Division Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 3 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Division is a way to share things equally or split them into smaller groups. Imagine you have some candies, and you want to give the same number of candies to your friends. Division helps you figure out how many candies each friend gets or how many groups you can make. It’s like the opposite of multiplication, where we combine things. Division is about breaking things into equal parts.

Example: You have 12 candies and want to share them equally among 3 friends. Division helps you find out that each friend gets 4 candies because 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Division Using Equal Grouping and Equal Sharing
Division can be done in two ways: equal grouping and equal sharing.

Equal Grouping
- This is when you know how many items you have, and you want to divide them into groups. You find out how many groups you can make.
- Example: You have 10 chocolates, and you want to put 2 chocolates in each bag. How many bags can you make? You divide 10 by 2. So, 10 ÷ 2 = 5. You can make 5 bags, with 2 chocolates in each.
Equal Sharing
- This is when you know how many groups you want to make, and you want to find out how many items each group gets.
- Example: You have 15 balloons, and you want to share them equally among 5 children. How many balloons does each child get? You divide 15 by 5. So, 15 ÷ 5 = 3. Each child gets 3 balloons.
Division as Repeated Subtraction
Division can also be thought of as subtracting the same amount again and again until nothing is left. This is called repeated subtraction. You keep subtracting the number you’re dividing by until you reach 0, and you count how many times you subtracted.
Example: You have 12 apples, and you want to give 3 apples to each friend. How many friends can you give apples to? Start with 12:
- 12 - 3 = 9 (1st friend)
- 9 - 3 = 6 (2nd friend)
- 6 - 3 = 3 (3rd friend)
- 3 - 3 = 0 (4th friend)
You subtracted 3 four times, so 12 ÷ 3 = 4. You can give apples to 4 friends.
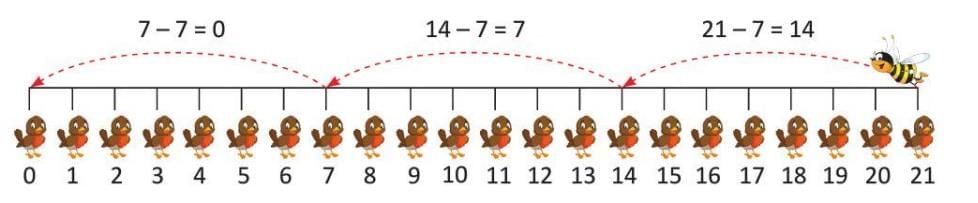
Division on a Number Line
A number line is a line with numbers marked on it, like a ruler. You can use it to show division by jumping backward in equal steps.
- How it works: Start at the number you’re dividing (the total), and jump back by the number you’re dividing by. Count how many jumps you make until you reach 0.
Example: Divide 21 by 7 using a number line.
- Start at 21 on the number line.
- Jump back by 7 each time: 21 to 14 (1 jump), 14 to 7 (2 jumps), 7 to 0 (3 jumps).
- You made 3 jumps, so 21 ÷ 7 = 3.
Division Facts
Division facts are simple division problems that you should know by heart, just like multiplication tables. They help you solve division quickly.
Examples of Division Facts:
- When any number is divided by 1, the answer is the number itself. For example, 6 ÷ 1 = 6 and 9 ÷ 1 = 9.
- A number cannot be divided by 0. For example, 6 ÷ 0 is not possible.
- When any number is divided by itself, the answer is 1. For example, 5 ÷ 5 = 1 and 2 ÷ 2 = 1.
- When we divide 0 by any number, the answer is 0. For example, 0 ÷ 3 = 0 and 0 ÷ 82 = 0.
- Any number ending in 0 can be divided by 10. For example, 40 ÷ 10 = 4 and 70 ÷ 10 = 7.
