Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Industries
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Industry? |

|
| Classification of Industries |

|
| Factors Affecting Location of Industries |

|
| Industrial System |

|
| Distribution of Major Industries |

|
| Jamshedpur |

|
What is Industry?
Industry refers to economic activities concerned with the production of goods, extraction of natural resources, and the provision of services.
 IndustrySecondary Activities:
IndustrySecondary Activities:
- Raw materials are transformed into more valuable products.
- Example: Pulp is made into paper, and paper is made into a notebook.
- Each stage of manufacturing adds value and utility to the product.
Classification of Industries
Industries are classified based on the type of economic activity they are involved in and the nature of the products they produce. Industries can be classified on the basis of raw materials, size and ownership.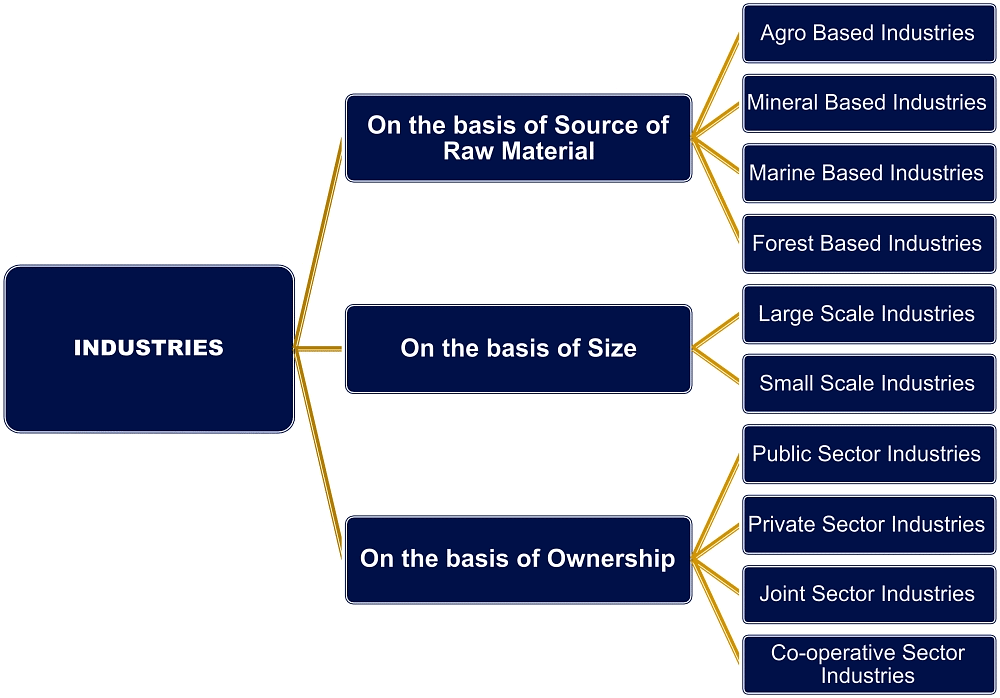 Basis of Classification of Industries
Basis of Classification of Industries
1. Classification on the Basis of Raw Materials
Industries may be agro-based, mineral-based, marine-based and forest-based depending on the type of raw materials they use.
(i) Agro-Based Industries: Agro-based industries are those that use plants and animals to make their products.
Examples of these industries include food processing, making vegetable oil, producing cotton clothes, making dairy products like milk and cheese, and creating leather products.
 Agro- Based Industries
Agro- Based Industries
(ii) Mineral-Based Industries: Mineral-based industries are important industries that use minerals from the earth as their raw materials. These industries make products that are used by other industries.
For example, iron is made from iron ore in a mineral-based industry. This iron is then used to make many other things like big machines, materials for buildings, and railway coaches.
Mineral-based industries.
(iii) Marine-Based Industries: Marine-based industries are businesses that use things from the sea and oceans to make their products.
