Some plant leaves look red, violet, or brown because they have more colored pigments than green chlorophyll, which hides the green color. Some of these pigments also assist in photosynthesis. You can perform an iodine test on such leaves to detect starch, which shows that photosynthesis has occurred.
Life Processes in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 10 Free PDF
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How Do Plants Grow? |

|
| How Do Plants Get Food for Their Growth? |

|
| How Do Leaves Exchange Gases During Photosynthesis? |

|
| Terms to Remember |

|
Introduction
All living beings grow and need food for their growth. While animals eat food to grow, what about plants? Have you ever seen plants eating like animals? As animals grow, their size and weight increase, and their bodies change. What changes do you notice in plants as they grow? Food provides nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, along with water, all essential for growth.
Food provides nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, along with water, all essential for growth.
Let’s explore how plants obtain these nutrients for their growth.
How Do Plants Grow?
Plant growth involves visible changes such as the emergence of new leaves and branches, increased height, and a thicker stem.
These changes occur as plants obtain essential resources like water, sunlight, and nutrients from their environment.
Role of Sunlight and Water
- Sunlight provides energy for food production, while water is crucial for nutrient transport and maintaining plant structure.
- Plants grown with both sunlight and water show better growth, with more leaves, greater height, and vibrant green leaves, compared to those lacking either resource.

- For instance, a plant without water may wilt or die, and one without sunlight may have pale or yellow leaves due to reduced food production.