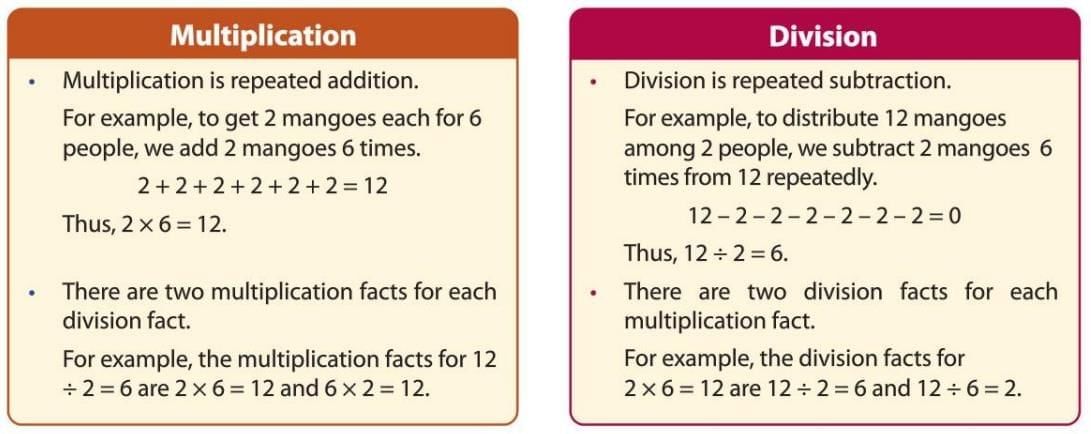
Relation between Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division are like best friends—they work together! If you know a multiplication fact, you can figure out a division fact.
Word Problems
Word problems are stories that use division to solve real-life situations. You need to read the problem carefully, find the total and the number to divide by, and then solve.
Examples
Example 1: A teacher has 20 pencils to share equally among 4 students. How many pencils does each student get?
- Total pencils = 20
- Number of students = 4
- Divide: 20 ÷ 4 = 5
- Each student gets 5 pencils.
Example 2: There are 18 cookies, and you want to put 3 cookies in each jar. How many jars can you fill?
- Total cookies = 18
- Cookies per jar = 3
- Divide: 18 ÷ 3 = 6
- You can fill 6 jars.
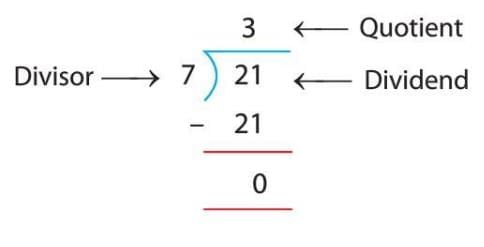
Long Division Method
The long division method is a step-by-step way to divide bigger numbers. It’s like breaking a big problem into smaller steps.
Steps for Long Division:
- Write the number to be divided (dividend) inside a division symbol and the number you’re dividing by (divisor) outside.
- See how many times the divisor fits into the first part of the dividend.
- Write the answer above, multiply, subtract, and bring down the next digit.
- Repeat until all digits are used. The number obtained at above is the quotient.
Example: Divide 21 by 7.
- Step 1: Write 21 ÷ 7.
- Step 2: How many times does 7 go into 1? It doesn’t, so look at 21.
- Step 3: How many times does 7 go into 21? 7 × 3 = 21, so write 3 above 21.
- Step 4: Subtract: 21 - 21 = 0. No digits left to bring down.
- Answer: 21 ÷ 7 = 3.
Practice Questions
- You have 16 candies to share equally among 4 friends. How many candies does each friend get?
- Divide 20 by 5 using repeated subtraction. How many times did you subtract 5?
- Use a number line to divide 12 by 3. How many jumps did you make?
- If 6 × 4 = 24, what is 24 ÷ 4? Use the relation between multiplication and division to explain.
- A shop has 30 apples, and they want to pack 6 apples in each bag. How many bags can they make?
|
67 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Division Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 3 ICSE
| 1. What is division using equal grouping? |  |
| 2. How can division be understood as repeated subtraction? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of using a number line for division? |  |
| 4. How are multiplication and division related? |  |
| 5. What are some common strategies for solving division word problems? |  |