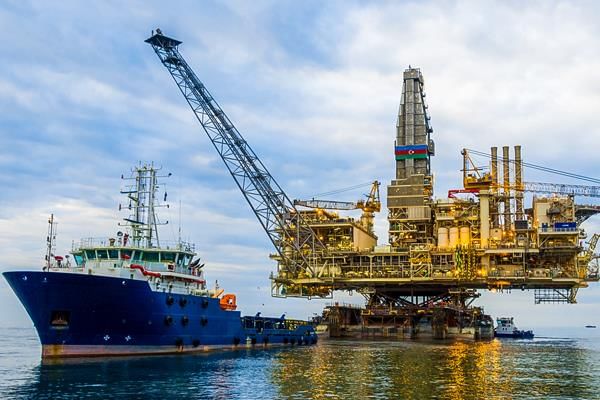 Marine-based industries.
Marine-based industries.
Examples of these industries include processing seafood or making fish oil.
(iv) Forest-Based Industries: Forest-based industries are businesses that use things from the forest to make their products.

Examples of these industries include making paper from trees, creating medicine from plants found in the forest, manufacturing furniture using wood from trees, and constructing buildings using timber from the forest.
2. Classification on the Basis of Size
Size refers to the amount of capital invested, number of people employed and the volume of production. Based on size, industries can be classified into small scale and large scale industries.
(i) Small Scale Industries: Cottage or household industries are small businesses where products are made by hand by skilled artisans. Examples of cottage industries include basket weaving, pottery, and other handmade crafts. These industries require less money and advanced technology compared to large-scale industries that make a lot of products.

(ii) Large-Scale Industries: Large-scale industries require more money to invest in capital and use advanced technology. The production of automobiles and heavy machinery is a large-scale industry.
3. Classification on the Basis of Ownership
Industries can be classified into private sector, state owned or public sector, joint sector and cooperative sector.
(i) Private Sector: Private sector industries are businesses owned and run by individuals or a group of people.
(ii) Public Sector or State-Owned Industries: Industries owned and operated by the government are Public Sector Industries. Example: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Steel Authority of India Limited.
(iii) Joint Sector: Joint sector industries are businesses that are owned and run by both the government and individuals or a group of people. An example of a joint sector industry is Maruti Udyog Limited.
