Introduction to Accounting Chapter Notes | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
Accounting has evolved beyond bookkeeping to include areas like forensic accounting, e-commerce, financial planning, and environmental accounting. This shift happened because accounting offers valuable data that helps managers and others make informed decisions. As a result, accounting is now viewed as an information system that gathers and shares economic data with various users. This chapter introduces the nature, need, and scope of accounting in this new context.
Meaning of Accounting
Accounting definitions have changed as the economy and the roles of accountants have grown.
- 1941 (AICPA): In 1941, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) defined accounting as the skill of recording, classifying, and summarising financial activities in monetary terms, along with explaining the outcomes.
- 1966 (AAA): In 1966, the American Accounting Association (AAA) described accounting as a process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to assist people in making informed decisions.
- 1970 (Accounting Principles Board, AICPA): In 1970, the Accounting Principles Board of AICPA highlighted that accounting's role is to provide quantitative information, mainly financial, about economic entities, which is useful for economic decision-making.
Accounting can thus be defined as the process of identifying, measuring, recording, and communicating necessary information regarding the economic events of an organisation to those who need it.
Modern Definition of Accounting
Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, recording, and communicating information about an organisation’s economic events to those who need it. This process connects decision-makers with economic activities.
Key Aspects of Accounting
- Economic Events: Business activities that impact finances.
- Identification, Measurement, Recording, and Communication: The core steps in processing financial information.
- Organisation: The entity whose activities are being recorded.
- Interested Users of Information: Those who rely on accounting information for decision-making, such as investors, managers, and regulators.
Accounting has grown from simple record-keeping to a comprehensive tool for making well-informed economic decisions.
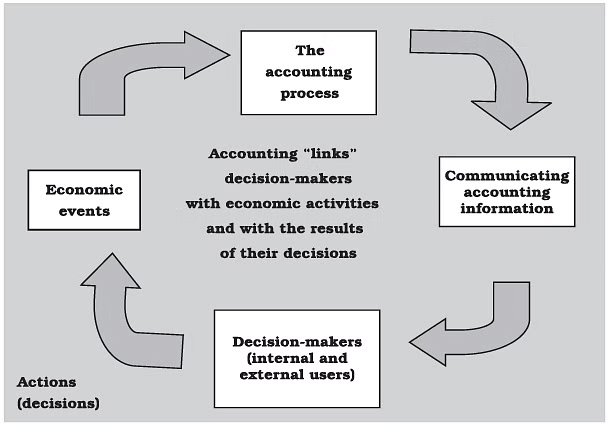
Economic Events
- Business organisations participate in many important economic events that are vital for their functioning.
- An economic event is a major incident that affects a business and involves transactions that can be counted in money.
- These events serve as the basis for accounting since they indicate the financial activities of a company.
- For example, when a company buys machinery and gets it ready for production, there are various financial transactions involved:
- The purchase price of the machine.
- Transport costs to deliver the machine.
- Expenses for preparing the site where the machine will be placed.
- Installation charges for setting up the machine.
- Costs related to trial runs before actual production starts.
- Accounting plays a key role in identifying and organising these transactions that relate to a specific economic event. Economic events can be divided into external and internal events:
- External events involve parties or entities outside the organisation.
- Internal events happen within the organisation’s own departments.
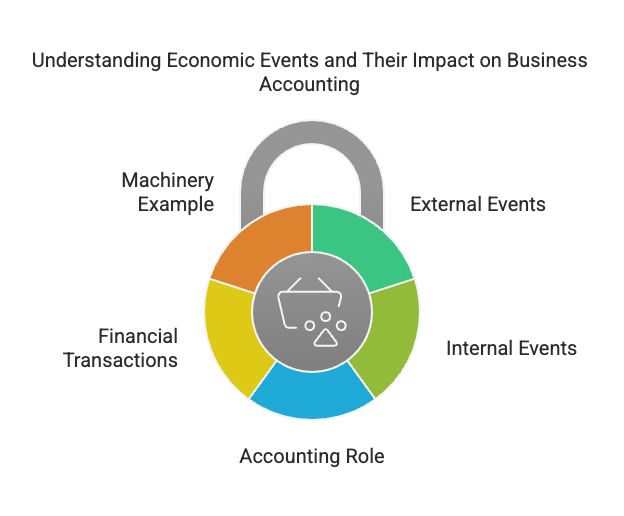
External Events
External events involve transactions between the organisation and external parties.
