Diversity in the Living World Chapter Notes | Science Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Diversity in Plants and Animals Around Us |

|
| How to Group Plants and Animals? |

|
| Plants and Animals in Different Surroundings |

|
Introduction
Imagine walking through a park on a bright, sunny morning. You hear birds chirping, see butterflies fluttering over colourful flowers, and notice trees of all shapes and sizes standing tall around you.
- Have you ever wondered why each tree looks different?
- Why do birds have unique chirps?
- Or how some animals live on land while others thrive in water?

The world around us is full of fascinating plants and animals, each playing its part in making nature vibrant and alive.
In this chapter, we’ll explore the variety of life around us—known as biodiversity. Through stories, activities, and examples, you’ll learn how plants and animals adapt to their surroundings, how they depend on one another, and why it’s important to protect the beautiful diversity of our planet.
Diversity in Plants and Animals Around Us
Diversity means the variety and differences found among living things in a particular area. When we talk about the diversity in plants and animals around us, we are looking at how many different types of plants and animals live in a specific place and how they are different from each other.
Diversity in Plants
Plants can be very different from one another in several ways, such as their size, shape, and the way they grow.Here are some ways plants can differ:
1. How can you measure the height of a plant accurately?
Plants can have different heights, and measuring their height helps understand their growth.
Examples of Plant Heights:
 Different heights of different plants
Different heights of different plants
Different heights of Plants
- Tall: Some plants, like mango trees, grow very tall and have a strong, thick trunk.
- Short: Other plants, like rose bushes, are much shorter and closer to the ground.
2. What do the stems of plants look like?
The stem provides structure and support to a plant.
Stem usually grows above the ground. The stem makes the main structural framework of the plant. The stem bears leaves, branches, buds, flowers and fruits.
 Stem of Plant
Stem of Plant
Types of Stems:
- Hard: Plants like the banyan tree have hard, woody stems that provide strong support.
- Soft: Smaller plants like mint have soft, green stems that are flexible and not as strong as woody stems.
4. What are some common shapes of leaves that you can see in different plants?
The leaf is a thin, flat, and green structure which arises from the node of the stem. The green colour of leaves is due to the presence of chlorophyll.
 Different leaves of different plants
Different leaves of different plants
- Shape: Leaves come in different shapes; for example, banana leaves are broad and large, helping the plant capture more sunlight.
- Arrangement: Leaves can be arranged in different patterns on the stem. For instance, neem leaves grow opposite each other on the branch.
- Venation: The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called venation.

- Reticulate Venation: Veins form a network, common in dicot plants like hibiscus and peepal.
- Parallel Venation: Veins run parallel to each other, common in monocot plants like grass and wheat.
4. What different colours can you see in the flowers around you?
Flower is the most beautiful and colourful part of a flowering plant. It is the reproductive part of a plant.
 Different Flowers different colours
Different Flowers different colours
- Colour: Flowers have various colours, like the bright red of a hibiscus flower, which can attract pollinators.
- Scent: Some flowers, like jasmine, have a strong, pleasant scent that also helps attract insects for pollination.
Diversity in Animals
Animals around us show amazing variety in size, shape, habitat, diet, and movement.Here are some ways animals can differ:
1. Where does the animal live?
The habitat is the natural environment where an animal lives.
 Turtle in WaterExamples of habitats:
Turtle in WaterExamples of habitats:
- Land: Cows, lions, squirrels.
- Water: Fish, turtles.
- Air: Birds like sparrows and eagles (nests on trees).
- Both Land and Water: Frogs (amphibians).
2. What kind of food does the animal eat?
Animals have different diets based on their needs:
 Different diets of different animals
Different diets of different animals
- Herbivores: Eat plants or grass (e.g., cows, deer).
- Carnivores: Eat meat or insects (e.g., lions, snakes).
- Omnivores: Eat both plants and meat (e.g., bears, crows).
