the bottom of ponds or oceans.
- Body has many tiny pores to draw in water and one large pore to expel it.
- Examples: Sponge, Sycon.
Cnidaria or Coelenterata (Hollow Sac-like Animals)
- Aquatic animals with a sac-like body and a single opening (mouth).
- Mouth surrounded by tentacles used for catching food and swimming.
- Body is radially symmetrical, divisible into two identical halves along any plane.
- Examples: Jellyfish, Hydra, Sea-anemone.
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
- Body is thin and flattened.
- Mostly parasitic, living inside the bodies of other animals (hosts).
- Tapeworm lives in the human intestine, can grow up to six meters, and absorbs digested food.
- Examples: Tapeworm, Liver fluke.
Nematoda (Roundworms)
- Body is rounded and unsegmented.
- Most are tiny and parasitic, living in the bodies of animals, including humans.
- Roundworms like Ascaris live in the human small intestine, often in children due to poor hygiene.
- Examples: Ascaris (roundworm in humans).
Annelida (Segmented Worms)
- Body is made up of rings or segments.
- Soft, moist body wall used for breathing.
- Have special organs called nephridia for excretion.
- Examples: Earthworm, Leech.
Arthropoda (Animals with Jointed Legs)
- Body divided into head, thorax, and abdomen, often covered with a tough chitin layer.
- Have jointed legs for movement.
- Divided into four classes:
Crustacea:
- Head and thorax are fused, with many jointed legs.
- Mainly live in water.
- Examples: Crab, Shrimp, Lobster, Prawn.
Myriapoda:
- Body has many segments, each with one or two pairs of legs.
- Examples: Centipede, Millipede.
Insecta:
- Body divided into head, thorax, and abdomen.
- Have three pairs of jointed legs.
- Head has a pair of antennae and mouthparts.
- Examples: Ant, Housefly, Butterfly.
Arachnida:
- Head and thorax are fused.
- Have four pairs of jointed legs.
- Lack antennae.
- Examples: Spider, Ticks, Scorpion.
Mollusca (Soft-bodied Shelled Animals)
- Body is soft and unsegmented.
- Body enclosed in a hard shell.
- Move using a muscular foot.
- Examples: Snail, Slug, Pearl oyster, Octopus.
Echinodermata (Spiny-skinned Animals)
- Body is rough and spiny.
- Mainly marine animals.
- Move using tube feet.
- Body is radially symmetrical.
- Examples: Starfish, Sea urchin.
Vertebrates (Animals with Backbone)
- Vertebrates have a backbone (vertebral column) and are divided into five classes.
Class Pisces (Fishes)
- Aquatic animals with a streamlined body (narrow at both ends).
- Swim using fins.
- Body covered with scales.
- Breathe through gills.
- Examples: Rohu, Catla, Mahasheer, Electric ray fish, Dogfish.
Class Amphibia (Frogs and Toads)
- Can live in water and on land.
- Lay eggs in water.
- Body covered with slimy, slippery skin.
- Breathe through lungs and skin.
- Examples: Frog, Toad.
Class Reptilia (Lizards and Snakes)
- Mostly live on land, some in water.
- Skin is dry and scaly.
- Breathe through lungs.
- Females lay soft-shelled eggs on land.
- Have four short legs for crawling (except snakes).
- Examples: Lizards, Snakes, Turtles, Tortoises, Crocodiles.
Class Aves (Birds)
- Body covered with feathers.
- Have wings for flying.
- Bones are hollow and light for flight.
- Legs have scales, and toes have claws.
- Jaws have a horny beak without teeth.
- Females lay hard-shelled eggs.
- Examples: Peacock, Parrot, Pigeon, Bulbul, Sparrow.
- Some birds cannot fly, e.g., Ostrich (largest bird), Penguin, Kiwi.
Class Mammalia (Milk-nourishing Animals)
- Body covered with hair.
- Have projecting external ears.
- Give birth to live young ones (except monotremes).
- Young ones feed on milk from mammary glands in mothers.
- Usually have a tail (except humans) and four limbs.
- Examples: Cow, Dog, Deer, Camel, Lion, Tiger, Elephant, Rat, Humans.
