Communication Skills Chapter Notes | Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Communication? |

|
| The Communication Cycle |

|
| Types of Communication |

|
| Basic Writing Skills for AI |

|
What is Communication?
Communication involves sharing information, ideas, thoughts, or feelings between people, systems, or devices using various means like words, actions, visuals, or signals. In the context of Artificial Intelligence (AI), communication refers to the interaction between humans and AI systems, as well as the exchange of data, such as when a weather app displays forecasts.
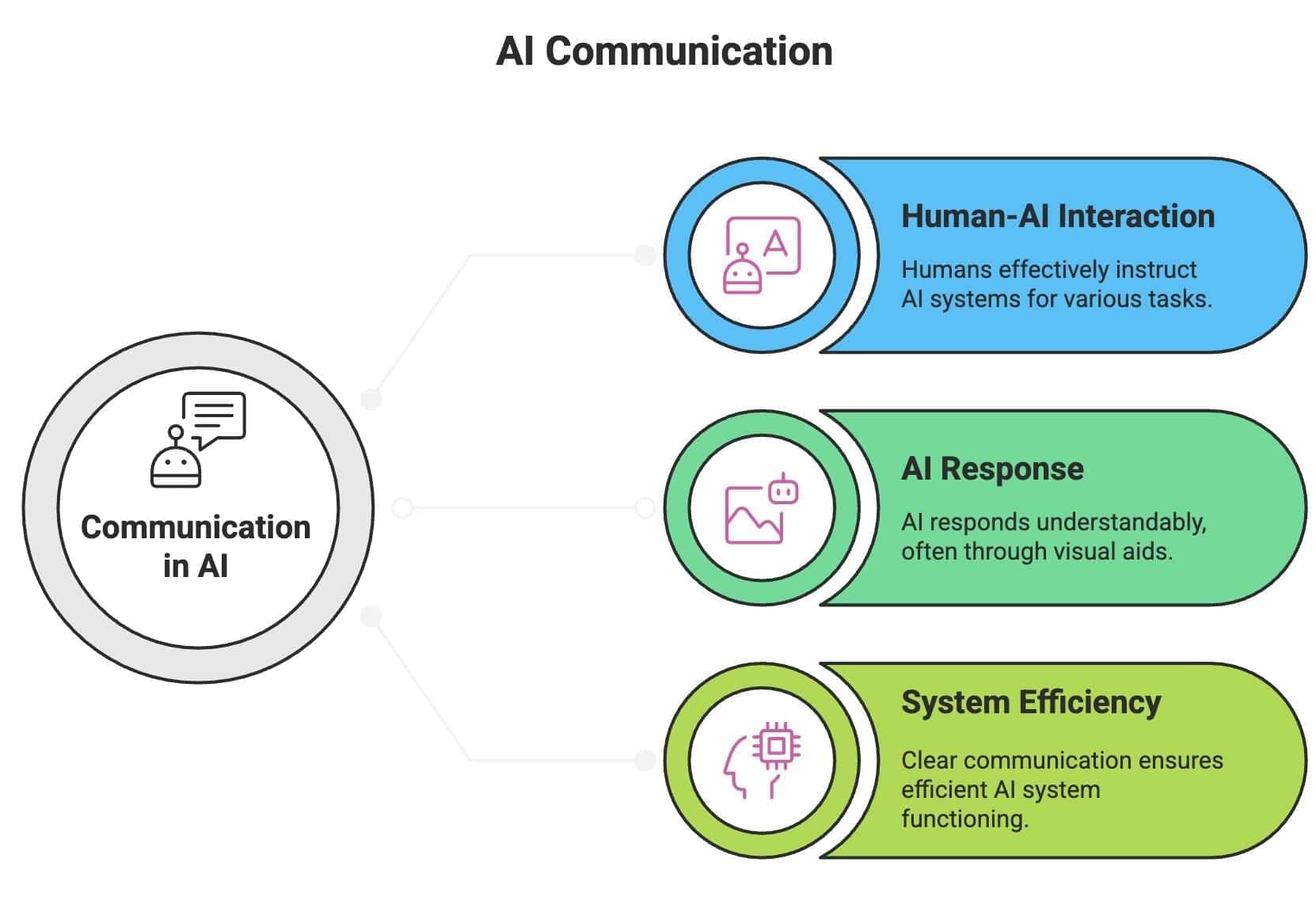
Why is Communication Important in AI?
