Gastrointestinal Physiology Chapter Notes | Physiology - NEET PG PDF Download
Structure-Function Relationship
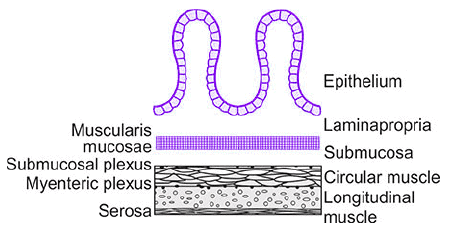 The general histology of the wall of the GI tract, seen in transverse cross section.
The general histology of the wall of the GI tract, seen in transverse cross section.
General Histology of GI Tract Wall: The wall of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, seen in transverse cross-section, consists of multiple layers with specific functions.
Mucosa Components:
- Epithelium: Secretes fluid, electrolytes, enzymes, or mucus into the lumen, aiding digestion and protection.
- Lamina Propria: Primarily connective tissue containing blood vessels and lymph nodes, providing structural support and nutrient delivery.
- Muscularis Mucosae: A thin muscle layer whose contractions alter the mucosa's shape, creating ridges and valleys to modify the absorptive or secretory surface area.
- Submucosa: Composed of loosely woven collagen and elastin connective tissue, containing glands, larger blood vessels, and the submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus, a nerve network regulating local secretions and blood flow.
- Smooth Muscle Layers: Responsible for GI motility, consisting of an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer, with the myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus located between them, controlling motility.
- Small Intestine Epithelium Renewal: The entire epithelium is replaced every 3-6 days, making it one of the body’s fastest-growing tissues.
- Small Intestine Structure:
- Villi: Finger-like projections, approximately 1 mm long, with 20-40 villi per mm², increasing surface area for absorption.
- Columnar Cells: Villi are covered by columnar cells with a brush border (microvilli), enhancing absorption efficiency.
- Glycocalyx: A carbohydrate-rich layer lining the brush border, aiding in protection and selective absorption.
- Crypts of Lieberkuhn: Intestinal glands between villi, simple tubular glands that do not penetrate the muscularis mucosa, involved in secretion and cell renewal.
- Crypt Cells:
- Proliferative cells responsible for intestinal epithelium renewal.
- Capable of secreting fluid and electrolytes.
- Some differentiate into mucus-secreting goblet cells.
- A few migrate to crypt bases, becoming Paneth cells, which secrete defensins (natural antibiotics) and guanylin, regulating chloride secretion.
Gastrointestinal Motility
Types of Motility:
- Electrical Activity: Basic Electric Rhythm (BER), a spontaneous rhythmic fluctuation in smooth muscle membrane potentials.
- Mechanical Activity:
- Fed State Motility:
- Peristalsis: Propulsive movement, with mass movement as a modified form in the large intestine.
- Segmentation: Non-propulsive mixing movement, with haustration as a modified form in the large intestine.
- Fasting State Motility: Migrating Motor Complex (MMC), the primary motility during fasting.
Basic Electric Rhythm (BER)
- Definition: Spontaneous, rhythmic fluctuations in GI smooth muscle membrane potentials, ranging between -65 mV and -45 mV.
- Origin: Starts from the mid-portion of the stomach, specifically along the greater curvature in the proximal body, serving as the dominant pacemaker to entrain the rest of the stomach.
- Presence: Found throughout the GI tract except the esophagus and proximal stomach.
- Cause: Generated by pacemaker cells called interstitial cells of Cajal.
- Location of Cajal Cells:
- Stomach and Small Intestine: Located in the outer circular muscle layer near the myenteric plexus.
- Colon: Positioned at the submucosal border of the outer circular muscle layer.
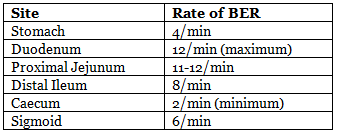
- Rate of BER:
- Function: BER coordinates contractions like peristalsis and other motor activities but does not directly cause contractions. Spike potentials, superimposed on the most depolarizing BER waves, trigger contractions and increase muscle tension.