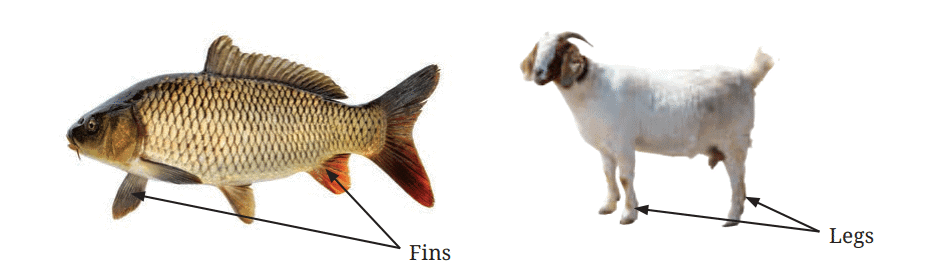
3. How does the animal move?
Animals use different body parts to move, depending on their species:
- Walking: Cats and dogs use their legs to walk or run.
- Flying: Birds like sparrows and eagles use their wings to fly.
- Swimming: Fish like goldfish and dolphins use fins to swim.
- Crawling: Snakes and lizards crawl using their body muscles.
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different plants, animals, and other living organisms found in a particular region or environment. For Example, trees offer food and shelter to certain birds and animals, while animals aid in seed dispersal by consuming fruits, and so on.

How to Group Plants and Animals?
Can you find a group of plants or animals that have something in common? For example, do any of them have similar colors, shapes, or sizes?
- Grouping plants and animals simplifies the study and understanding of their vast diversity, making it easier to identify, compare, and classify them.
- It helps in understanding evolutionary relationships and ecological roles, ensuring effective communication and research among scientists.
How to group Plants?
Grouping plants helps in understanding their characteristics and categorizing them based on common features.
Based on Height
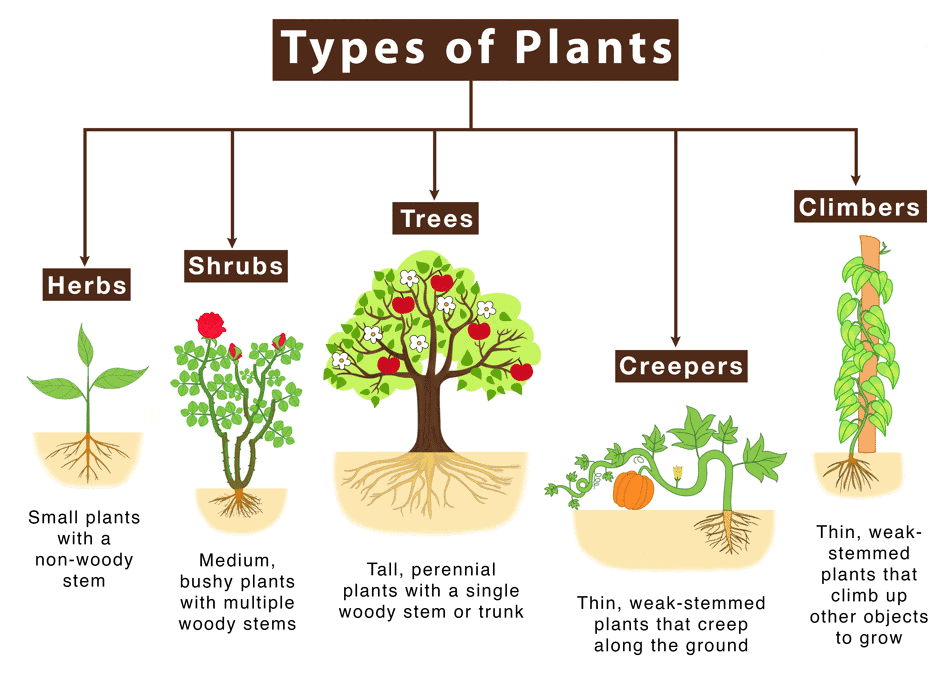
- Trees are plants that grow very tall and have hard, thick, brown, and woody stems. Their branches usually start higher up on the stem, away from the ground. Examples: Mango, banyan, acacia, coconut, poplar, willow, etc.
- Shrubs are plants that are not as tall as trees. They have many brown woody stems that start branching close to the ground. These stems are hard but not as thick as the stems of trees. Examples: Lemon, Coriander, Henna, Rose, etc.
- Herbs are typically small plants with soft and green stems. An example of a herb is the tomato plant. Examples: Wheat, paddy, cabbage, grass, coriander, etc.
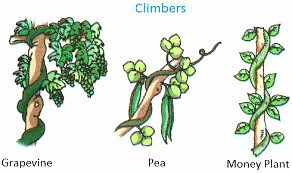
- Climbers have very thin, long and weak stems which cannot stand upright, but they can use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight. These types of plants use special structures called tendrils to climb. Examples: ea plant, grapevine, sweet gourd, money plant, jasmine, runner beans, green peas, etc.