Examples of external events include:
- Sale of merchandise to customers.
- Rendering services to customers by ABC Limited.
- Purchasing materials from suppliers.
- Paying monthly rent to the landlord.
Internal Events
Internal events, on the other hand, occur entirely within the different departments of an enterprise.
Examples of internal events include:
- Supply of raw materials or components by the stores' department to the manufacturing department.
- Payment of wages to employees.
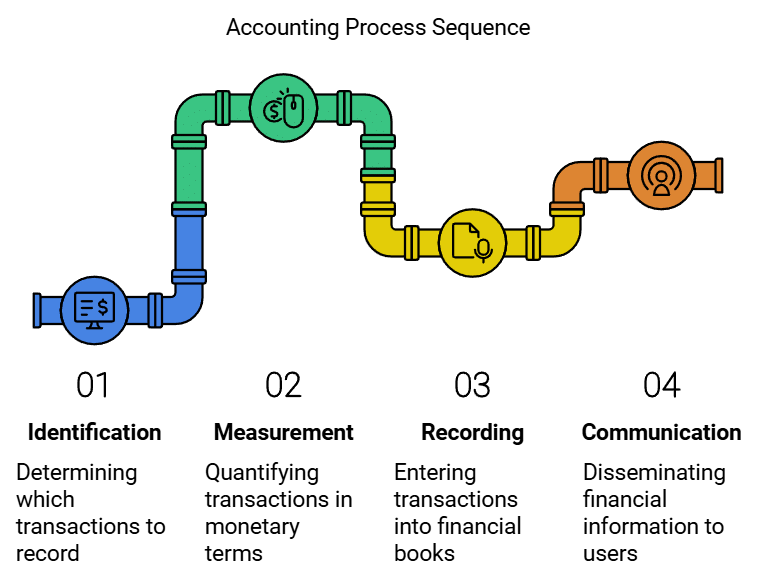
Identification, Measurement, Recording and Communication
Accounting is a methodical approach to finding, assessing, logging, and sharing financial details about an entity's economic activities. It serves as a way to convey essential financial information about businesses and is often called the language of business.
Steps of Accounting
Accounting involves several key steps to ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting.
1. Identification
- Identification in accounting refers to the process of determining which transactions and events should be recorded in an organisation's financial books.
- It involves observing various activities and selecting those that have a financial impact and are relevant to the organisation.
- Not all events are recorded; only those with financial significance are included.
- For example, while the value of human resources or changes in managerial policies are important, they are not recorded in the books.
- However, transactions like sales, purchases, and salary payments are recorded as they have a direct financial impact.
2. Measurement
- Measurement in accounting involves quantifying business transactions and events in monetary terms, using a standard unit of measurement such as rupees and paise.
- If an event cannot be expressed in monetary terms, it is not considered for recording in the financial accounts.
- This is why certain important events like the appointment of a new managing director or changes in personnel are not reflected in the books of accounts.
3. Recording
- Recording is the process of entering identified and measured economic events into the books of account in monetary terms and in chronological order.
- It involves summarising financial information according to established practices to ensure it is readily available when needed.
- The recording process is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and facilitating future reference and analysis.
4. Communication
- Communication in accounting refers to the dissemination of identified, measured, and recorded economic events to management and other internal and external users in a structured format. In simple terms, communication in accounting means sharing important financial information with people who need it—like managers, owners, or outsiders such as investors.
- This is typically done through accounting reports, which provide valuable information for assessing financial performance, planning and controlling business activities and making informed decisions.
- The accounting information system should ensure that the right information reaches the right person at the right time.
- Reports can be generated daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly based on user needs, and the accountant's ability to present relevant information effectively is crucial in this process.
Organisation
An organisation encompasses any business entity, regardless of its profit orientation.