(iv) Co-operative: Co-operative sector industries are businesses that are owned and run by the people who provide the raw materials or work in the industry, or sometimes both. Anand Milk Union Limited and Sudha Dairy are examples of successful cooperative ventures.
Factors Affecting Location of Industries
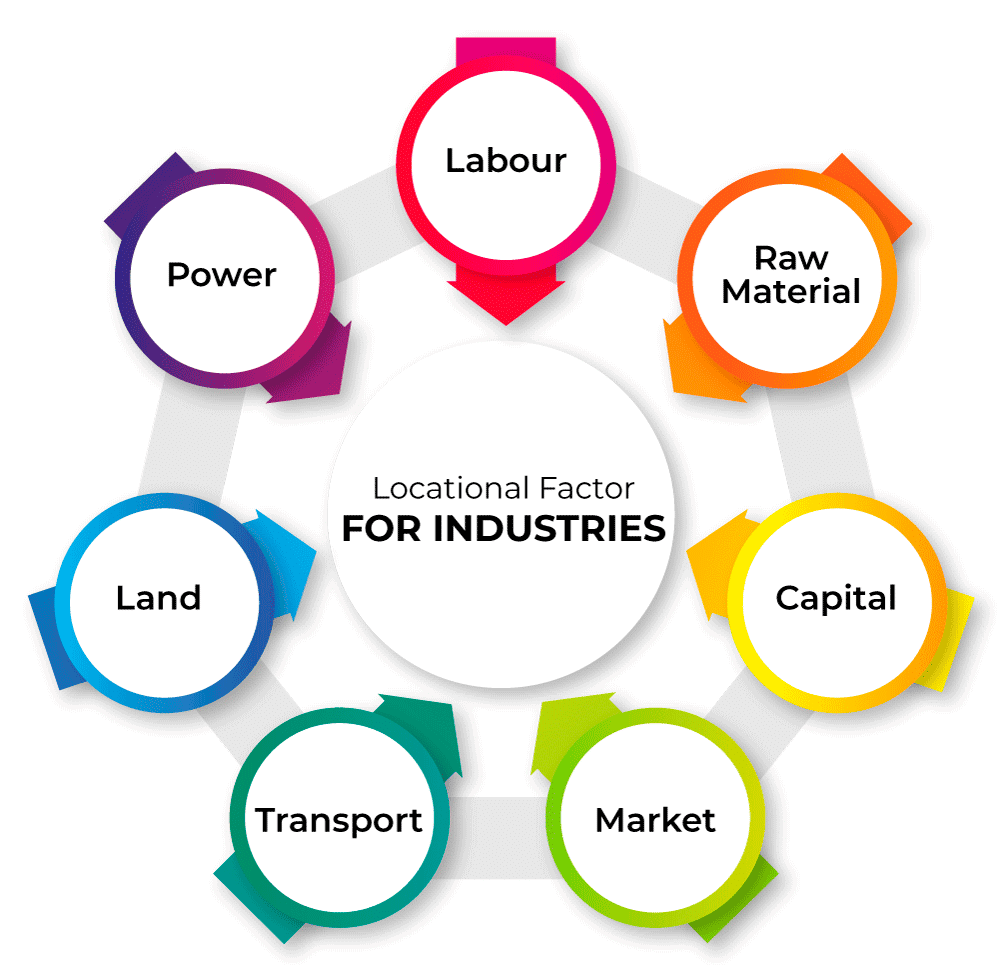
- Raw Material Availability: Industries are situated in areas where there is easy access to necessary raw materials.
- Land Accessibility: The availability of suitable land is a crucial factor influencing the location of industries.
- Water Resources: Proximity to water sources is essential for industries, especially those requiring water for production processes.
- Labor Force: Industries tend to be located where there is an ample supply of skilled and unskilled labor.
- Power Supply: Accessibility to a reliable and affordable power supply is a significant determinant in industrial location.
- Capital Availability: Regions with easy access to financial resources and capital tend to attract industries.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Well-developed transportation networks, including roads, railways, and ports, play a pivotal role in industry location.
- Market Proximity: Industries often choose locations near their target markets to reduce transportation costs and enhance market reach.
Industrial System
An industrial system involves three main parts: inputs, processes, and outputs.
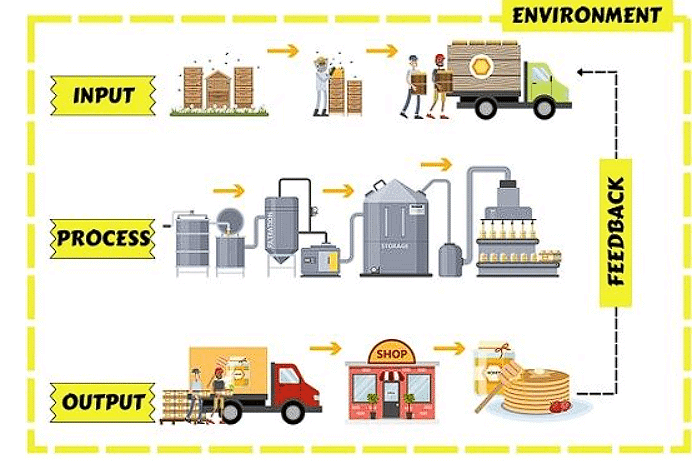
(i) Inputs in the industrial system are the materials, workers, and expenses for things like land, transportation, and power.
(ii) Processes involve various activities that transform the raw materials into finished products.
(iii) Outputs are the final products and the income generated from selling them.
For example, in the textile industry, the inputs may include cotton, workers, factories, and transportation costs. The processes involve steps like ginning (separating cotton fibers), spinning (turning fibers into yarn), weaving (creating fabric), dyeing (adding colors), and printing (adding patterns or designs).