- Creepers are plants that creep on the ground. They have very fragile, long, thin stems that can neither stand erect nor support all their weight. Examples: watermelon, strawberry, pumpkin and sweet potatoes.
Based on Leaves
Leaves can have different shapes and sizes. For example, the broad leaves of a mango tree are different from the thin leaves of grass. Leaves have veins that provide support and transport water and nutrients. The pattern of these veins is called venation.
Parallel venation: If the veins run parallel to one another from the base to the tip of the leaf, the leaf is said to have parallel venation, e.g., banana and onion. Parallel VenationReticulate venation: Leaves of some plants have veins arranged in a net-like pattern on both sides of the midrib. This kind of venation is called reticulate venation, e.g., Peepal (Bodhi) and Mango.
Parallel VenationReticulate venation: Leaves of some plants have veins arranged in a net-like pattern on both sides of the midrib. This kind of venation is called reticulate venation, e.g., Peepal (Bodhi) and Mango.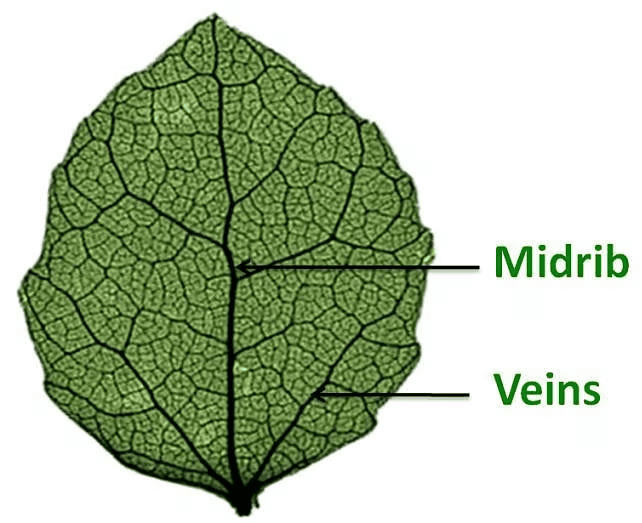
Note: Generally, plants with reticulate venation have taproots while those with parallel venation have fibrous roots.
Chickpea (chana) is another example of a plant with taproots and reticulate venation in leaves. Wheat is an example of a plant with fibrous roots and parallel venation in its leaves.
Based on Roots
Roots are the parts of a plant that grow underground and help the plant stay anchored in the soil.
There are two main types of roots:
- Taproots: This is composed of a main root which grows from the base of the stem. Many branches and sub-branches come out of the main root (tap root).
Examples: Peas, radishes, carrots, mangoes, marigolds, mustard, etc.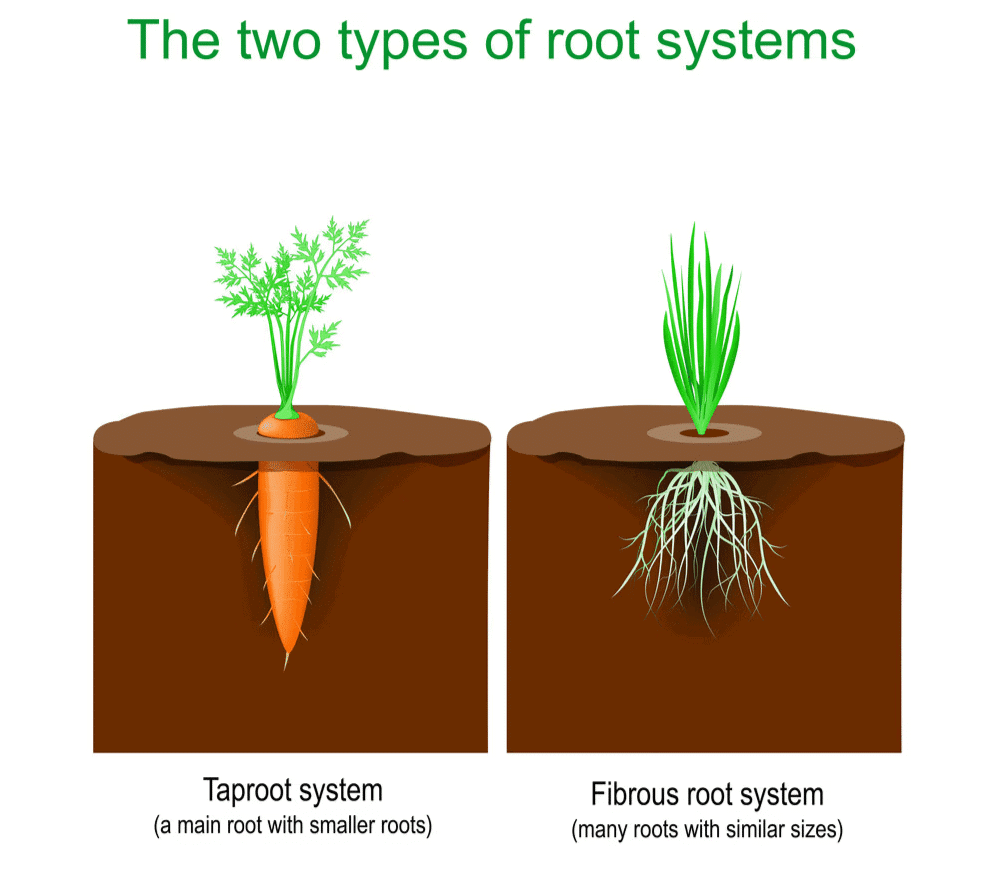
- Fibrous Roots: In this type, a cluster of thin fibre-like roots arise from the base of the stem. These roots spread out in the soil.
Examples: Maize, grass, wheat, millet, etc.
Based on Seeds
Seeds are the small parts of a plant that can grow into a new plant.
There are two main types of seeds based on the number of cotyledons (the first leaves that appear from the seed):
- Dicotyledons (Dicots): These seeds have two cotyledons, which can be split into two parts. An example of a dicot seed is a chickpea. Plants with dicot seeds usually have reticulate venation (a net-like pattern of veins on the leaves) and a taproot system.
- Monocotyledons (Monocots): These seeds have a single, thin cotyledon. An example of a monocot seed is maize (corn). Plants with monocot seeds typically have parallel venation (veins running parallel on the leaves) and a fibrous root system.