- Spike Potentials: Depolarization due to Ca²⁺ influx, repolarization due to K⁺ efflux.
- Factors Affecting BER:
- Acetylcholine: Increases spike potential frequency, enhancing muscle tension.
- Epinephrine: Decreases spike potential frequency, reducing muscle tension.
- Force of Contraction: Depends on spike potential frequency, not amplitude.
Peristalsis
- Definition: A reflex contraction of the gut wall in response to stretch (e.g., by food), present from the esophagus to the rectum.
- Mechanism: Stretching the gut wall triggers a wave of circular contraction behind the stretch and relaxation in front, driven by the enteric nervous system with modulation by the extrinsic autonomic nervous system.
- Enteric Nervous System Role: Peristalsis persists in isolated intestinal segments if ends are joined correctly, but not if reversed.
- Sequence of Events:
- Stretch releases serotonin, stimulating the myenteric plexus.
- Retrograde Direction: Cholinergic neurons activate neurons releasing substance P and acetylcholine, causing contraction behind the stimulus.
- Anterograde Direction: Neurons release nitric oxide (NO), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), and ATP, causing relaxation in front of the stimulus.
- Movement: Peristaltic waves move orally to caudally, propelling GI contents at 2-25 cm/s.
Mass Movement
- Definition: A specialized form of peristalsis unique to the colon.
- Frequency and Timing: Occurs 3-4 times daily post-meal, each lasting ~3 minutes, with strong movements often initiated after the morning meal, more prominent in infants.
- Mechanism: Starts due to colon distension, propagating as a contraction ring, forcing fecal matter into the rectum, triggering the defecation reflex.
- Initiation Factors:
- Gastrocolic or duodenocolic reflex.
- Intense parasympathetic nerve stimulation.
- Colon distension.
- Inhibition:
- Destruction of Auerbach’s (myenteric) plexus abolishes mass movement.
- Proximal colon is relatively autonomous, innervated by the vagus nerve.
- Distal colon relies more on extrinsic vagal innervation, so nerve injury abolishes movement in this region.
Segmentation
- Definition: The predominant motor activity in the fed state, dividing the bowel into segments, also known as pendulous movement due to its to-and-fro motion.
- Function: Non-propulsive, moves chyme bidirectionally for greater mixing with intestinal secretions, slowing chyme progression compared to peristalsis.
- Muscle Involvement: Involves circular muscle contractions, unlike peristalsis, which involves longitudinal muscle contractions.
- Occurrence: Occurs in both the large and small intestines.
- Initiation: Starts simultaneously in the duodenum and ileum in response to local distension.
- Rate: Matches BER rates, e.g., 12/min in the duodenum.
Migrating Motor Complex (MMC)
- Definition: Motor and electrical activities of GI smooth muscle during fasting, starting in the stomach and migrating to the distal ileum.
- Rate: Moves at ~5 cm/min during fasting, inhibited by meals, resuming 90-120 minutes post-meal, occurring every ~90 minutes until the next meal.
- Control: Regulated by motilin, secreted by Mo cells in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon, with maximum secretion in the duodenum-jejunum.
- Function: Not fully clear, but likely clears stomach and small intestine contents between meals, increasing pancreatic, gastric, and bile secretions during each MMC. Food intake halts MMC, replacing it with peristalsis and other BER/spike potential activities.
Gastric Emptying
- Regulation: Primarily via neural vagovagal reflexes, with receptors in the upper intestine responding to food osmolality and chemical composition (H⁺, lipids), triggering neural and hormonal inhibition of gastric emptying.
- CCK Role: Inhibits gastric emptying as a hormone and stimulates vagal afferent fibers, inducing a vagovagal reflex to reduce emptying.
- Factors Affecting Gastric Emptying:
- Volume: Larger volumes empty faster due to neural reflexes and gastrin release, increasing motility.
- Consistency: Liquids empty faster than solids, which must be reduced to 2-3 mm particles.
- Food Type:
- Carbohydrates: Rapid emptying.