Industrial Regions
- Industrial regions are formed when multiple industries set up near each other and share the advantages of being close.
- Some major industrial regions in the world are found in eastern North America, western and central Europe, eastern Europe, and eastern Asia.
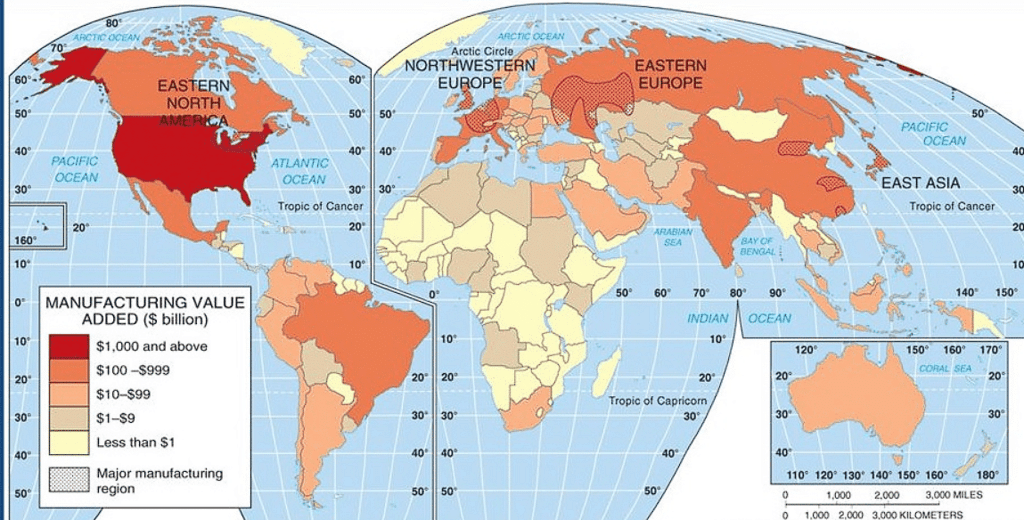
- These industrial regions are often located in temperate areas, close to seaports, and especially near coal fields.
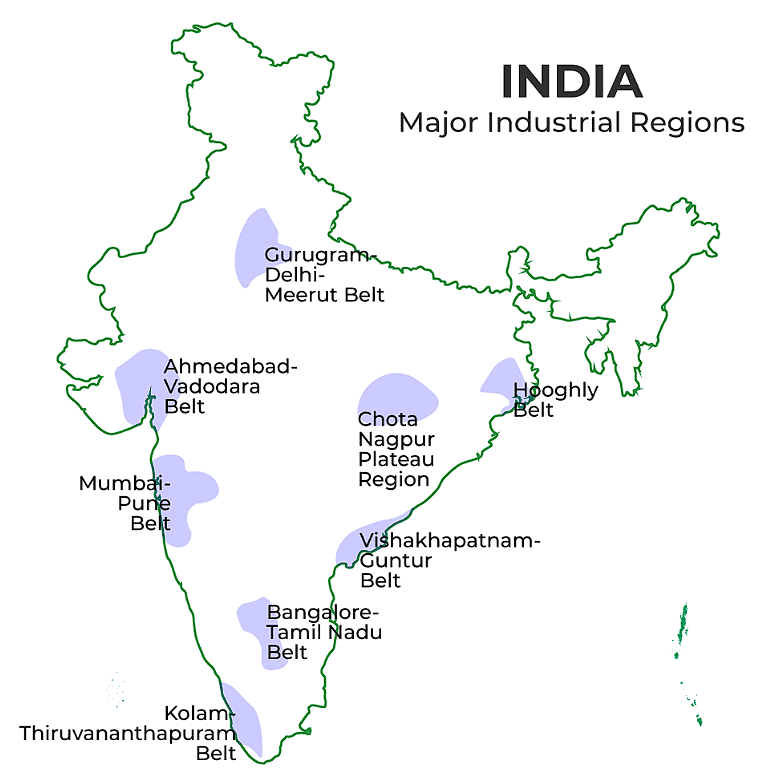
- In India, there are several industrial regions such as the Mumbai-Pune cluster, Bangalore-Tamil Nadu region, Hugli region, Ahmedabad-Baroda region, Chottanagpur industrial belt, Vishakhapatnam-Guntur belt, Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut region, and the Kollam Thiruvanathapuram industrial cluster.