Fascinating Fact
The ancient Indian text Vrikshayurveda states, “Trees do not produce fruits and flowers merely because they are planted.”
This text contains valuable observations about plant growth, soil, and farming methods to improve crop health and yield.
Based on practical experience and long-term patterns, it systematically guides agricultural practices.
For example, it describes ways to prepare organic manure using water, barley, and seeds like green gram, black gram, and horse gram.
How Do Plants Get Food for Their Growth?
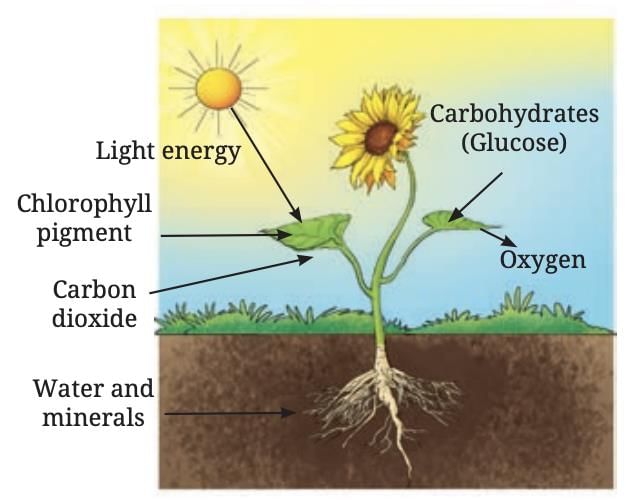
Unlike animals, plants produce their own food through a process called photosynthesis, primarily in their leaves. This food, stored as starch (a carbohydrate), provides energy and building blocks for growth.
Leaves: The 'Food Factories' of Plants
Leaves are the primary sites for food production due to their broad, flat structure and the presence of chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures sunlight. Chlorophyll enables leaves to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food.
Starch Production
- Leaves store food as starch, a carbohydrate.
- The presence of starch can be confirmed by an iodine test, where a leaf turns blue-black if starch is present.
- This indicates that the leaf has produced food.
Dive Deeper
Decolourisation of a leaf in the beginning of testing enables us to easily observe colour change and, thus, the presence of starch.
Fascinating Facts
Chlorophyll
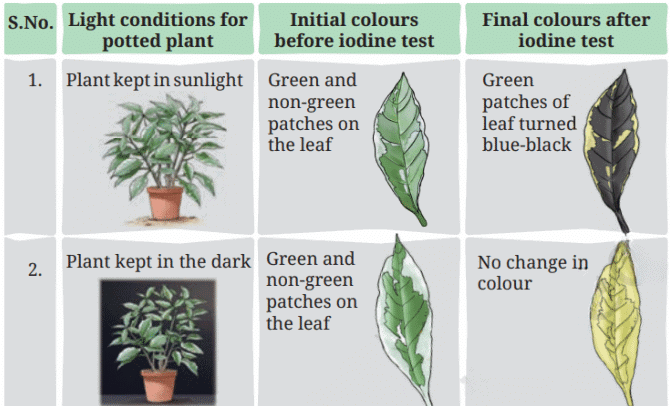
Leaves have green and non-green patches due to the presence or absence of chlorophyll.
Starch is produced only in the green parts of the leaf where chlorophyll is present.
Non-green patches usually lack sufficient chlorophyll and do not produce detectable starch.
The presence of starch can be confirmed by performing an iodine test, where starch turns blue-black.
Leaves exposed to sunlight produce starch, while leaves kept in darkness do not, even if they have green patches.
This shows that chlorophyll, in the presence of sunlight, is essential for the preparation of starch in plants.
Because leaves produce food through this process, they are often called the “food factories” of plants.
Role of Air in Food Preparation
Air, specifically carbon dioxide, is a key component in photosynthesis. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air to produce food.
Carbon Dioxide Requirement
Carbon dioxide from the air is essential for plants to prepare food (starch).
When a leaf is kept in an environment without carbon dioxide, starch is not produced in that part.
This shows that carbon dioxide is a key ingredient required for photosynthesis.
Oxygen Release During Photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, plants release oxygen gas.
Oxygen production is evident when plants are exposed to sunlight, and bubbles of oxygen can be observed.
The release of oxygen confirms that photosynthesis happens only in the presence of sunlight.
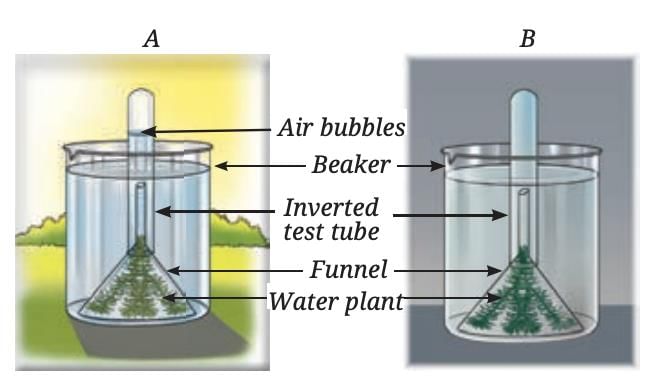 Activity showing the release of oxygen during photosynthesis
Activity showing the release of oxygen during photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: In a Nutshell
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (a simple carbohydrate) and oxygen.
- Glucose serves as an immediate energy source and can be converted into starch for storage.
- The word equation for photosynthesis is:
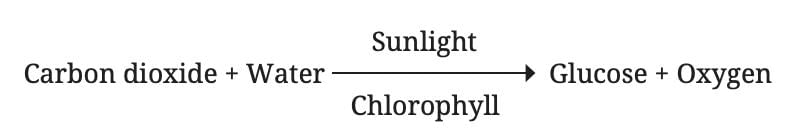
- Oxygen is released as a by-product, which is vital for the survival of other living beings.
- Photosynthesis occurs mainly in leaves but also in other green parts of the plant containing chlorophyll.
Know A Scientist: Rustom Hormusji Dastur
Many scientists worldwide have contributed to understanding photosynthesis. In India, Rustom Hormusji Dastur (1896–1961) was a notable plant scientist who studied this process. He served as the head of the Botany Department at the Royal Institute of Science, Bombay (now the Institute of Science, Mumbai) from 1921 to 1935. Dastur researched how factors like water availability, temperature, and light color affect photosynthesis, highlighting their importance in the process.
How Do Leaves Exchange Gases During Photosynthesis?
Leaves have tiny pores called stomata on their surface, which facilitate the exchange of gases during photosynthesis and respiration.