Communication is crucial in AI for several reasons:
- It enables humans to effectively give instructions to AI systems, such as when using AI-based educational tools.
- It allows AI to respond in a manner that humans can easily understand, like presenting data through graphs.
- It ensures the efficient functioning of AI systems by facilitating the clear processing of inputs and outputs.
Communication skills are vital for effective interaction in both human and AI contexts.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand how messages are created, sent, received, and understood.
- Recognise how communication is used in AI tools like chatbots, voice assistants, and apps.
- Learn to express ideas clearly when interacting with AI or writing for communication.
- Develop basic skills to analyse communication in technology.
Example: When you say, “Hey Siri, play my favourite song,” you’re communicating with an AI. Siri listens, understands, and responds by playing the song—this is an example of a communication process in action.
The Communication Cycle
The communication cycle explains how information is exchanged between a sender and a receiver, including the crucial role of feedback. When applied to AI, it shows how humans and machines share information, much like asking a question and getting an answer from a virtual assistant.
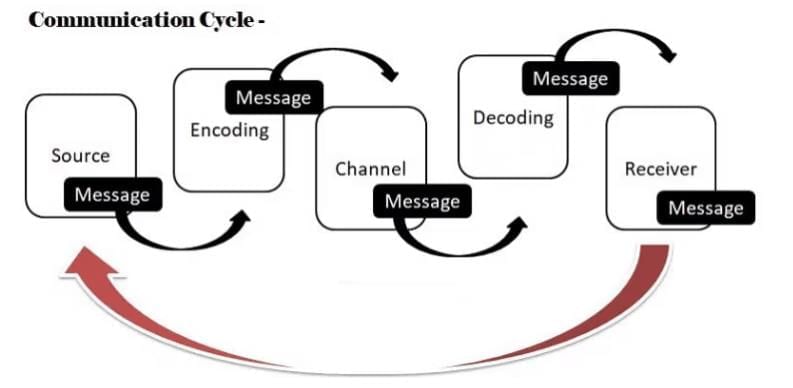
Steps in the Communication Cycle:
- Sender: This is the person or system starting the communication. For example, when you ask a chatbot, “What time is it?”
- Message: This is the information or idea being shared. In our example, the message is the question “What time is it?”
- Encoding: This step involves converting the message into a format that can be sent, like text or voice. For instance, you either type or say the question into your device.
- Channel: The channel is the medium used to send the message, such as speech, text, or images. For example, you can use an app on your phone or a microphone to ask the question.
- Receiver: The receiver is the person or system getting the message. In this case, the chatbot receives your question.
- Decoding: This is when the receiver interprets or understands the message. For example, the chatbot figures out that you’re asking for the time.
- Feedback: Feedback is the response from the receiver, completing the cycle. For instance, the chatbot replies, “It’s 6:45 PM.”
AI Example: When you ask Google Assistant for directions, you are the sender, your question is the message, and the assistant’s response is the feedback. If the AI misunderstands, you provide more feedback, restarting the cycle.
Activity 1: Map the Cycle
Scenario: Imagine you’re telling a smart speaker to set an alarm for 7 AM. Write down each step of the communication cycle (sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, feedback) for this interaction.
Example Answer:
- Sender: Me
- Message: “Set an alarm for 7 AM.”
- Encoding: Speaking the command.
- Channel: Voice through the smart speaker’s microphone.
- Receiver: The smart speaker (e.g., Amazon Echo).
- Decoding: The AI processes the command to understand it.
- Feedback: The speaker says, “Alarm set for 7 AM.”
Types of Communication
Communication can be categorised into four main types, all of which are utilised in AI systems to interact with users or process information.
1. Verbal Communication
- Definition: Verbal communication involves using spoken words or sign language to convey information. In the context of AI, this is how voice assistants like Siri or Alexa comprehend and respond to spoken commands.
- Examples
- Asking a virtual assistant, “What’s the weather today?”
- Using sign language to interact with an AI that recognises gestures.