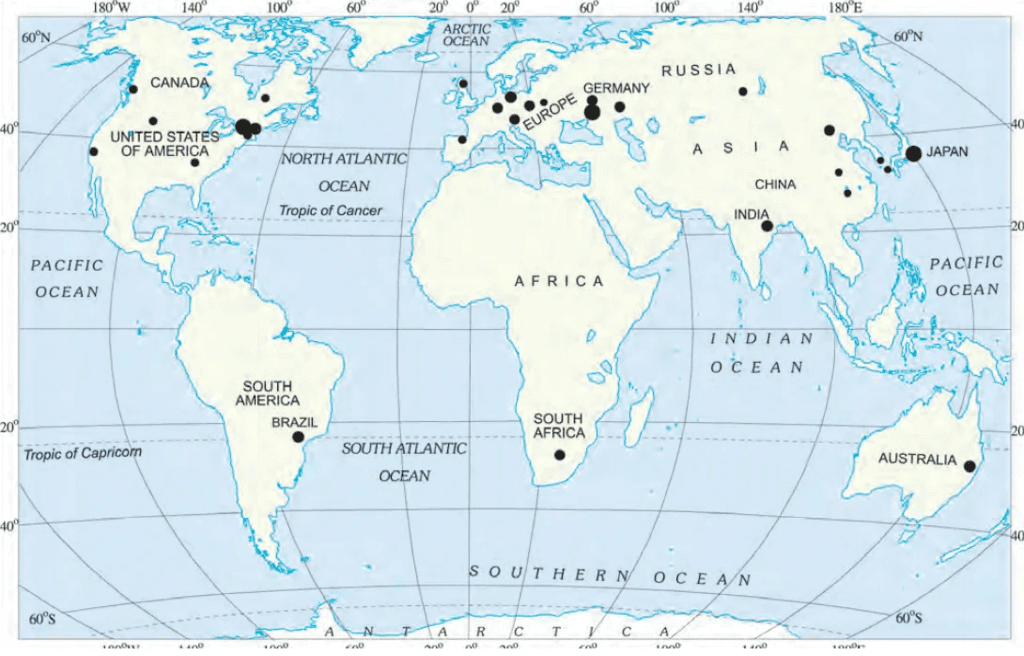
Distribution of Major Industries
- The main industries in the world are iron and steel, textiles, and information technology (IT). Iron and steel and textiles have been around for a long time, while IT is a newer industry that is growing quickly.
- The iron and steel industry is found in countries like Germany, USA, China, Japan, and Russia.
- The textile industry is concentrated in India, Hong Kong, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. The major centers in the IT industry are Silicon Valley in Central California and the Bangalore region in India.
Industrial DisasterThe occurrence of industrial accidents and disasters is often attributed to technical failures or irresponsible handling of hazardous materials.
Incident 1: One of the most severe industrial disasters took place in Bhopal on December 3, 1984, around 00:30 a.m., involving a technological mishap at the Union Carbide pesticide factory. The release of highly toxic Methyl Isocyanate (MIC) gas, along with Hydrogen Cyanide and other byproducts, resulted in an official death toll of 3,598 by 1989. Survivors continue to face various health issues such as blindness, impaired immune systems, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Incident 2: on December 23, 2005, in Gao Qiao, Chongqing, China, a gas well blowout led to 243 fatalities, 9,000 injuries, and the evacuation of 64,000 individuals. Many casualties occurred as people were unable to escape the explosion, suffering burns to their eyes, skin, and lungs from the released gas.