 Moncots and Dicots
Moncots and Dicots
How to group Animals?
Grouping animals helps in studying their behavior, characteristics, and features they share.
Based on Movement
- Flying: Animals that use wings to move through the air, like birds.
- Running/Walking: Animals that use their legs to run or walk on the ground, like dogs and horses.
- Crawling: Animals that move by crawling on their bodies, like snakes.
- Hopping/Jumping: Animals that hop or jump using their legs, like frogs and rabbits.
These categories help us understand and organize animals based on their movement and the body parts they use to move.
Plants and Animals in Different Surroundings
Plants and animals live in different places like deserts, mountains, oceans, and forests. Each has special features to survive in their surroundings. For example, camels store water to live in deserts, while fish have fins to swim in water. Let’s see how they adapt to these places!
In the Desert
- Plant: Cactus plants with thick and fleshy stems that store water to survive the hot, dry conditions.
 Desert Plants
Desert Plants - Animal: Camels with long legs, wide hooves, and the ability to store food in their humps, helping them walk on sand and survive without water for days.
 Desert Animals
Desert Animals
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Diversity in the Living World
|
Download as PDF |
On Mountains
- Plant: Deodar trees with a conical shape and sloping branches that allow snow to slide off easily, helping them survive in cold, snowy regions.
 Trees on Mountains
Trees on Mountains - Animal: Mountain goats that are adapted to the cold and rocky terrain, allowing them to move easily on steep slopes.
 Animals on Mountains
Animals on Mountains
In the Ocean
- Plant: Seaweed and other marine plants that thrive underwater.
 Plants underwater
Plants underwater - Animals: Fish with streamlined bodies and fins that help them move easily in water.
 Animals underwater
Animals underwater
In the Forest
- Plant: Various trees, like bamboo, grow tall and provide shelter to many animals.
 Forest Plants
Forest Plants - Animal: Lions, which live and hunt in dense forests.
 Forest Animals
Forest Animals
Rhododendron
Rhododendrons are plants that produce beautiful bright flowers. They can be found in different regions and may look different depending on where they grow.
 Rhododendrons
Rhododendrons
- Rhododendrons are plants that produce beautiful bright flowers. They can be found in different regions and may look different depending on where they grow.