- Proteins: Slower emptying.
- Fats: Slowest emptying.
- Duodenal Factors: Distension, acidity (pH <4), and high/low osmolality of chyme (fat/protein products) inhibit emptying via the enterogastric reflex, particularly sensitive to irritants and acids.
- Substance Emptying Rates:
- Isotonic saline: Most rapid.
- Hypo/hypertonic saline: Slower.
- Calories (especially lipids) or acid: Further slows emptying.
- Typical Emptying Time: A mixed meal (~1500 mL of solids, liquids, and gastric juice) takes ~3 hours to empty into the duodenum.
Hormonal Control Of Intestinal Motility
- Hormones Increasing Motility: CCK, motilin, VIP, gastrin, serotonin, ghrelin.
- Hormones Decreasing Motility: Secretin, glucagon, hydrogen sulfide.
- Motilin: Stimulates stomach and small intestine motility during fasting, with half the potency of CCK.
- CCK: The major hormone for intestinal motility.
- Hormonal Effects Table:
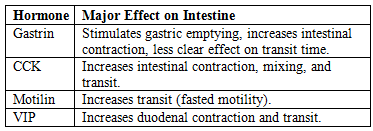
Gastrointestinal Hormones
Major GI Hormones Table: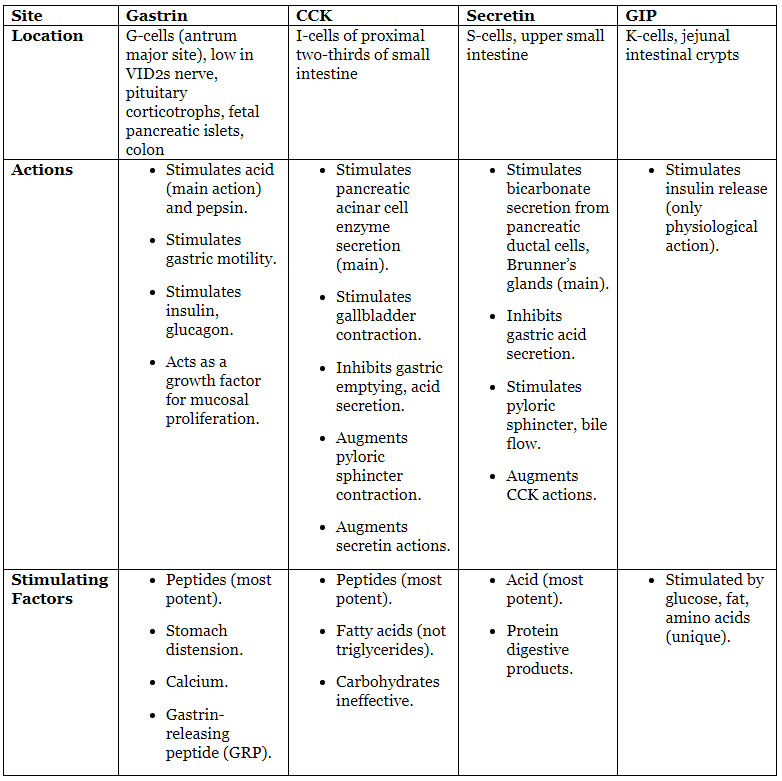
- GIP Note: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, formerly called gastric inhibitory polypeptide.
Gastrointestinal Secretion
Daily Secretion Characteristics Table: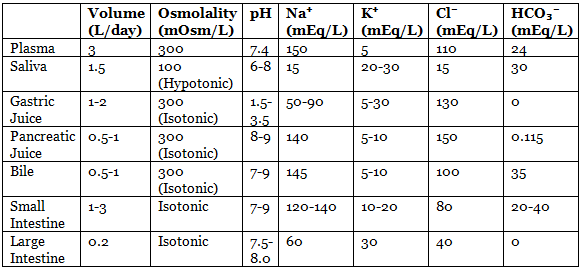
- Brunner’s Gland Secretion: pH 8-8.9, secretes ~200 mL/day.