Risk Reduction Measures
- Spatial Planning: Densely populated residential areas should be situated at a considerable distance from industrial zones.
- Public Awareness: Individuals residing near industrial areas should be informed about the storage of toxins or hazardous substances and the potential effects in the event of an accident.
- Fire Safety: Improvements should be made to fire warning and fighting systems within industrial facilities.
- Storage Limitations: The storage capacity of toxic substances should be restricted to minimize potential hazards.
- Pollution Control: Industries should enhance pollution dispersion qualities to reduce the environmental impact of potential accidents.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Industries
|
Download as PDF |
Distribution of Major Industries
- Iron and Steel Industry: Major locations: Germany, USA, China, Japan, Russia.
- Textile Industry: Major locations: India, Hong Kong, South Korea, Japan, Taiwan.
- Information Technology Industry: Major hubs: Silicon Valley (Central California), Bangalore (India).
Iron and Steel Industry
The iron and steel industry, like other sectors, involves various inputs, processes, and outputs, serving as a key feeder industry supplying raw materials to other sectors. Inputs for this industry include iron ore, coal, limestone, labor, capital, site, and infrastructure.
The process of converting iron ore into steel involves stages such as smelting and refining in a blast furnace, ultimately producing steel, which is used as raw material by other industries.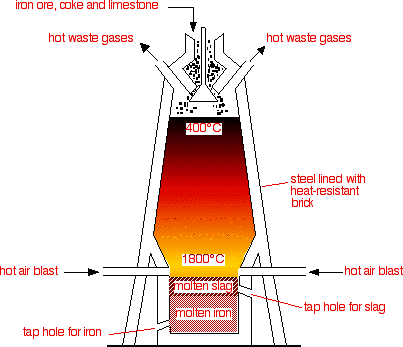 From iron ore to steel in a blast furnace
From iron ore to steel in a blast furnace
- To make steel from iron ore, there are several steps involved. First, the raw material, iron ore, is placed in a blast furnace where it is heated and melted. After that, it goes through a refining process. The final result is steel, which can be used by other industries as a raw material.
- Steel is a strong material that can be easily shaped, cut, or turned into wire. By adding small amounts of other metals like aluminium, nickel, or copper, special types of steel called alloys can be created. Alloys give steel unique properties such as extra hardness, toughness, or resistance to rust.
- Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry because it is widely used in many things we use every day. Whether it's ships, trains, trucks, cars, or even the safety pins and needles we use, they are largely made of steel. In fact, almost everything around us is either made of iron or steel or has been created using tools and machines made from these metals.
Evolution of Iron and Steel Industry
- Before 1800 A.D., the iron and steel industry was established where there was easy access to raw materials, power supply, and running water.
- Over time, the industry found a new ideal location near coal fields and close to canals and railways.
- After 1950, the industry shifted to large areas of flat land near seaports due to the growth of steel works and the need to import iron ore from overseas.
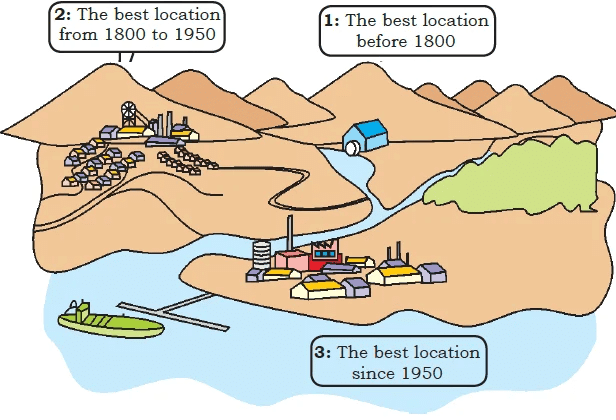 The changing location of the iron and steel industry
The changing location of the iron and steel industry
- The iron and steel industry in India has flourished by making use of raw materials, affordable labour, efficient transportation, and access to the market.
- Important steel producing centres in India include Bhilai, Durgapur, Burnpur, Jamshedpur, Rourkela, and Bokaro.