Classification of Invertebrates and Vertebrates at a Glance
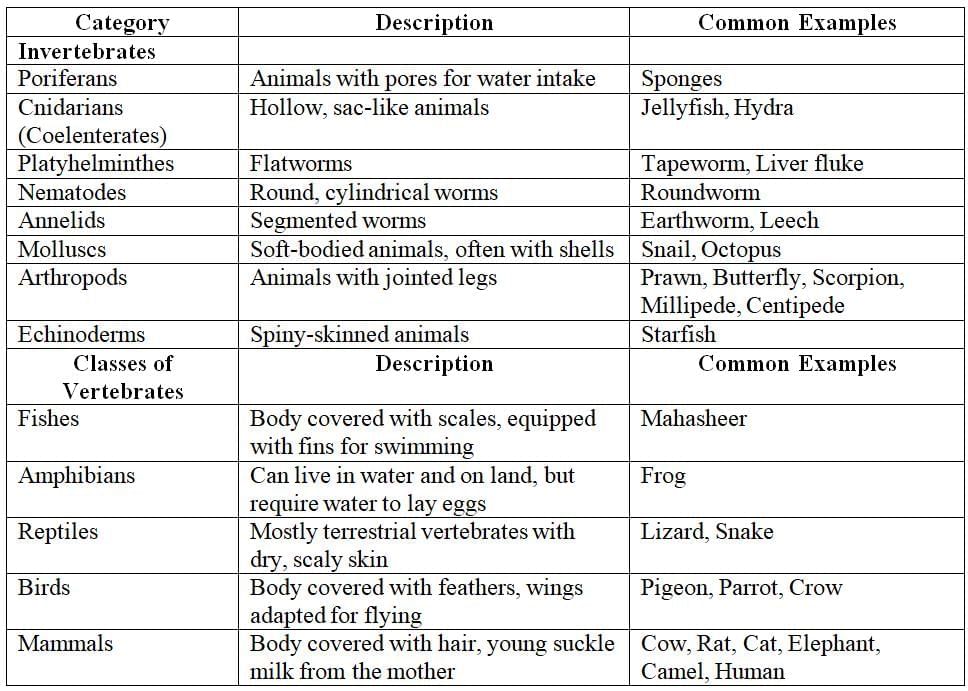
The document Classification of Animals Chapter Notes | Biology Class 7 ICSE is a part of the Class 7 Course Biology Class 7 ICSE.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
20 videos|44 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Classification of Animals Chapter Notes - Biology Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What are the main differences between invertebrates and vertebrates? |  |
Ans. Invertebrates are animals that lack a backbone, while vertebrates have a backbone or spinal column. Invertebrates make up about 95% of all animal species and include groups such as insects, arachnids, and mollusks. Vertebrates, which include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, generally have more complex structures and systems, including a well-developed nervous system and internal skeleton.
| 2. Can you provide examples of invertebrates and vertebrates? |  |
Ans. Yes, examples of invertebrates include jellyfish, octopuses, crabs, and earthworms. On the other hand, examples of vertebrates include humans, dogs, eagles, frogs, and sharks. This classification helps in understanding the vast diversity within the animal kingdom.
| 3. Why are invertebrates considered important for ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Invertebrates play crucial roles in ecosystems as they contribute to pollination, decomposition, and nutrient cycling. They serve as a food source for many vertebrates and are essential for maintaining the balance in various habitats. Additionally, invertebrates like bees and butterflies are important for pollinating plants, which is vital for food production.
| 4. How do invertebrates and vertebrates reproduce? |  |
Ans. Invertebrates can reproduce in various ways, including sexual and asexual reproduction. For example, many insects lay eggs, while some, like jellyfish, can reproduce by budding. Vertebrates typically reproduce sexually, with most species laying eggs or giving live birth. The reproductive methods can vary widely among vertebrate groups, often involving complex mating behaviors.
| 5. What role do scientists play in classifying animals into invertebrates and vertebrates? |  |
Ans. Scientists, particularly biologists, use various criteria such as physical characteristics, genetic information, and evolutionary relationships to classify animals into invertebrates and vertebrates. This classification helps in understanding biodiversity, studying animal behavior, and implementing conservation strategies, as it provides insights into how different species interact with their environments.
Related Searches
















