Grade 12 Exam > Grade 12 Notes > Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for Grade 12 > Chapter Notes: Extracting Information from Data
Extracting Information from Data Chapter Notes | Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for Grade 12 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Extracting Information from Data |

|
| Metadata |

|
| Problems Collecting and Processing Data |

|
| Data Biases |

|
| Key Terms |

|
Introduction
This chapter explores how to extract meaningful information from data, a key skill in the AP Computer Science Principles course. It covers the importance of large data sets, the role of computers in processing big data, scalability, metadata, and challenges like data uniformity and biases. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing trends and solving problems across various fields.
Extracting Information from Data
- Data analysis allows us to identify trends, make connections, and solve problems in fields like science and history.
- A single or small number of data points may not show clear trends and could be outliers, making conclusions unreliable.
- Large data sets, known as big data, provide more comprehensive patterns for analysis.
- Correlation between data points suggests a relationship but does not prove causation, indicating areas for further research.
- As the world becomes more interconnected, the volume of accessible data grows, increasing the need for efficient data processing.
- Example: Visualizing global shipping in 2012 required tracking millions of shipments over months, demonstrating the scale of big data.
- Computers process data faster and with fewer errors than humans, especially for large data sets.
- For very large data sets, multiple computers or parallel systems may be needed.
- Server farms, housed in data centers or smaller facilities, are built to handle intense data processing needs.
Scalability
- Scalability is a system’s ability to handle increasing or decreasing amounts of data without changing its core operations.
- A scalable system may require additional resources, like more servers, but maintains its functionality.
- More scalable systems can process and store larger amounts of data efficiently.
- The power of a computer impacts its data processing capability; stronger computers handle data better.
Question for Chapter Notes: Extracting Information from DataTry yourself: What does correlation between data points suggest?View Solution
Metadata
- Metadata is information about data, providing context like a label on a package or clothing tag.
- Example: Metadata for a YouTube video includes the title, creator, description, tags, upload date, and file size.
- Changing or deleting metadata does not affect the data itself (e.g., editing a video’s description doesn’t change the video).
- Metadata helps organize and find data by enabling sorting and grouping.
- It provides additional details, such as creation dates, to assess data relevance (e.g., determining if information is outdated).
Metadata Example
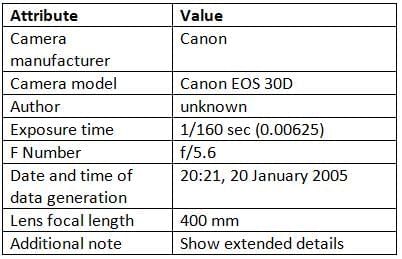
Problems Collecting and Processing Data
- Data sets, large or small, can be challenging to work with, but computers help address these issues.
- Data may lack uniformity due to inconsistent collection methods.
- Example: In a survey about favorite classes, responses like “AP CSP,” “AP Comp Sci,” and “AP Computer Science Principles” vary in format, complicating analysis.
- Non-uniform data can also result from combining data from sources with different formatting standards (e.g., 12-hour vs. 24-hour time).
- Cleaning data is the process of standardizing data by removing inconsistencies, duplicates, or invalid entries to improve data quality.
Data Biases
- Data sets may contain biases that lead to inaccurate or unfair conclusions.
- Example: In a favorite class survey, biases may arise because:
- Only those with strong opinions may respond, underrepresenting those indifferent to school.
- The survey is limited to one school, where a teacher’s quality might influence results more than the subject.
- The survey’s context (e.g., posted in an AP CSP class vs. a basketball group chat) can skew results.
- Societal factors like race or gender can introduce bias.
- Collecting more data does not eliminate bias; identifying and correcting biases (e.g., surveying multiple schools) is necessary.
Question for Chapter Notes: Extracting Information from DataTry yourself:What are data biases?
View Solution
Key Terms
- Big Data: Massive, complex datasets that traditional methods struggle to manage or analyze.
- Cleaning Data: The process of correcting or removing errors, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies in a dataset to improve its quality.
- Correlation: A statistical measure showing how two variables relate or move together.
- Data Centers: Facilities housing computer systems and networks for storing, managing, and processing large datasets.
- Data Biases: Systematic errors or prejudices in data that lead to inaccurate or unfair conclusions.
- Metadata: Descriptive information about data, like format, authorship, or creation date, aiding in organization and management.
- Scalability: A system’s ability to handle increasing workloads or users without losing efficiency.
- Server Farms: Large groups of interconnected servers in dedicated facilities for hosting or processing data.
The document Extracting Information from Data Chapter Notes | Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for Grade 12 is a part of the Grade 12 Course Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for Grade 12.
All you need of Grade 12 at this link: Grade 12
FAQs on Extracting Information from Data Chapter Notes - Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for Grade 12
| 1. What is metadata and why is it important in data analysis? |  |
Ans.Metadata is data that provides information about other data. It is important in data analysis because it helps users understand the context, quality, and structure of the data, making it easier to interpret and use effectively.
| 2. What are some common challenges in data collection? |  |
Ans.Common challenges in data collection include ensuring data accuracy, dealing with missing or incomplete data, managing large volumes of data, and obtaining data from reliable sources. These issues can affect the overall quality and usability of the data.
| 3. How can data biases impact research outcomes? |  |
Ans.Data biases can lead to skewed results and misinterpretations in research. If certain groups are overrepresented or underrepresented in the data, the findings may not accurately reflect reality, leading to incorrect conclusions and potentially harmful decisions.
| 4. What key terms should I know when studying data analysis? |  |
Ans.Key terms to know include metadata, data bias, data collection, data processing, and data visualization. Understanding these terms is essential for grasping the fundamental concepts of data analysis and its applications.
| 5. What strategies can be used to address data biases? |  |
Ans.Strategies to address data biases include using diverse data sources, implementing rigorous data collection methods, regularly reviewing and auditing data for biases, and applying statistical techniques to adjust for known biases in the data.
Related Searches














