Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Notes Maths Chapter 7
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Cartesian System |

|
| Coordinates of a Point in Cartesian Plane |

|
| Summary |

|
Introduction
Suppose I put a small dot on a sheet of paper with a pen. Can you locate this dot on the paper if I tell you that the dot is at the lower right corner of the paper?
 Now, you are able to see the dot but, can you tell me the exact position of the dot?
Now, you are able to see the dot but, can you tell me the exact position of the dot?
You will see that the information given above is not sufficient to fix the position of the dot.
Now, if I tell you that the point is nearly 2 cm away from the bottom line of the paper then this will give some idea but still is not sufficient because this would mean that the point could be anywhere, which is 2 cm away from the bottom line.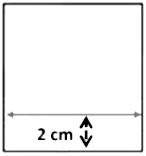 Therefore, to fix the position of the dot we have to specify its distance from two fixed lines, the right edge and the bottom line of the paper. Therefore, if I say that the dot is also 1 cm away from the right edge of the paper, then we can easily fix the position of the dot.
Therefore, to fix the position of the dot we have to specify its distance from two fixed lines, the right edge and the bottom line of the paper. Therefore, if I say that the dot is also 1 cm away from the right edge of the paper, then we can easily fix the position of the dot.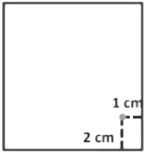 We see that position of any object lying in a plane can be represented with the help of two perpendicular lines.
We see that position of any object lying in a plane can be represented with the help of two perpendicular lines.
Coordinate geometry is the branch of mathematics where we study the position of an object on a plane with reference to two mutually perpendicular lines in the same plane.

Cartesian System
Number Line
- The number line is used to represent the numbers by marking points on a line at equal distances.
- On a number line distances from the fixed point are marked in equal units positively in one direction and negatively in the other.
- This fixed point from which the distances are marked is called the origin. In the figure 0 denotes the origin.
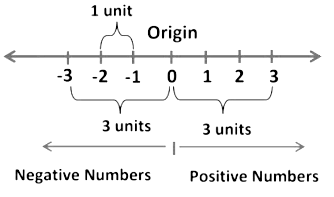
3 on number line is located at a distance of 3 units on the right side of origin 0. Similarly, -3 is located at the same distance from origin but on its left side.
In Cartesian system, two perpendicular lines are used, one of them is horizontal (XX’) and the other is vertical (YY’).
- The horizontal line X'X is called the x — axis and the vertical line Y'Y is called the y — axis.
- The point where X'X and Y'Y intersect is called the origin (denoted by O).
- Directions OX and OY are the positive directions of X - axis and Y - axis, respectively.
- Similarly, directions OX' and OY' are the negative directions of X -axis and Y - axis, respectively.