Based on the scale of operations and the extent of activities, it could take the form of:
- sole proprietorship
- partnership
- cooperative society
- company
- local authority
- municipal corporation
- or any other collective of individuals
Interested Users of Information
- Many users require financial information to make significant decisions. These users are typically divided into two main groups: internal users and external users.
- Internal users include the Chief Executive, Financial Officer, Vice President, Business Unit Managers, Plant Managers, Store Managers, Line Supervisors, etc.
- External users encompass current and potential investors (shareholders), creditors (banks and other financial institutions, debenture-holders, and other lenders), tax authorities, regulatory agencies (Department of Company Affairs, Registrar of Companies, Securities Exchange Board of India, Labour Unions, Trade Associations, Stock Exchange), and customers.
Internal Users
These are individuals within the organisation who require financial information for decision-making purposes.
Internal users include:
- Chief Executive
- Financial Officer
- Vice President
- Business Unit Managers
- Plant Managers
- Store Managers
- Line Supervisors
External Users
These are individuals or entities outside the organisation who need financial information for various reasons.
External users include:
- Present and potential investors (shareholders)
- Creditors (banks, financial institutions, debenture-holders, and other lenders)
- Tax authorities
- Regulatory agencies (e.g., Department of Company Affairs, Registrar of Companies, Securities Exchange Board of India)
- Labour unions
- Trade associations
- Stock exchanges
- Customers
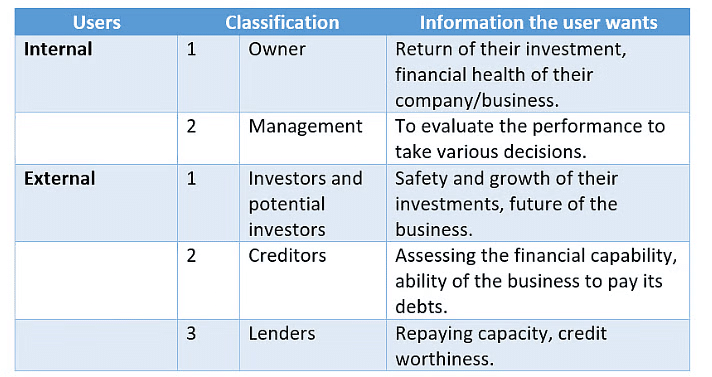
Why do the Users Want Accounting Information?
- The owners or shareholders use financial information to check if they are receiving a good return on their investment and to evaluate the overall financial health of their company. In simple words, the people who own the company (like shareholders) look at financial data to see if their money is being used well and if the business is in good financial shape.
- Directors and managers utilize this information to make comparisons, both inside the company and with other businesses. They analyze how their company performs against industry standards to identify its strengths and weaknesses. Put simply, Company leaders (directors and managers) use the same data to compare performance within different parts of the company and with other companies. They want to know if their business is doing better or worse than others.
- Management focuses on ensuring that the money invested in the company is earning a proper return and that the company can pay its debts, thus remaining solvent. In other words, the goal of management is to make sure the business is earning enough profit and has enough money to pay what it owes, so it stays financially healthy.
- Creditors, or lenders, are interested in understanding if they will be repaid. They pay special attention to liquidity, which refers to the company's ability to meet its financial obligations as they arise (whether it has enough cash or easily available funds to pay its bills on time).
- Potential investors examine this information to decide whether or not to put their money into the company.
- Government bodies and regulatory agencies, like the Registrar of Companies and customs departments, require financial details to ensure that various taxes, such as Value Added Tax (VAT) and Income Tax (IT), are paid. This is also to protect the interests of investors and creditors and to comply with legal requirements set by laws like The Companies Act 2013 and SEBI.
Accounting as a Source of Information
This chapter helps you understand accounting as a system that collects and shares important information. It also explains the different types of accounting—like financial, cost, and management accounting—and shows why each one is useful.