- These pores allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and oxygen to exit as a by-product.
- Stomata also play a role in respiration by allowing oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release.
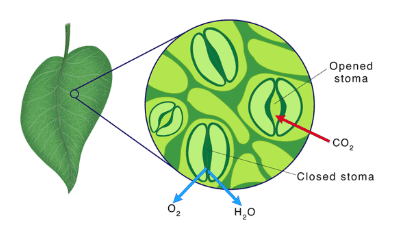 Stomata
Stomata
Transport in Plants
Plants have a transport system to move water, minerals, and food to different parts, ensuring growth and survival.
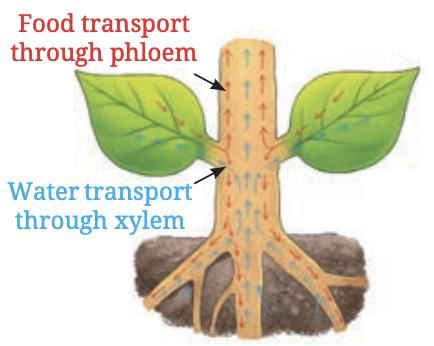
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are transported to other parts of the plant through specialized tissues called Xylem.
All living beings need water to grow, and plants use water for photosynthesis.
Water and minerals from the soil are absorbed by the roots of plants.
Minerals are essential nutrients for plant growth.
Water and minerals travel from the roots to other parts of the plant through a tissue called xylem.
The xylem consists of thin tube-like structures in stems, branches, and leaves that carry water and dissolved minerals upward.
The movement of water and minerals can be demonstrated by placing plant twigs in colored water, where the color travels up the stem and into leaves and flowers.
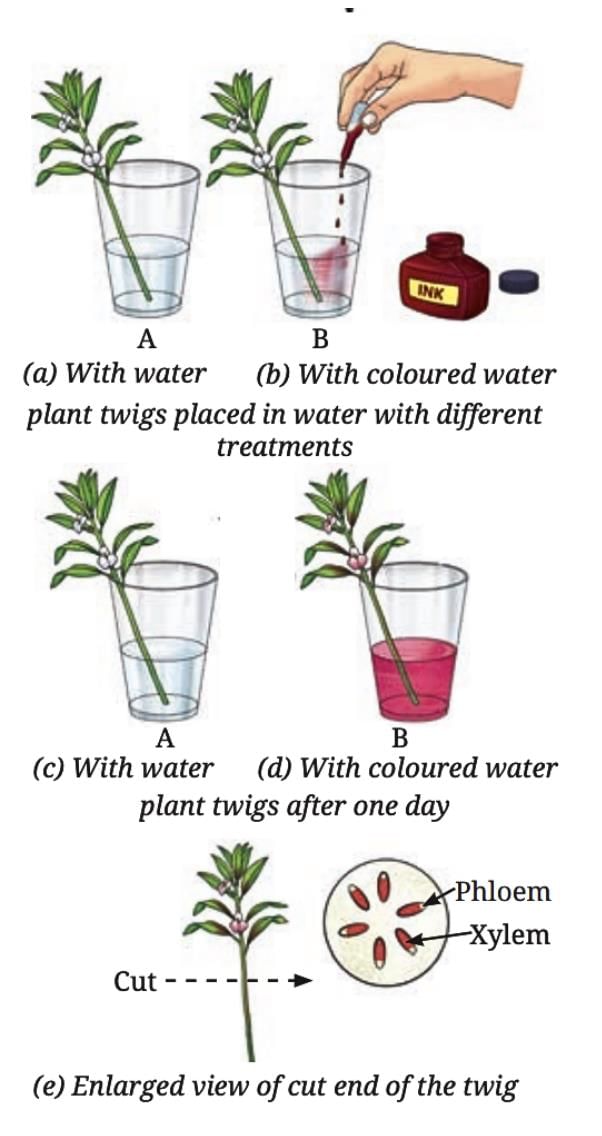
Water transported through the xylem supports various functions in the plant.
Transport of Food
Food produced in the leaves (glucose or starch) is distributed to non-green parts of the plant, such as roots, stems, and fruits, for growth and storage, through specialized tissue called phloem
- Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis, where food is prepared.
- The phloem is vascular tissue that transports food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- This ensures that areas not involved in photosynthesis, like roots and developing fruits, receive the energy and nutrients they need.
- Some of this transported food is stored in other parts of the plant, such as seeds and roots.
Do Plants Respire?
Plants, like animals, respire to produce energy for growth and other functions. Respiration occurs in all parts of the plant, whether green or non-green.
During respiration, plants break down glucose using oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The word equation for respiration is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + EnergyThe energy released supports processes like growth, cell repair, and nutrient transport.
An experiment with soaked moong bean seeds shows that carbon dioxide is released during respiration, which turns lime water milky.
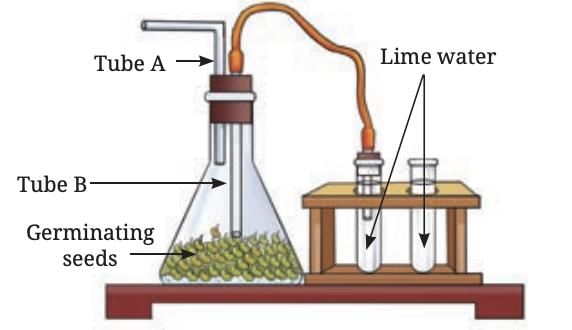
This carbon dioxide comes from the seeds respiring inside the flask.
The energy produced in respiration is used by plants for growth and development.
All parts of the plant, whether green or non-green, carry out respiration.
Plants have distinct processes for synthesizing food (photosynthesis), transporting food, and using it to produce energy (respiration).
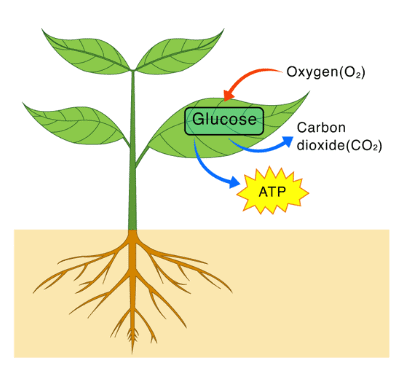 Respiration in Plants
Respiration in Plants
Terms to Remember
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants use sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll: A green pigment in leaves that captures sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Stomata: Tiny pores on leaf surfaces that allow gas exchange (carbon dioxide in, oxygen out) during photosynthesis and respiration.
- Xylem: Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem: Vascular tissue that transports food (glucose or starch) from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Respiration: The process by which plants break down glucose using oxygen to release energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Glucose: A simple carbohydrate produced during photosynthesis, used as an energy source or stored as starch.
- Starch: A carbohydrate stored in plants, produced from glucose during photosynthesis.
FAQs on Life Processes in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 10 Free PDF
| 1. What are the main stages of plant growth? |  |
| 2. How do plants make their own food? |  |
| 3. What role do roots play in a plant's growth? |  |
| 4. How do plants transport water and nutrients? |  |
| 5. What are some important terms related to plant life processes? |  |