Quadrant
The axes (plural of the word ‘axis’) divide the plane into four parts. These four parts are called the quadrants (1/4), numbered I, II, III and IV anticlockwise from OX.
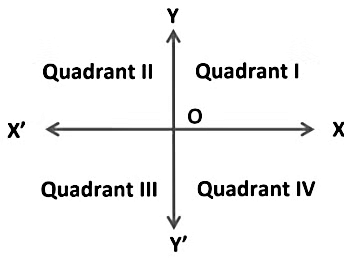
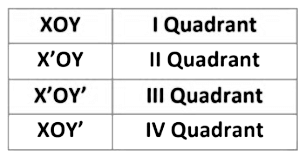
The plane consists of the axes and the four quadrants. We call the plane, the Cartesian plane, or the coordinate plane, or the xy-plane. The axes are called the coordinate axes.
A plane is a flat surface that goes infinitely in both directions.
Coordinates of a Point in Cartesian Plane
- The coordinates of a point are written as (x, y)
- The perpendicular distance of a point from the y axis measured along the x-axis is called its x coordinate, or abscissa. For point A (3,-10) and point B (-1,5) value of abscissa is +3 and for B, it is -1.
- The perpendicular distance of a point from the x axis measured along the y axis is called its y coordinate, or ordinate. For point A (3,-10) and point B (-1,5) value of ordinate is -10 and for B, it is 5 .
- In stating the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the x -coordinate comes first, and then the y - coordinate. We place the coordinates in brackets. Therefore, coordinates of A are (3,2) and B are (-1, -2).
Example 1: Point P is on the x-axis and is at a distance of 3 units from the y-axis to its left. Write the coordinates of point P.
Sol: Point P is at a distance of 3 units towards left, from y-axis.
Coordinates of point P are (-3, 0).
Example 2: Find distances of points C (-3, -2) and D (2, 1) from x-axis and y-axis.
C (-3, -2)
Sol: Distance from x − axis = 2 units
Distance from y − axis = 3 unitsD (2, 1)
Distance from x − axis = 1 units
Distance from y-axis = 2 unit
Example 3: Locate and write the coordinates of a point:
(a) lying on the x-axis to the left of origin at a distance of 4 units. b) above x-axis lying on the y-axis at a distance of 4 units from the origin.
b) above x- axis lying on y- axis at a distance of 4 units from origin.
Sol: (a) The given point is at a distance of 4 units towards left from the y-axis and at a zero distance from the x-axis. Therefore, the x − coordinate of the point is -4 and the y − coordinate is 0.
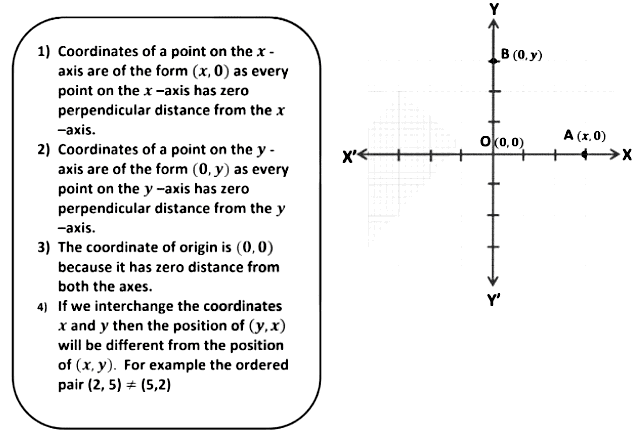
Hence, the coordinates of the given point are (-4, 0). Coordinates of a point on the x-axis are of the form (x, 0) as every point on the x-axis has zero perpendicular distance from the x-axis.
(b) The given point is at a zero distance from the y-axis at a distance of 4 units from the x-axis. Therefore, the x − coordinate of the point is 0 and the y − coordinate is 4. Hence, the coordinates of the given point are (0, -4). Coordinates of a point on the y-axis are of the form (0, y) as every point on the y-axis has zero perpendicular distance from the y-axis.
Signs of Coordinates in different Quadrants
Example 4: Write the quadrant in which each of the following points lie:
(i) (-2, -4)
(ii) (1, -4)
(iii) (-3, 2)
Sol: (i) (-2, -4)
Here, x coordinate = -2 and y coordinate = -4
As x coordinate and y coordinate both are negative (x < 0, y < 0) ,the given point lies in III quadrant.(ii) (1, -4)
Here, x coordinate = 1 and y coordinate = -4
As x coordinate is positive and y coordinate is negative (x > 0, y < 0 ) the given point lies in IV quadrant.(iii) (-3, 2)
Here, x coordinate = -3 and y coordinate = 2
As x coordinate is negative and y coordinate is positive (x < 0, y < 0 ) the given point lies in II quadrant.
Example 5: If the coordinates of a point M are (-2, 9) which can also be expressed as (1 + x, y2) and y > 0, then find in which quadrant do the following points lie: P(y, x), Q(2, x), R(x2, y − 1), S(2x,−3y)
Sol: We know,
(-2, 9) = (1 + x , y2)
∴ -2 = 1 + x ⇒ x = -2 – 1
x = -3
9 = y2 ⇒ y = ± 3
Now, it is given that y > 0, so we choose the positive value of y.
So, y = 3
Therefore, x = -3 and y = 3
(i) P (y, x)
P (y, x) = P (3, -3) (∵ y = 3 and x = -3)
As x coordinate is positive and y coordinate is negative (x > 0, y < 0 ) the given point lies in IV quadrant.
(ii) Q (2, x)
Q (2, x) = Q (2, -3) (∵ x = -3)
The x coordinate is positive and y coordinate is negative (x > 0, y < 0 ) so the given point lies in IV quadrant.
(iii) R (x2, y −1)
x2 = (−3)2 = 9; y −1 = 3 – 1 = 2
R (x2, y −1) = (9, 2)
As x coordinate and y coordinate both are positive (x > 0, y > 0) ,the given point lies in I quadrant.
(iv) S (2x, −3y)
2x =2 × (-3) = -6; -3y = -3 × 3 = -9
S (2x, −3y)= S (-6, -9)
As x coordinate and y coordinate both are negative (x < 0, y < 0),the given point lies in III quadrant.
Summary
Coordinate System Basics: To determine the position of a point in a plane, two perpendicular lines are necessary: one horizontal and one vertical.
Cartesian Plane: The plane defined by these two lines is known as the Cartesian or coordinate plane. The lines themselves are referred to as the coordinate axes.
Axes Names: The horizontal line is called the x-axis, and the vertical line is called the y-axis.
Quadrants: The coordinate axes divide the plane into four sections, each called a quadrant.
Origin: The point where the x-axis and y-axis intersect is known as the origin.
Coordinates Definition: The distance of a point from the y-axis is called its x-coordinate, or abscissa. The distance from the x-axis is called its y-coordinate, or ordinate.
Coordinate Notation: The coordinates of a point are denoted as where is the abscissa and is the ordinate.
Axis Points: Points on the x-axis have coordinates of the form and points on the y-axis have coordinates .
Origin Coordinates: The coordinates of the origin are .
Quadrant Coordinates: Points in the first quadrant have coordinates , in the second quadrant , in the third quadrant , and in the fourth quadrant , where and denote positive and negative real numbers, respectively.
Coordinate Uniqueness: If , then the coordinates are not equal to . However, if , then .
|
40 videos|471 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Notes Maths Chapter 7
| 1. What is the Cartesian system and how is it used in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the coordinates of a point in the Cartesian plane? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the origin in the Cartesian plane? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the different quadrants in the Cartesian plane? |  |
| 5. How do you plot a point given its coordinates in the Cartesian plane? |  |
