Bile Secretion
- Volume: ~500 mL/day secreted by the liver.
- Absorption: Maximum absorption in the terminal ileum via enterohepatic circulation (5-12 times daily).
- Mechanism: Hepatocytes actively secrete osmotically active compounds (bile acids, glutathione, conjugated compounds, bicarbonate, chloride) into the canalicular space, followed by passive water movement through tight junctions.
- Bile Acids: Major solutes and primary osmotic driving force for bile flow.
- Gallbladder Concentration: Concentrates bile 5-20 fold via active Na⁺ transport, followed by secondary absorption of Cl⁻, water, and other diffusible constituents.
- pH Characteristics:
- Pancreatic juice: Most alkaline.
- Gastric juice: Most acidic.
- Ion Concentrations:
- K⁺: Highest concentration in large intestine fluid, followed by saliva; highest total amount in saliva (concentration × volume).
- Na⁺: Highest in bile, followed by pancreatic and small intestinal secretions.
- Cl⁻: Highest in gastric juice, followed by bile.
- HCO₃⁻: Highest in pancreatic juice, followed by ileum.
- Expulsion:
- Gallbladder contracts rhythmically within 30 minutes post-meal, primarily stimulated by CCK (released by fat/protein digestion products in the duodenum).
- CCK Actions: Contracts gallbladder smooth muscle and relaxes the sphincter of Oddi.
- Secretin: Stimulates water and HCO₃⁻ secretion into bile, augments CCK-induced gallbladder contraction.
- GIP: No effect on gallbladder contraction.
- Vagal Activity: Also stimulates gallbladder contraction.
- Bile pH: Gallbladder bile (pH 6.5) is slightly acidic compared to liver bile (pH 7.4).
- Choleretics: Substances (e.g., bile salts) that increase hepatic bile secretion.
- Cholagogue: CCK is the most potent, triggered by fatty acids and amino acids in the duodenum, causing gallbladder contraction.
Salivary Secretion
Composition:
- Acinar saliva is isotonic, with Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻, and HCO₃⁻ concentrations similar to plasma.
- Ductal cells modify saliva by extracting Na⁺ and Cl⁻, adding K⁺ and HCO₃⁻, and are relatively impermeable to water.
Flow Rate Effects:
- Low Flow: Saliva is hypotonic, slightly acidic, low in Na⁺, Cl⁻, and HCO₃⁻, but rich in K⁺.
- High Flow: Saliva is closer to isotonic, with higher pH, Na⁺, Cl⁻, and HCO₃⁻ (HCO₃⁻ secretion selectively stimulated), and lowest K⁺.
- Volume and pH: ~1.5 L/day, pH ~7.0.
- Components:
- Ptyalin (Salivary α-Amylase): Digestive enzyme with a minor role in starch digestion.
- Mucin: Glycopeptide that lubricates food.
Regulation:
- Parasympathetic: Dominant, produces high-volume, watery, enzyme-rich secretion.
- Sympathetic: Produces small amounts of thick, viscous, mucous secretion.
Gastric Secretions
Gastric Cell Types and Secretions:
- Parietal (Oxyntic) Cells: In the body, secrete HCl and intrinsic factor.
- Chief (Peptic) Cells: In the body, secrete pepsinogen.
- G Cells: In the antrum, secrete gastrin.
- Mucous Neck Cells: In oxyntic glands, secrete mucus.
Stimuli for Acid Secretion: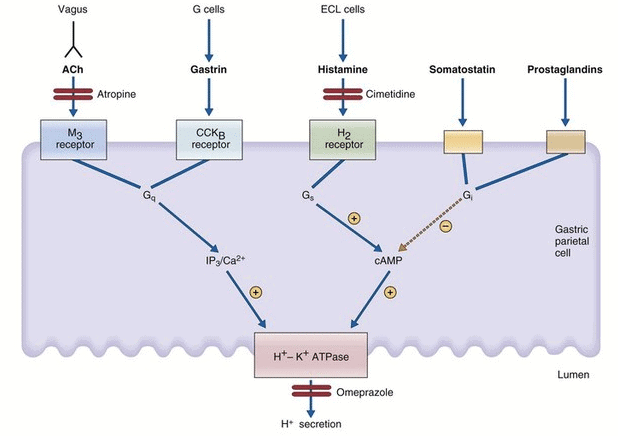 Regulation of acid secretion in parietal cell.
