Geometry and Maps Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 3 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Straight and Curved Lines |

|
| Horizontal and Vertical Lines |

|
| Drawing Lines |

|
| Shapes |

|
| Solids |

|
| Dot Grid |

|
| Reading the Position |

|
| Tangram |

|
| Tiling |

|
| Map |

|
Introduction
The chapter "Geometry and Maps" introduces students to the basics of shapes, lines, and spatial understanding. It covers how to draw and identify different types of lines, such as straight and curved, and explores two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) shapes. Students will learn to create shapes using tools like rulers and compasses, work with dot grids to form figures, and understand concepts like tangrams and tiling. Additionally, the chapter teaches simple map-reading skills to help locate places using landmarks and directions. These topics build a foundation for understanding geometry and spatial relationships in a fun and engaging way.
Straight and Curved Lines
- Straight line: Formed by stretching a rope tightly from both ends.

- Curved line: Created when the rope is loosened or shaped into curves.
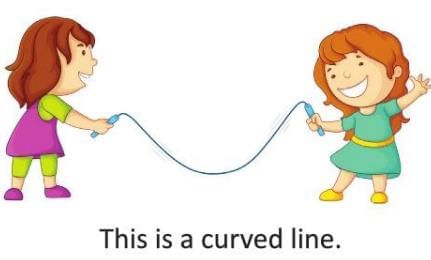
- Slanting line: A straight line formed by raising one end of a stretched rope.

Horizontal and Vertical Lines
- Horizontal line: A straight line that goes from left to right.

- Vertical line: A straight line that goes from top to bottom.

Drawing Lines

- Ruler or scale: Used to draw and measure straight lines.
- Holding the ruler: Keep the ruler steady to avoid movement while drawing.
- Pencil: Use a well-sharpened pencil for precise lines.
- Other tools for straight lines: Items like a pencil box or book can help draw straight lines but cannot measure them.
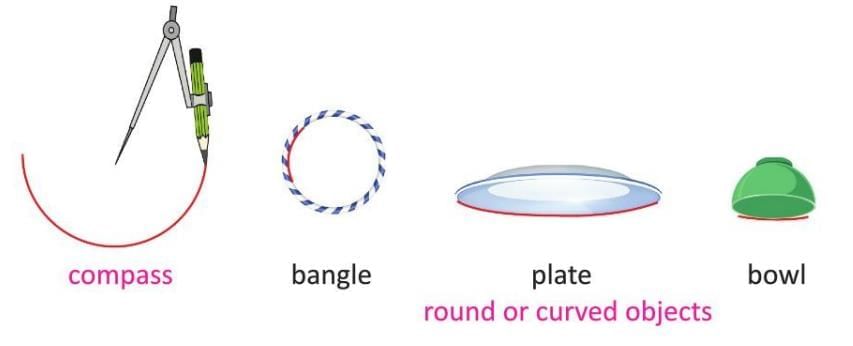
- Compass: Used to draw curved lines accurately.
- Other ways to draw curved lines: Use round objects like bangles, plates, or bowls, or draw freehand.
Shapes
- Plane figure or 2D shape: A shape with only length and breadth, no height.
- Corner: The point where two straight lines meet in a plane figure.
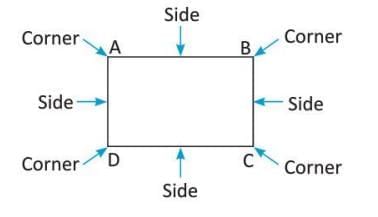
- Side: A straight line connecting two adjacent corner points.
- Diagonal: A line joining opposite, non-adjacent corners in a straight-sided shape.