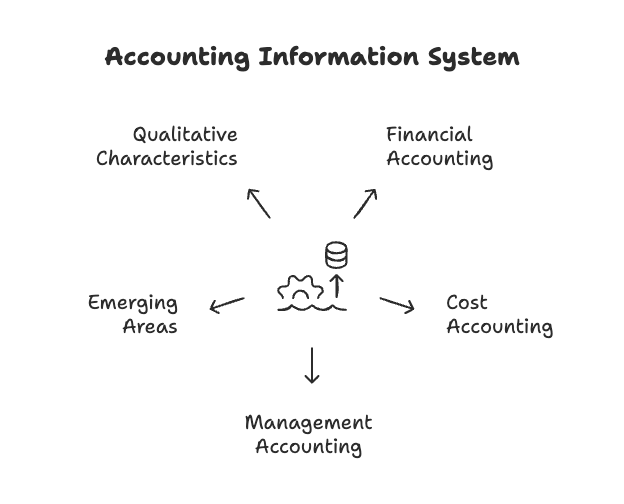
Accounting as an Information System:
- Accounting is a systematic process of interrelated activities that starts with identifying transactions and concludes with preparing financial statements. Each step in this process generates information, which is not the end goal but a means to share information with different user groups. This information helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
Dissemination of Information:
Dissemination of information is a crucial function of accounting. To be useful, accounting information should:
- Provide data for economic decision-making
- Serve users who rely on financial statements as their primary source of information
- Offer insights for predicting and evaluating potential cash flows in terms of amount, timing, and uncertainty
- Assess management’s ability to use resources to achieve goals effectively
- Disclose underlying assumptions on matters subject to interpretation, evaluation, prediction, or estimation
- Inform about activities impacting society
Role of an Accountant:
The accountant's role in generating accounting information involves:
- Observing, screening, and recognising events and transactions
- Measuring and processing these events and transactions
- Compiling reports containing accounting information for users
- The information must be relevant, adequate, and reliable for decision-making.
Users of Accounting Information:
Accounting significantly contributes to society by supplying information to management at all levels and to those with a direct financial interest in the business, such as current and potential investors and creditors. Additionally, accounting information is essential for those with an indirect financial interest, such as regulatory agencies, tax authorities, customers, labour unions, trade associations, stock exchanges, and others.
Sub-disciplines of Accounting
The differing needs of internal and external users have led to the development of sub-disciplines within accounting:
Financial Accounting:
Financial accounting involves:
- Keeping systematic records of financial transactions
- Preparing and presenting financial reports to measure organizational success and financial soundness
- Relating to past periods and serving the stewardship function
- Providing financial information to all stakeholders
Cost Accounting:
Cost accounting focuses on:
- Analyzing expenditures to determine the cost of products or services
- Fixing prices for products or services
- Controlling costs and providing costing information for decision-making
Management Accounting:
Management accounting involves:
- Providing accounting information to internal personnel for decision-making, planning, and controlling operations
- Drawing relevant information from financial and cost accounting for budgeting, profitability assessment, pricing decisions, and capital expenditure decisions
- Generating future-oriented information relevant to decision-making, such as sales forecasts, cash flows, purchase requirements, and environmental data
Emerging Areas in Accounting:
The scope of accounting has expanded to include new areas such as:
- Human Resource Accounting
- Social Accounting
- Responsibility Accounting
Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information
Qualitative characteristics refer to the attributes of accounting information that enhance its understandability and usefulness. For accounting information to be decision-useful, it must possess the characteristics of reliability, relevance, understandability, and comparability.
Reliability
- Reliability means that users must be able to depend on the information provided. The reliability of accounting information is determined by the degree of correspondence between what the information conveys about the transactions or events that have occurred, measured, and displayed. Reliable information should be free from error and bias and faithfully represent what it is meant to represent.
To ensure reliability, the information disclosed must be:
- Credible: The information should come from a trustworthy source.
- Verifiable: Independent parties should be able to verify the information using the same method of measurement.
- Neutral: The information should be presented without bias.
- Faithful: The information should accurately represent what it claims to represent.
Relevance
For information to be relevant, it must be timely, help in making predictions, provide feedback, and affect user choices by:
- Helping to form predictions about the outcomes of past, present, or future events, and/or
- Validating or adjusting earlier evaluations.