Regulation of acid secretion in parietal cell.
- Vagal Stimulation:
- Direct Pathway: Vagus innervates parietal cells, stimulating H⁺ secretion via acetylcholine (ACh) at muscarinic (M₃) receptors.
- Indirect Pathway: Vagus innervates G cells, stimulating gastrin secretion via gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP), which promotes H⁺ secretion. Atropine blocks only the direct pathway.
- Gastrin: Released post-meal, stimulates H⁺ secretion via CCK_B receptors on parietal cells (direct) and histamine release from ECL cells (indirect, major pathway).
- Histamine: Released from enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells, stimulates H⁺ secretion via H₂ receptors on parietal cells, the dominant physiological mediator.
Inhibition of H⁺ Secretion:
- Low pH (<3.0): Inhibits gastrin secretion, reducing H⁺ secretion.
- Somatostatin:
- Direct: Binds parietal cell receptors, inhibiting adenylyl cyclase via Gi protein.
- Indirect: Inhibits histamine and gastrin release.
- Prostaglandins: Inhibit H⁺ secretion by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase, reducing cAMP.
- Upper Intestine Factors: Food, protein breakdown products, or irritants trigger reverse enterogastric reflex.
- Hormones: Secretin, gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP), and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) have slight to moderate inhibitory effects.
Phases of Acid Secretion:
- Basal (Interdigestive): ~10% of maximal meal response, shows circadian rhythm (highest in evening, lowest in morning).
- Stimulated Phases:
- Cephalic (20-30%): Triggered by chewing/swallowing, mediated by vagus (parasympathetic).
- Gastric (60-70%): Triggered by distension (vagovagal reflexes) and digested proteins (gastrin-histamine).
- Intestinal (10%): Triggered by distension (entero-oxyntin) and digested proteins (circulating amino acids).
- All Phases: Gastrin and ACh stimulate ECL cells, releasing histamine.
Pancreatic Secretion
Composition:
- High volume, isotonic.
- Na⁺ and K⁺ concentrations similar to plasma.
- Much higher HCO₃⁻ and lower Cl⁻ than plasma.
- Contains pancreatic lipase, amylase, and proteases.
Flow Rate Effects:
- Low Flow: Isotonic fluid, mainly Na⁺ and Cl⁻.
- High Flow: Isotonic fluid, mainly Na⁺ and HCO₃⁻.
Stimulation:
- Secretin: Acts on ductal cells to increase HCO₃⁻ secretion.
- CCK: Acts on acinar cells to increase enzyme secretion (amylase, lipases, proteases) and potentiates secretin’s effect on HCO₃⁻ secretion.
- ACh (Vagovagal Reflexes): Stimulates enzyme secretion by acinar cells and potentiates secretin’s effect on HCO₃⁻ secretion.
Absorption Of Nutrients In Git
General Absorption: Nutrients absorbed along the entire small intestine, except for specific nutrients with localized absorption.
Specific Nutrient Absorption:
- Folate and Iron: Absorbed maximally in duodenum and proximal jejunum.
- Bile Salts and Cobalamin (Vitamin B12): Maximally absorbed in distal ileum, with minimal absorption in upper intestine.
- Bile Salts: Absorbed via Na⁺-dependent co-transport.
Carbohydrate Absorption:
- Hexose Transport: Most hexoses (e.g., glucose, galactose) are Na⁺-dependent, using SGLT-1 for secondary active transport from lumen to enterocytes.
- Fructose: Absorbed by Na⁺-independent facilitated diffusion via GLUT5.
- Basolateral Transport: Glucose, galactose, and fructose exit enterocytes into the interstitium/capillaries via GLUT2.
- Glucose Absorption Rate: Maximum ~120 g/h.