Square
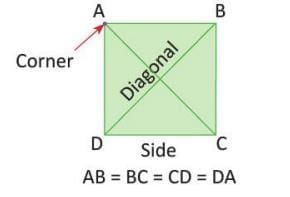
Has four equal sides, four corners, and two diagonals.
Rectangle

Has four sides (two short, two long), with opposite sides equal, four corners, and two diagonals.
Triangle
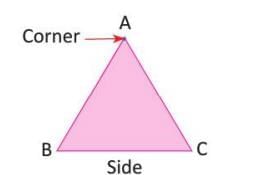
Has three sides, three corners, and no diagonals.
Circle

Has no sides, corners, or diagonals; made of a curved line.
Oval

A flattened circle with no sides, corners, or diagonals.
- Straight-line shapes: Triangle, square, and rectangle are made of straight lines.
- Curved-line shapes: Circle and oval are made of curved lines.
Solids
- Solid or 3D shape: A shape with length, breadth, and height.
- Face: The flat surface of a solid.
- Edge: The side where two faces of a solid meet.
- Vertex: The point where two edges of a solid meet.
Cube:

A solid with six square-shaped flat faces, 12 straight edges, and eight vertices.
Cuboid:

A solid with six flat faces (four rectangular, two may be rectangular or square), 12 straight edges, and eight vertices; opposite faces are equal.
Sphere:
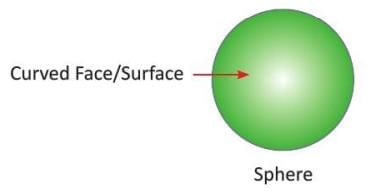
A solid with one curved face, no flat faces, edges, or vertices.
Cylinder:

A solid with two flat faces, one curved face, two curved edges, and no vertices.
Cone:
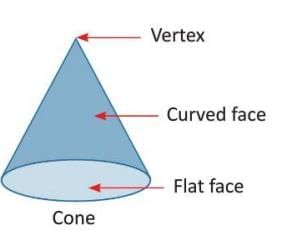
A solid with one flat face, one curved face, one curved edge, and one vertex.
Dot Grid
- Dot grid: An arrangement of dots placed at equal distances horizontally and vertically.
- Uses: Straight and curved lines can be drawn by joining dots to create various shapes and figures.
- Creative shapes: Interesting shapes and figures can be made using both straight and curved lines on a dot grid.

Reading the Position
- Grid division: A dot grid is divided into rows and columns to locate points.
- Naming: Rows are numbered (e.g., 1, 2, 3, …), and columns are labeled (e.g., A, B, C, …).
- Position of points: The position of a point is written as (row, column), e.g., (1, C) for a point in the first row and column C.
- Example: For a triangle, vertices might be at (1, C), (3, A), and (3, E); for a square, vertices might be at (5, F), (5, H), (7, F), and (7, H).

Tangram
- Tangram: A Chinese puzzle made of seven pieces (tans) cut from a square.
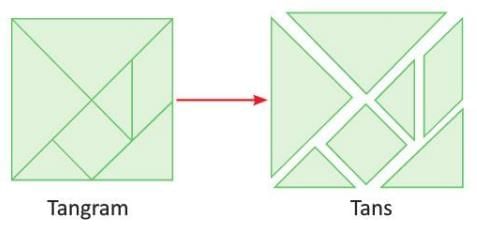
- Uses: Tans can be arranged to form shapes, letters, animal figures, and other designs, such as a duck, old man, or letters like C and E.

Tiling
- Tiling or tessellation: Arranging tiles to cover a surface without any gaps between them.
- Examples: Tiles on walls or floors in kitchens, bathrooms, or rooms, with various shapes, sizes, designs, and colors.
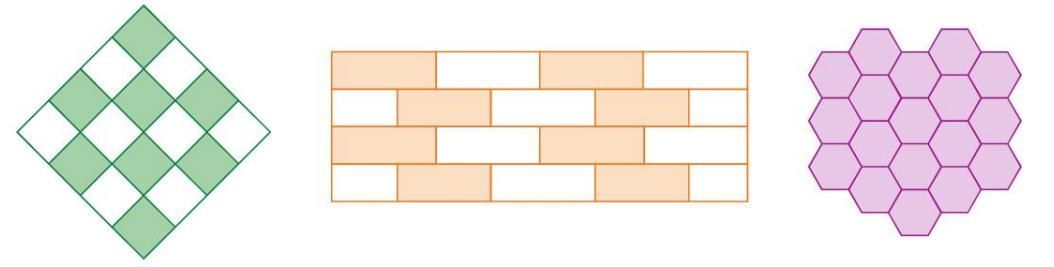
- Proper tiling: Tiles fit perfectly with no spaces between them.
- Non-tiling: Arrangements with gaps between tiles are not considered tiling.