It’s not enough for financial information to be relevant and reliable at a certain time, in a specific situation, or for a particular reporting entity. It’s also crucial that users of general-purpose financial reports can compare different aspects of an entity over various periods and against other entities.
Understandability
- Understandability refers to the ability of decision-makers to interpret accounting information in the same way it is prepared and communicated to them.
- The qualities that differentiate good communication from bad in a message are crucial to its understandability. A message is considered when it is clear and easily understood.
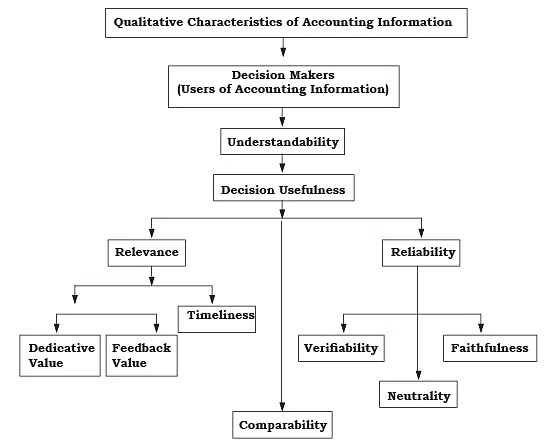 The qualitative characteristics of accounting information
The qualitative characteristics of accounting information
To communicate effectively, accounting information must be understood by the recipient in the same way it was presented by the sender. Accountants should display comparable information in the clearest way possible without losing relevance and reliability.
Comparability
- It is essential that financial information is not just relevant and reliable at a specific moment or for a particular situation.
- Simply being relevant and reliable at one time, in one circumstance, or for one reporting entity is not enough.
- Users of general-purpose financial reports must be able to compare different aspects of an entity across various time periods and with other entities.
- For accounting reports to be comparable, they need to cover the same period, employ a standard unit of measurement, and follow a similar format for reporting.
Objectives of Accounting

Accounting serves as a crucial information system with the primary goal of providing valuable information to various users, both internal and external. This information is typically presented in the form of financial statements, such as the profit and loss account and balance sheet, especially for external users. For internal management, additional information is provided as needed from the accounting records. The main objectives of accounting can be summarized as follows:
- To keep a systematic and complete record of business transactions in the books of accounts according to specified principles and rules to avoid the possibility of omissions and fraud.
- To ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred during a particular accounting period which further helps in knowing the financial performance of a business.
- To ascertain the financial position of the business by means of a financial statement i.e. balance sheet, which shows assets on one side and capital & liabilities on the other side.
- To provide useful accounting information to users like owners, investors, creditors, banks, employees and government authorities, etc., who analyze them as per their requirements.
- To provide financial information to the management, which helps in decision-making, budgeting and forecasting.
Role of Accounting
- For many years, the role of accounting has evolved alongside changes in the economy and the growing needs of society.
- Accounting involves describing and analyzing large amounts of data from a business through measurement, classification, and summarization.
- This process condenses the data into reports and statements that reveal the financial health and performance of the business.
- Because of this function, accounting is often referred to as the language of business.
- Additionally, accounting provides a service by delivering numerical financial information that assists users in various ways.
- As a system for information, accounting gathers and shares economic data about a business with a wide range of interested parties.
- However, it is important to note that accounting information is focused on past transactions and is inherently quantitative and financial.
- It does not include qualitative or non-financial information.
- These limitations of accounting should be considered when using the information provided.
Different Roles of Accounting:
- As a language - it is seen as the main way to discuss business, used for sharing information about companies.
- As a historical record - it serves as a timeline that shows all the financial transactions of a business, using the actual amounts that were involved.
- As current economic reality - it helps to identify the true income of a business, showing how wealth changes over time.
- As an information system - it acts as a link between the source of information (the accountant) and the users who need that information (external users) through a communication method.
- As a commodity - specialized information is treated as a valuable service that people want, with accountants ready and able to provide it.