Protein Absorption:
- Amino Acids:Transported by at least seven systems:
- Five Na⁺-dependent co-transporters, two requiring Cl⁻.
- Two Na⁺-independent systems.
- Di-/Tripeptides: Transported by PepT1, a co-transporter using H⁺ instead of Na⁺.
- Protein Antigens: Absorbed by microfold (M) cells overlying Peyer’s patches, particularly for bacterial/viral proteins.
- Efficiency: Only 2-5% of small intestinal protein escapes digestion/absorption.
- Maximal Absorption: Duodenum (highest), jejunum (moderate), ileum (lowest).
Fat Absorption:
- Mechanism: Lipids enter enterocytes by passive diffusion; long-chain fatty acids use FATP4 transporter.
- Efficiency: ≥95% of ingested fat absorbed on moderate intake.
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K): Absorbed with micelles, maximally in duodenum.
- Water-Soluble Vitamins: Absorbed in upper small intestine, except vitamin B12 (ileum).
Iron Absorption:
- Location: Almost exclusively in duodenum.
- Form: Dietary iron is mostly ferric (Fe³⁺), but ferrous (Fe²⁺) is absorbed.
- Conversion: Fe³⁺ reduced to Fe²⁺ by ferric reductase (part of DMT1 transporter).
- Transport:
- DMT1: Proton-coupled transporter (Nramp2) for Fe²⁺ and other divalent cations (Zn, Mn, Co, Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb) into enterocytes.
- Ferroportin 1: Basolateral transporter for Fe²⁺ exit.
- Hephaestin: Facilitates ferroportin 1, not a transporter itself.
- Storage and Plasma Transport: Some Fe²⁺ stored as ferritin in enterocytes; the rest exits via ferroportin 1, is oxidized to Fe³⁺, and binds to transferrin in plasma.
Calcium and Magnesium:
- Location: Best absorbed in proximal small intestine.
- Mechanism: Via vitamin D-dependent carrier proteins TRPV6 (calcium, magnesium) and TRPV7 (magnesium).
- Calbindin: Intracellular protein buffering Ca²⁺ to aid absorption.
Vitamin Absorption:
- Vitamin B12 and Folate: Na⁺-independent absorption.
- Other Water-Soluble Vitamins: (Thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxine, pantothenate, biotin, ascorbic acid) absorbed via Na⁺-dependent co-transporters.
Water Absorption:
- Daily Fluid Load: ~9 L in adults.
- Small Intestine: Absorbs 7000 mL (78%), with jejunum (5-6 L) and ileum (~2 L).
- Colon: Absorbs 1900 mL (21%).
- Stool: ~100 mL (1%).
Dietary Fiber
- Source: Plant foods, primarily polysaccharides in cell walls.
- Resistance: Resistant to digestion by endogenous GI enzymes.
- Types:
- Carbohydrate: Pectin, cellulose, hemicellulose, inulin.
- Noncarbohydrate: Lignin.
- Functions:
- Bulky meals with low caloric content.
- Stimulates softer, more frequent fecal matter.
- Reduces post-prandial glycemia.
- Lowers blood cholesterol.
- Protects against colonic cancer, diverticulitis, and irritable bowel syndrome.
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs):
- Composition: 2-5 carbon weak acids (60% acetate, 25% propionate, 15% butyrate).
- Production: Generated in the colon by bacterial fermentation of complex carbohydrates, resistant starches, and dietary fiber.
- Absorption: Via specific transporters in colonic epithelial cells, promoting Na⁺ absorption.
- Functions:
- Contribute to caloric intake.
- Trophic effect on colonic epithelial cells.
- Combat inflammation.
- Maintain acid-base equilibrium.
Control of Food Intake and Metabolic Rate
Regulation of Food Intake:
- Hypothalamic Centers:
- Hunger Centers: Lateral hypothalamic (LH) nuclei.
- Satiety Centers: Ventromedial hypothalamic (VMH) nuclei.
- Other Nuclei: Paraventricular and arcuate nuclei play major roles in regulating food intake and energy expenditure.