- For example, in the Shola forests of Nilgiris, rhododendrons are shorter with smaller leaves, which helps them survive the strong winds on mountain tops. In contrast, in the mountains of Sikkim, rhododendrons are taller. These differences help the plant adapt to the specific conditions of each region.
Adaptations
Adaptations are special features or behaviors that help plants and animals survive in their specific surroundings. These adaptations make it easier for them to find food, stay safe, and live in their environment.
 For example:
For example:
- Camels have long legs and humps that store fat, helping them survive in the hot desert.
- Fish have fins and gills, allowing them to swim and breathe underwater.
- Cactus have thick stems to store water and spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss in the desert.
Adaptations are like nature’s way of making sure every living thing has what it needs to live where it does.
Habitats
A habitat is the natural environment where a plant or animal lives, providing the necessary conditions for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and space. Different plants and animals are adapted to live in specific habitats that suit their needs. Different Habitats
Different Habitats
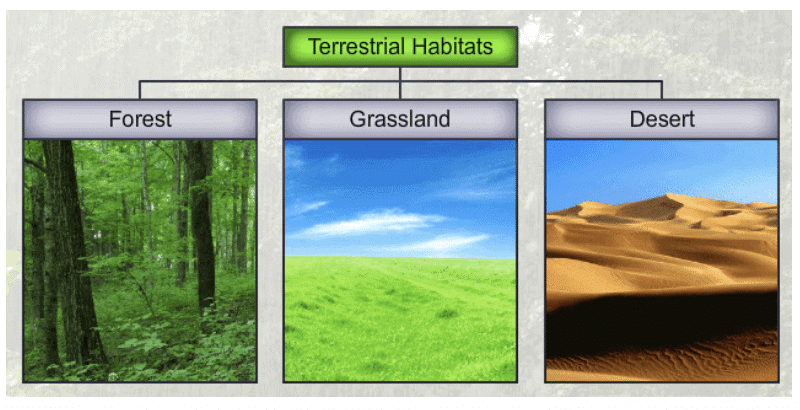
Types of Habitats
Terrestrial (Land-based) Habitats:
- Forests: Dense areas with a variety of trees and wildlife. Examples include tropical rainforests with species like tigers, monkeys, and a wide variety of trees and plants.
- Deserts: Dry areas with less vegetation and specialized animals. Examples include cactus, camels, and snakes adapted to conserve water and withstand high temperatures.
- Grasslands: Open areas with grasses and few trees. Examples include zebras, lions, and grasses that can survive with less water.
- Mountains: High regions with cold climates and unique plants and animals like snow leopards, yaks, and pine trees.
Aquatic (Water-based) Habitats:
- Some examples of aquatic habitats are ponds, lakes, rivers, and oceans
Amphibious Habitats:
- Some animals, such as frogs, can live in water as well as on land. These are called amphibians
Protecting Biodiversity
Talk to parents, grandparents, and neighbors to learn about plants, birds, insects, or animals they used to see frequently in their childhood but are rare now.
Such changes often happen due to habitat destruction, which leads to:
- Loss of homes, food, and other resources for plants and animals.
- A decline in biodiversity.
Examples of Declining Populations
- Bengal Tiger: Population reduced due to habitat loss caused by human activities.
- Cheetah: Lost natural habitats; reintroduction efforts began in 2022 under the "Cheetah Reintroduction Project."
- Great Indian Bustard: Declining population; habitats in Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra have been declared protected areas.
Government Initiatives for Conservation

- Project Tiger (1973): Protects the Bengal Tiger.
- Cheetah Reintroduction Project (2022): Aims to restore the population of cheetahs.
- Protected Areas: Habitats for the Great Indian Bustard were declared as protected in specific states.
Sacred Groves
- Definition: Sacred groves are undisturbed patches of forests protected by local communities.
- Features:
- Home to diverse plants, animals, and medicinal plants.
- Cutting trees or harming animals in these areas is prohibited.
- Importance: Sacred groves are valuable for preserving biodiversity.
|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Diversity in the Living World Chapter Notes - Science Class 6
| 1. What is the importance of diversity in plants and animals? |  |
| 2. How can we group plants and animals effectively? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of plants and animals in different surroundings? |  |
| 4. Why is it necessary to study the diversity of living organisms? |  |
| 5. How do environmental factors influence the diversity of plants and animals? |  |