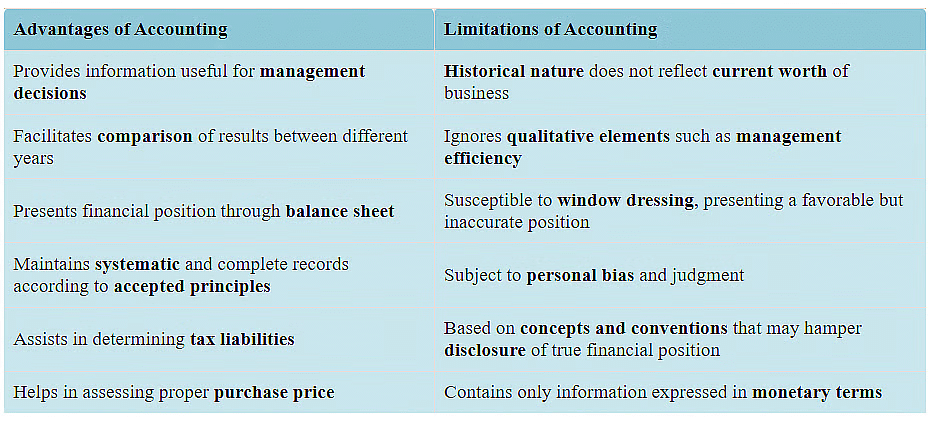
Advantages and Limitations of Accounting
Basic Terms in Accounting
Entity
- An entity refers to something that exists distinctly on its own.
- A business entity is a specific business organization, such as Super Bazaar, Hire Jewellers, or ITC Limited.
- An accounting system is designed for a particular business entity, which is also known as an accounting entity.
Transaction
- This term describes an event involving value exchanged between two or more entities.
- Examples of transactions include:
- purchasing goods
- receiving money
- making payments to creditors
- incurring expenses
- Transactions can be categorized as either cash transactions or credit transactions.
Assets
- Assets are resources owned by a business that can be expressed in monetary terms.
- They represent items of value that the business uses in its operations.
- For instance, Super Bazaar has a fleet of trucks that are employed for delivering food products. These trucks provide economic benefits to the company. Such items are recorded on the asset side of Super Bazaar's balance sheet.
- Assets can be divided into two main categories: current assets and non-current assets.
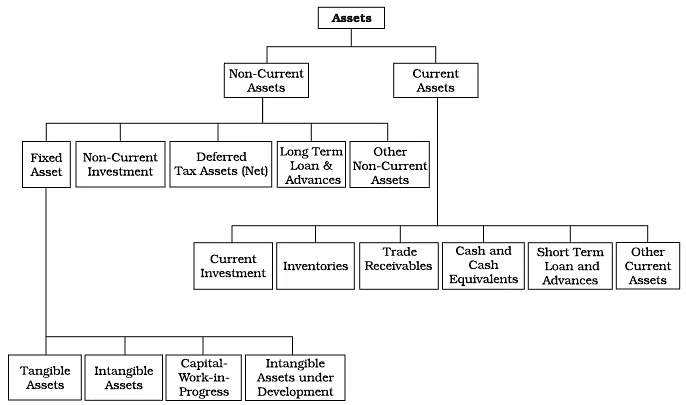 Classification of Assets
Classification of Assets
Liabilities
- Liabilities are debts or obligations that a business must repay in the future.
- They show what creditors claim on the company's assets.
- Both small and large businesses often need to borrow money or buy goods on credit.
- For instance, on March 25, 2005, Super Bazar bought goods worth ₹10,000 on credit from Fast Food Products. When Super Bazar prepares its balance sheet on March 31, 2005, Fast Food Products will be listed as a creditor under liabilities. If Super Bazar also takes out a loan for three years from Delhi State Co-operative Bank, this loan will also appear as a liability on its balance sheet.
- Liabilities are categorized into current and non-current types.
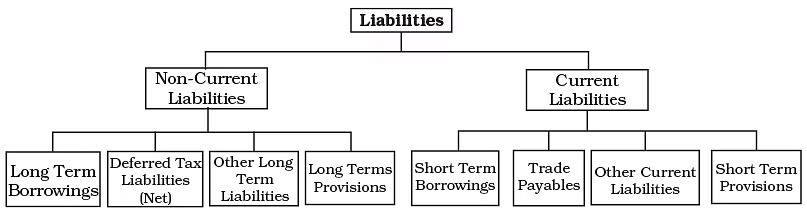 Classification of Liabilities
Classification of Liabilities
Capital
- The money that the owner invests in the business is called capital.