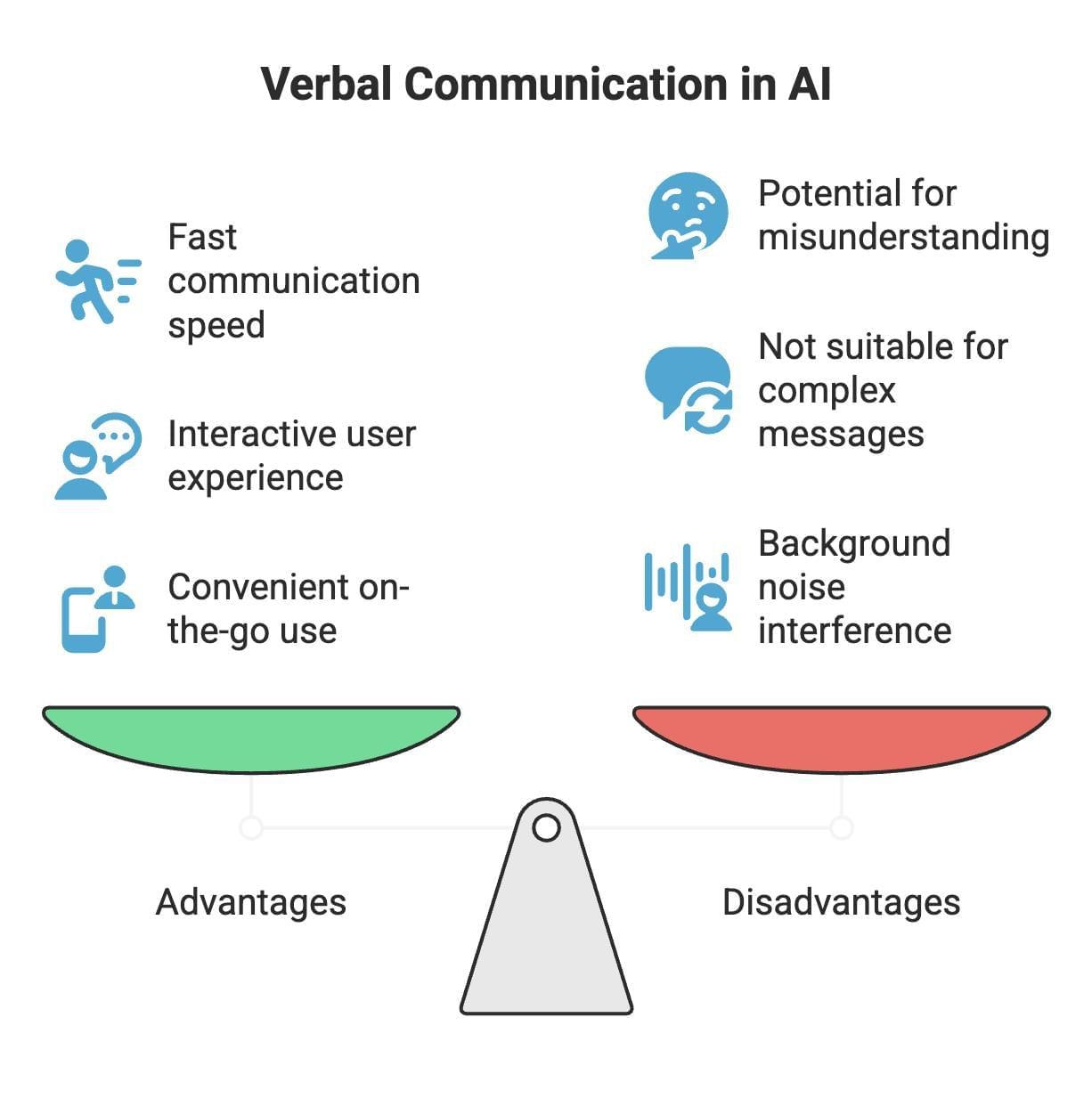
- Advantages
- Fast: Verbal communication allows for quick questions and responses.
- Interactive: Users can clarify or ask follow-up questions immediately.
- Convenient: There’s no need to write or type, making it easy to use on the go.
- Disadvantages
- Can be misunderstood: Background noise or unclear speech might confuse the AI.
- Not suitable for complex messages: Long explanations are hard to follow verbally.
- AI Connection: Voice assistants rely on verbal communication to process commands. For example, when you say, “Call Mom,” the AI decodes your voice and makes the call.
2. Non-Verbal Communication
- Definition: Non-verbal communication involves sharing information without words, using body language, facial expressions, or gestures. In AI, systems like facial recognition software utilise non-verbal cues to understand emotions or actions.
- Examples
- Smiling to show happiness, which an AI camera might detect.
