Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 Notes - Inside Our Earth
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Earth? |

|
| Interior of the Earth |

|
| Rocks & Types of Rocks |

|
| Rock Cycle |

|
| Minerals |

|
What is Earth?
Earth is our living planet, made up of different layers that work together to support life and constantly shape the world around us.
- Dynamic Nature of Earth: Earth, our homeland, is a dynamic planet. It continuously undergoes changes both inside and outside, shaping its surface and interior.
- Composition of Earth: The Earth is composed of three main layers: the crust, mantle, and core. Each layer has distinct characteristics and plays a crucial role in the planet's structure.
Interior of the Earth
The Earth is made up of several concentric layers with one inside another, similar to an onion.
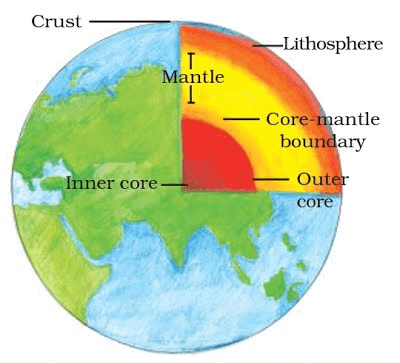
Crust:
- The outermost and thinnest layer.
- Thickness: Approximately 35 km on continental masses and 5 km on ocean floors.
- Composition:
Continental Crust: Primarily composed of silica (Si) and alumina (Al), forming a layer known as sial.
Oceanic Crust: Mainly consists of silica (Si) and magnesium (Mg), forming a layer called sima.
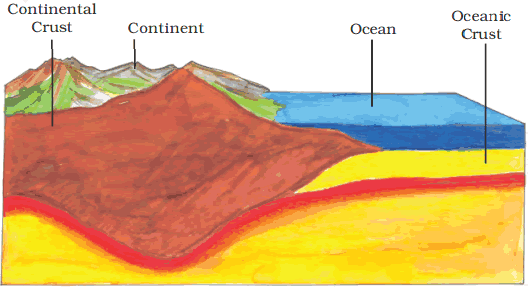 Continental crust and Oceanic crust
Continental crust and Oceanic crust
Mantle:
- Located beneath the crust, extending to a depth of about 2900 km.
- It is made of semi-solid rock that moves slowly, driving plate tectonics.
Core:
- The innermost layer of the Earth, with a radius of about 3500 km.
- Composition: Composed mainly of nickel (Ni) and iron (Fe), referred to as nife.
- Conditions: The core experiences extremely high temperatures and pressures, influencing the Earth’s magnetic field.
Rocks & Types of Rocks
Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock. It can be of different colour, size and texture.
The earth’s crust is made of various types of rocks.
Types of Rocks
There are three major types of rocks:
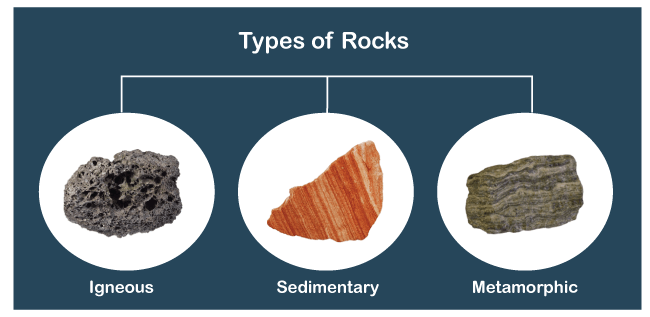
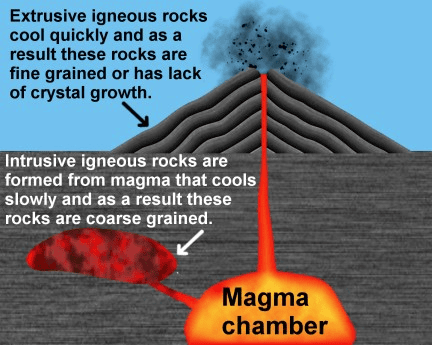
1. Igneous or Primary Rocks
When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks thus formed are called igneous or primary rocks.
They are of two types, extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rocks.
- Extrusive igneous rocks: When molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in such a way on the crust are called extrusive igneous rocks. For example, basalt. The Deccan plateau is made up of basalt rocks.
- Intrusive igneous rocks: Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are called intrusive igneous rocks. Granite is an example of such a rock. Grinding stones used to prepare paste/powder of spices and grains are made of granite.
 Types of Igneous Rocks
Types of Igneous Rocks
2. Sedimentary Rocks
- Rocks roll down and break into small fragments and these smaller particles are called sediments. These sediments are transported, compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks. These types of rocks are called sedimentary rocks.
- For example: Sandstone is made from grains of sand. These rocks may also contain fossils of plants, animals and other micro-organisms that once lived on them.
3. Metamorphic Rocks
- When the igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure they change into metamorphic rocks. The metamorphic rocks, which are still under great heat and pressure, melt down to form molten magma. This molten magma again can cool down and solidify into igneous rocks.
- For example: Clay changes into slate and limestone into marble
Rock Cycle
The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is called the rock cycle.
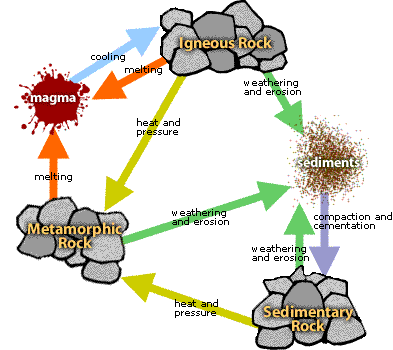 Rock Cycle
Rock Cycle
Process:
Magma Solidification: Deep inside the Earth, hot, molten rock called magma cools down and becomes solid. When this happens, it forms a type of rock known as igneous rock.
Weathering and Erosion: Over time, igneous rocks on the Earth's surface are broken down into smaller pieces by natural forces like wind, water, and temperature changes. These tiny fragments, called sediments, are carried away and eventually settle in layers to form sedimentary rocks.
Heat and Pressure: As layers of sedimentary and igneous rocks get buried deep within the Earth, they experience intense heat and pressure. This causes them to change into a new type of rock called metamorphic rock.
Melting: If metamorphic rocks are exposed to even more heat, they can melt back into magma. This molten magma can then cool and solidify once more, starting the rock cycle all over again.
Minerals
Minerals are naturally occurring substances found in the Earth that have specific physical properties and a definite chemical makeup.
Importance: Minerals play a crucial role in our lives, as they are essential for various industries and everyday activities.
Examples:
- Fuels: Minerals like coal, natural gas, and petroleum are vital energy sources.
- Industrial Use: Minerals such as iron, aluminum, gold, and uranium are used in manufacturing and construction.
- Medical Use: Some minerals are key ingredients in medicines.
- Agriculture: Minerals are important components of fertilizers, helping plants grow.
|
63 videos|356 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 Notes - Inside Our Earth
| 1. What are the different layers that make up the interior of the Earth? |  |
| 2. How do rocks and minerals play a role in shaping the Earth's surface? |  |
| 3. What is the rock cycle and how does it contribute to the Earth's geological processes? |  |
| 4. How do different types of rocks and minerals form within the Earth's interior? |  |
| 5. What are some common questions related to the topic of Inside Our Earth that students often have? |  |