- This investment can be made in cash or assets.
- Capital is considered a claim on the business's assets.
- Because of this, it appears on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Sales
- Sales represent the total income generated from selling goods or services to customers.
- Sales can be categorized into two types: cash sales and credit sales.
Revenues
- Revenues are the amounts earned by a business through sales of products or services.
- This is known as sales revenue.
- Other common sources of revenue include:
- Commissions
- Interest
- Dividends
- Royalties
- Rent received
- Revenue is also referred to as income.
Expenses
- Expenses are the costs a business incurs to earn revenue.
- They are usually measured by the value of assets used or services consumed during a specific time period.
- Common expense items include:
- Depreciation
- Rent
- Wages
- Salaries
- Interest
- Costs for utilities like heating, lighting, and water
- Telephone expenses
Expenditure
- Expenditure refers to spending money ortaking on a liability for a benefit, service, or property received.
- Examples of expenditure include purchases of:
1. Goods
2. Machinery
3. Furniture - If the benefit lasts less than a year, it is considered an expense (or revenue expenditure).
- If the benefit lasts over a year, it is considered an asset (or capital expenditure), like machinery or furniture.
Profit
- Profit is the amount by which revenues exceed expenses during a specific accounting period.
- Profit increases the owner's investment in the business.
Gain
- A gain is a profit that comes from events or transactions that are not part of regular business operations.
- Examples include selling fixed assets, winning legal cases, or the increase in asset value.
Loss
- A loss happens when expenses exceed revenues during a period.
- A loss decreases the owner's equity in the business.
- It can also mean losing money or value without getting anything in return, such as cash or goods lost through theft or fire.
- This includes losses from selling fixed assets.
Discount
- A discount is a reduction in the selling price of goods.
- There are two main types of discounts:
1. Trade discount: This is a percentage off the list price given at the time of sale. It's usually provided by manufacturers to wholesalers and by wholesalers to retailers.
2. Cash discount: This is a reduction in the amount owed if the buyer pays within a certain time frame. It encourages buyers to pay their bills promptly.
Voucher
- A voucher is proof of a transaction.
- Examples include:
1. A cash memo when goods are bought with cash.
2. An invoice for credit purchases.
3. A receipt when a payment is made.
Goods
- Goods are the products a business buys and sells.
- Items bought for business use are not classified as goods.
- For example:
1. A furniture dealer considers chairs and tables as goods.
2. A stationery merchant sees stationery as goods, while for others, it's an expense.
Drawings
- Drawings refer to money or goods taken out of the business by the owner for personal use.
- This action reduces the owner's investment in the business.
Purchases
- Purchases are the total amount of goods bought by a business, whether on credit or cash, for use or resale.
- In a trading business, purchases are made for resale.
- In a manufacturing business, raw materials are bought, processed into finished goods, and then sold.
- Purchases can be categorized as cash purchases or credit purchases.
Stock
- Stock (or inventory) includes goods, spare parts, and other items a business has on hand.
- It is referred to as stock on hand.
- In a trading business, closing stock is the amount of unsold goods at the end of an accounting period.
- In a manufacturing company, closing stock includes raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished goods.
- Opening stock is the amount at the beginning of the accounting period.
Debtors
- Debtors are individuals or entities that owe money to a business for goods or services purchased on credit.
- The total amount owed by debtors is shown on the balance sheet as sundry debtors on the asset side.
Creditors
- Creditors are individuals or entities that a business owes money to for goods or services received on credit.
- The total amount payable to creditors is listed on the balance sheet as sundry creditors on the liabilities side.
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Accounting Chapter Notes - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main objectives of accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of accounting? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between bookkeeping and accounting? |  |
| 4. How does the accounting equation relate to financial statements? |  |
| 5. What are some basic accounting terms one should know? |  |

