- Waving to signal an AI-controlled robot to stop.
- Advantages
- Adds meaning: Non-verbal cues can convey emotions or intentions without words. For instance, a smile can show you’re happy without saying it.
- Works in noisy environments: Gestures can replace words in loud settings.
- Fast: Actions like nodding or waving communicate messages instantly.
- Disadvantages
- Hard to interpret: A gesture might mean different things in different cultures.
- Limited for long messages: You can’t explain complex ideas with gestures alone.
- AI Connection: Some AI systems, like those in self-driving cars, read non-verbal cues (e.g., a pedestrian’s hand signal to stop). Emotion-detection AI analyses facial expressions to understand feelings.
3. Written Communication
- Definition: Written communication involves using text, such as messages, emails, or reports, to share information. In AI, this type of communication occurs in chatbots or text-based applications.
- Examples
- Typing a question to a chatbot, like “Find me a recipe for pizza.”
- Reading a text response from an AI app.
- Advantages
- Keeps a record: Written messages can be saved and reviewed later.
- Clear for complex ideas: Writing is effective for explaining detailed instructions.
- Easy to share: Text can be sent to many people at once.
- Disadvantages
- Takes time: Writing and reading are slower than speaking.
- Can be unclear: Poorly written messages might confuse the AI or the user.
- AI Connection: Chatbots on websites utilise written communication to respond to inquiries. AI systems also generate written reports, such as summarising data for a school project.
4. Multimodal Communication
- Definition: Multimodal communication involves integrating various types of communication, such as verbal, non-verbal, and written, to enhance interaction. In AI, this approach allows for a richer and more engaging user experience.
- Examples
- Using voice commands while simultaneously interacting with a touchscreen.
- Engaging with a virtual assistant that responds to both spoken words and visual cues.
- Advantages
- Enhanced interaction: Combining different communication modes can lead to better understanding and engagement.
- Versatility: Users have the flexibility to choose their preferred method of communication.
- Disadvantages
- Complexity: Integrating various forms of communication can complicate design and interaction processes.
- Potential for confusion: Users may misinterpret mixed signals when different communication modes are used together.
- AI Connection: AI systems that leverage multimodal communication can provide a more intuitive and seamless user experience by utilising different input types, making interactions smoother and more efficient.
5. Visual Communication
- Definition: Visual communication involves conveying information through images, videos, charts, or symbols. In the context of AI, this type of communication is utilised in dashboards, maps, and infographics to present data visually.
- Examples
- A weather app showing a sun icon for a sunny day.
- An AI system creating a pie chart to show the results of a survey.
- Advantages
- Simplifies Complex Data: Visuals like pictures and charts make intricate information easier to comprehend.
- Captivates Attention: Visual elements engage users and enhance the learning experience.
- Language-Independent: Images can be understood regardless of language barriers.
- Disadvantages
- Requires Design Expertise: Crafting impactful visuals can be difficult and may require design skills.
- Accessibility Issues: Individuals with visual impairments might struggle to interpret visual content.
- AI Connection: AI technologies can create visual representations, such as graphs, to illustrate data patterns. For instance, a fitness application might use a chart to display your daily step count. Additionally, AI incorporates visual indicators in applications like Google Maps to enhance the user experience.
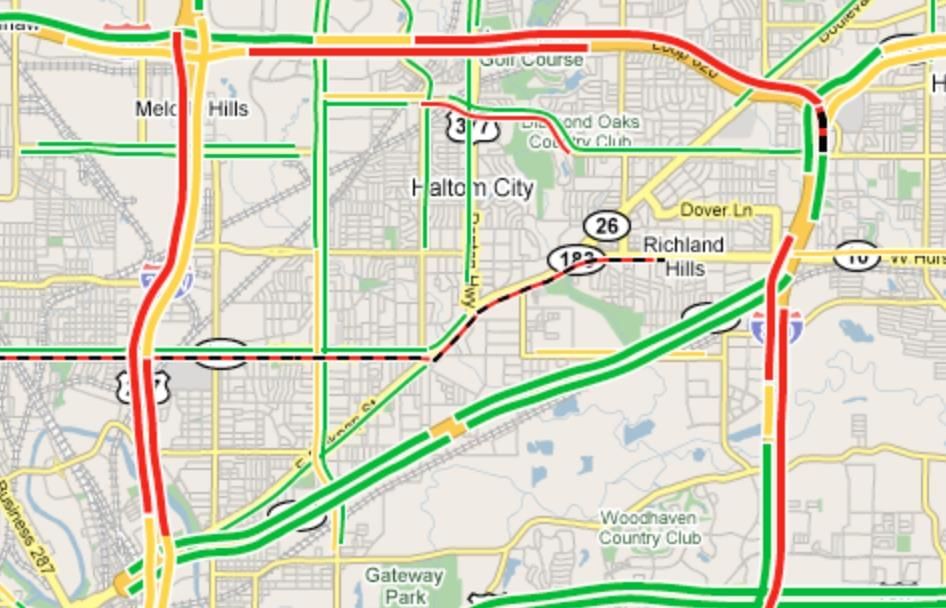 Colour coding for traffic used by Google Maps
Colour coding for traffic used by Google Maps
Activity 2: Identify Communication Types
Scenario: Imagine using a smart home app that controls lights, shows a temperature graph, and responds to voice commands. List one example of each communication type (verbal, non-verbal, written, visual) in this app.