- Arcuate Nuclei: Integration sites for GI and adipose tissue hormones regulating food intake and energy expenditure.
Neurons and Neurotransmitters:
- POMC Neurons: Produce α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) and cocaine- and amphetamine-related transcript (CART).
- NPY/AGRP Neurons: Produce orexigenic neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related protein (AGRP).
- α-MSH: Acts on melanocortin receptors (MCR4) in paraventricular nuclei, activating the sympathetic system via the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), reducing food intake and increasing energy expenditure.
- AGRP: Antagonizes MCR4 (inhibits α-MSH) and activates NPY receptor (Y1r), stimulating appetite.
- MCH and Orexins: Orexigenic peptides in LH neurons, influenced by AGRP and POMC neurons, with exact feeding targets unclear.
Peripheral Factors:
- Inhibitory (Anorexigenic): Insulin, leptin, and CCK inhibit AGRP-NPY neurons and stimulate POMC-CART neurons, reducing food intake.
- Stimulatory (Orexigenic): Ghrelin (from stomach) activates AGRP-NPY neurons, stimulating food intake.
Factors Influencing Feeding/Satiety Table: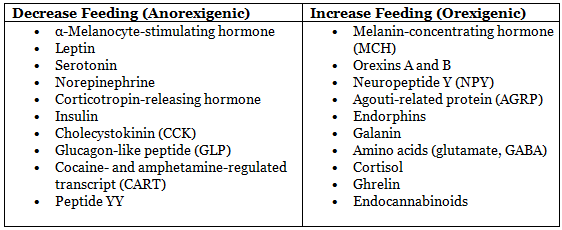
Leptin:
- Source: White adipose tissue, cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells.
- Function: Signals excess energy storage, sending anorexigenic signals to the hypothalamus to reduce fat storage and food intake.
- Levels: Increase with adiposity (high in obesity due to leptin resistance), postprandial, and decrease during fasting/diabetes.
- Other Roles: Regulates puberty onset, thermogenesis, immune response, inflammation, coagulation, fibrinolysis, and platelet aggregation.
- Mechanism: Acts via JAK-STAT3 pathway.
- Circulating Levels: 5-15 ng/mL (lean), up to 50 ng/mL (obese).
Ghrelin:
- Source: Primarily stomach, also pancreas and adrenal glands.
- Function: Orexigenic, stimulates appetite by activating AGRP-NPY neurons and suppressing leptin action.
- Levels: Peak preprandially, decrease post-meal.
- Mechanism: Increases synthesis/release of central orexins (NPY, cannabinoids).
Peptide YY:
- Source: Enteroendocrine L cells in distal ileum and colon basal crypts.
- Stimulants: Fat (major), carbohydrates, bile acids.
- Function: Anorexigenic, acts as an ileal brake controlling meal transit through the ileum, inhibits GI motility, pancreatic, and gastric secretion.
Basal Metabolic Rate
- Definition: Minimum energy expenditure for body survival, measured at rest in a thermoneutral environment, 12-14 hours post-meal.
- Contribution: Accounts for 50-70% (average 60%) of daily energy expenditure in sedentary individuals.
- Typical Value: ~65-70 calories/hour in a 70-kg man.
- Exercise: Maximum metabolic rate during exercise is ~10 times BMR.
Factors Affecting BMR Table: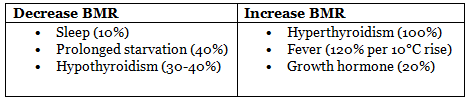
|
40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Gastrointestinal Physiology Chapter Notes - Physiology - NEET PG
| 1. What is the Basic Electric Rhythm (BER) and its role in gastrointestinal motility? |  |
| 2. How does peristalsis differ from segmentation in the gastrointestinal tract? |  |
| 3. What factors regulate bile secretion, and what role does it play in digestion? |  |
| 4. What components are found in salivary secretion, and what are their functions? |  |
| 5. How do gastric secretions contribute to the process of digestion? |  |
