- These steel centres are situated in a region that spans four states: West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh.
- Other significant steel centres in India are Bhadravati and Vijay Nagar in Karnataka, Visakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, and Salem in Tamil Nadu.
- These centres utilise local resources to contribute to the iron and steel industry.
 World: Major Iron Ore Producing Areas
World: Major Iron Ore Producing Areas
Jamshedpur
TISCO and Government Initiatives
- Before 1947, TISCO was the only iron and steel plant in India, privately owned.
- After Independence, the government established multiple iron and steel plants.
- TISCO, founded in 1907 in Sakchi (now Jamshedpur), Jharkhand, was strategically located.
Reasons for Choosing Sakchi
- Sakchi was close to the Bengal-Nagpur railway line, just 32 km from Kalimati station.
- It had easy access to iron ore, coal, and manganese deposits.
- Proximity to Kolkata provided a large market.
- Abundant water supply from the Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers.
- Government support ensured capital for further development.
Industrial Growth in Jamshedpur
- Several other industrial plants were established in Jamshedpur after TISCO.
- Production includes chemicals, locomotive parts, agricultural equipment, machinery, tinplate, cable, and wire.
 Location of Iron & Steel Industry in JamshedpurSignificance of Iron and Steel Industry in India
Location of Iron & Steel Industry in JamshedpurSignificance of Iron and Steel Industry in India
- The development of the iron and steel industry spurred rapid industrial growth in India.
- It serves as the foundation for various sectors in the Indian industry.
- The industry comprises large integrated steel plants, mini steel mills, secondary producers, rolling mills, and ancillary industries.
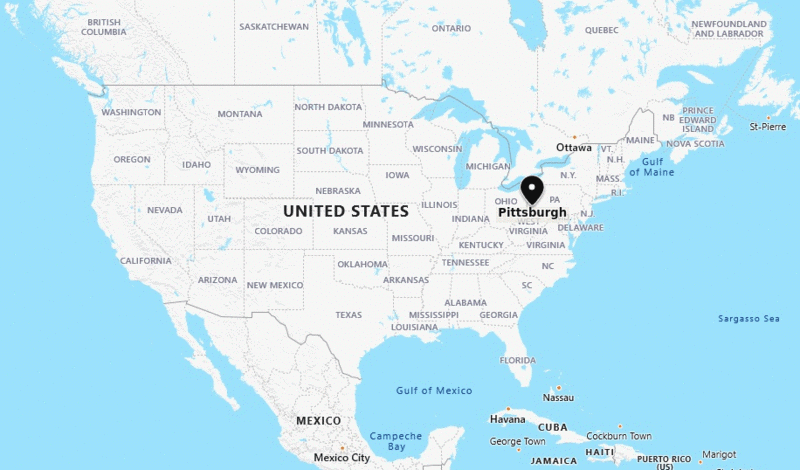
Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh is a major steel city in the United States.
 Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
Locational Advantages:
- Raw Materials:
- Coal: Locally available.
- Iron Ore: Sourced from iron mines in Minnesota, about 1500 km from Pittsburgh. - Transportation:
- Great Lakes Waterway: Provides an efficient route for shipping iron ore cheaply.
- Trains: Transport ore from the Great Lakes to Pittsburgh. - Water Supply:
- Rivers: Ohio, Monongahela, and Allegheny rivers supply water for the industry.
Current Industry Setup:
- Steel Mills:
- Most large steel mills are now located in the valleys of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, and along the Ohio River, rather than in Pittsburgh itself.
- Finished steel is transported to markets using both land and water routes. - Other Factories:
- Pittsburgh hosts various factories beyond steel mills.
- These factories use steel to produce products such as railroad equipment, heavy machinery, and rails.
|
66 videos|428 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Industries
| 1. What is industry and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How are industries classified? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the location of industries? |  |
| 4. What is an industrial system? |  |
| 5. What are some major industries in Jamshedpur? |  |