Map
- Map: A diagram showing the location of objects or places using directions and symbols for landmarks.
- Landmark: An easily recognizable building, place, or statue used to find directions.
- Map reading: Helps understand the direction and location of places.
- Example: A route from a bus stand to a house might involve landmarks like a milk booth, nursing home, and park.

Example:
The map of a local market is given below. Observe it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
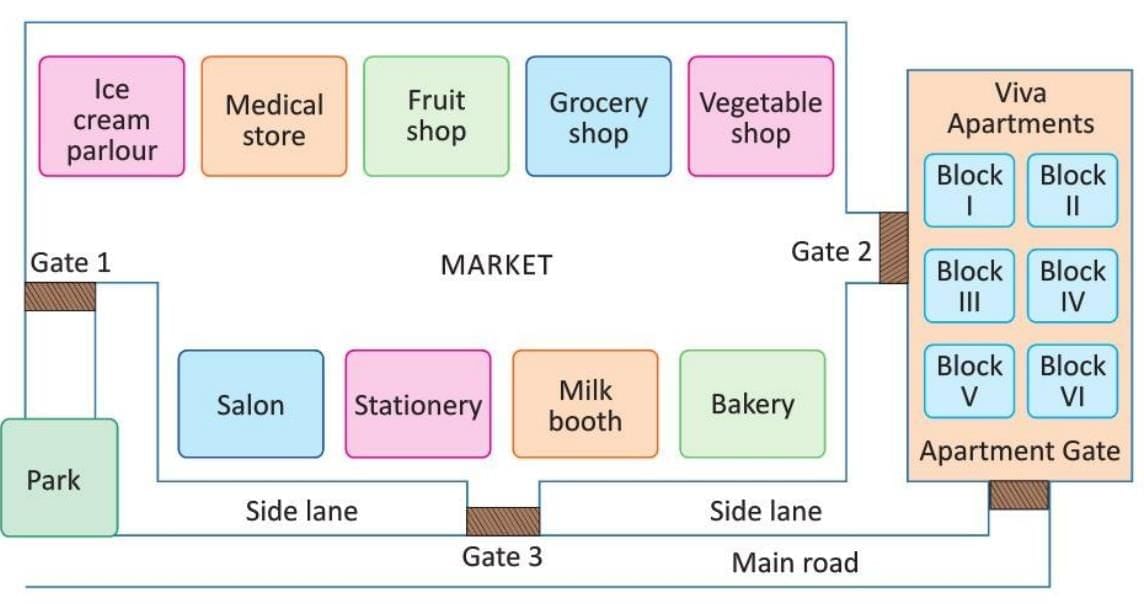
(a) Which gate will Sonia use to enter the market if she is coming from the park?
(b) If Rajat enters the market from gate 2, which shop will be to his right?
(c) When Shreya entered the market, the fruit shop was to her right. Which gate did she enter from?
(d) Which gate is the nearest to the milk booth?
(e) Which gate will one cross while going from the main road to Viva Apartments?
Solution:
(a) Gate 1
(b) Vegetable shop
(c) Gate 2
(d) Gate 3
(e) Gate 3
|
67 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Geometry and Maps Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 3 ICSE
| 1. What are the differences between straight and curved lines? |  |
| 2. How can I draw horizontal and vertical lines accurately? |  |
| 3. What are some common shapes I should know in geometry? |  |
| 4. What are solids in geometry and how are they different from shapes? |  |
| 5. How do I use a tangram to create shapes and improve spatial awareness? |  |