Example Answer:
- Verbal: Saying, “Turn on the light.”
- Non-Verbal: The app’s camera detecting your wave to turn off a device.
- Written: Typing, “Set the thermostat to 22°C.”
- Visual: A graph showing temperature changes over the day.
Communication in AI: Real-World Applications
AI systems use all types of communication to interact with users and process information. Here’s how:
- Verbal: Voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant listen to your spoken commands and reply with speech. For example, saying, “Play a song” prompts the AI to respond verbally.
- Non-Verbal: AI in security cameras or self-driving cars reads gestures or facial expressions. For instance, an AI might detect a frown to suggest you’re upset or recognise a pedestrian’s hand signal to stop.
- Written: Chatbots on websites or apps like WhatsApp use text to answer questions. For example, typing “What’s my order status?” to an online store’s chatbot gets a written reply.
- Multimodal: AI combines multiple types of communication—like voice, text, and visuals—for richer interaction. For example, a virtual assistant might understand your voice command while also displaying relevant information on a screen.
- Visual: AI creates visuals like maps, charts, or icons to present data. For example, a fitness tracker app uses a bar graph to show your daily steps.
Basic Writing Skills for AI
Writing clearly is crucial when giving instructions to AI or creating content for others. Students can practice writing to communicate effectively with AI systems or in AI-related projects.
Tips for Clear Writing:
- Use simple words: Instead of “commence,” say “start.”
- Write short sentences: “Turn on the light” is clearer than “Please initiate the illumination process.”
- Be specific: Say “Find me a recipe for chocolate cake” instead of “Find a recipe.”
- Check spelling and grammar: Mistakes can confuse AI or people.
Types of Sentences: Sentences are groups of words that express a complete idea. Understanding different types of sentences can help you give clearer instructions to AI and improve your writing.
- Declarative Sentence
- Shares information or facts.
- Ends with a period (.).
- Example: “AI helps with homework.”
- AI Use: Asking an AI to display a fact, like “Show today’s news.”
- Interrogative Sentence
- Asks a question.
- Ends with a question mark (?).
- Example: “What is the capital of India?”
- AI Use: Asking an AI for information, like “What’s the weather?”
- Exclamatory Sentence
- Shows strong emotion or excitement.
- Ends with an exclamation mark (!).
- Example: “Wow, this AI is so cool!”
- AI Use: Expressing feedback, though less common in AI interactions.
- Imperative Sentence
- Gives a command or request.
- Ends with a period (.) or exclamation mark (!).
- Example: “Play my favourite song.”
- AI Use: Giving direct instructions to AI, like “Set a timer for 10 minutes.”
Activity 3: Write for AI
Write one example of each sentence type (declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, imperative) that you could use to interact with an AI assistant.
Example:
- Declarative: “AI can solve math problems.”
- Interrogative: “What is 5 + 7?”
- Exclamatory: “That’s an amazing answer!”
- Imperative: “Solve this equation for me.”
|
32 videos|57 docs
|
FAQs on Communication Skills Chapter Notes - Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Class 9
| 1. What are the benefits of verbal communication? |  |
| 2. What are the disadvantages of verbal communication? |  |
| 3. How can irrelevant information impact verbal communication? |  |
| 4. What is nonverbal communication? |  |
| 5. How can body language impact communication skills? |  |





















