Introduction
Keshav visits his friend Jatin’s village in the Western Ghats and is amazed by the forests, streams, and especially the glowing dance of fireflies at night.
He learns from Jatin’s grandparents that fireflies use light to communicate, but their numbers are falling due to light pollution and deforestation.
On the way back to the city, Keshav watches the moonlit hills and wonders — does the Moon produce its own light?
Or is it just reflected sunlight, like he read in his science book? As he thinks, he notices something interesting: light always travels in a straight line.
Sources of Light
Light enables us to see objects and is produced by various sources, both natural and artificial.
Natural Sources of Light
These include the Sun, stars, fire, lightning, and certain animals (like fireflies) that emit their own light.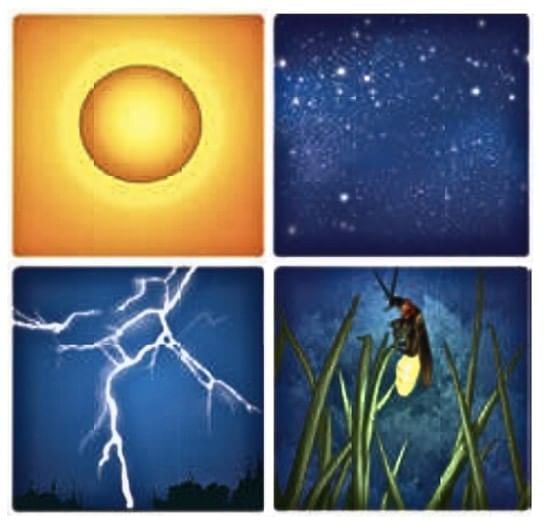 
Artificial Sources of Light
Humans have developed several artificial sources over time, beginning with fire created using fuels like oil and wax.
With technological advancement, electric lights such as bulbs, tube lights, and LED lamps have become common.
Luminous Objects
- These are objects that emit their own light.
- Examples include the Sun (the primary natural light source), stars, lightning, natural fire, and certain animals like fireflies.
Non-Luminous Objects
- These objects do not produce their own light but reflect light from luminous sources. The Moon is a non-luminous object that shines by reflecting sunlight.
- Other examples include planets like Mars and Venus, and everyday objects like mirrors.
Science and Society
LED lamps are energy-efficient, brighter, and longer-lasting than traditional bulbs. They help reduce electricity bills and are environmentally friendly. Recognizing these benefits, the Indian government actively promotes their use. However, used LED lamps must be properly recycled and not discarded in regular waste.
Question for Chapter Notes: Light: Shadows and Reflections
Try yourself:
What do fireflies use light for?Explanation
Fireflies use light to communicate.Just like how we use words to talk to our friends, fireflies use their glow to send messages to each other. This fascinating behavior helps them connect with one another, especially at night when they light up the dark.
Report a problem
Does Light Travel in a Straight Line?
Light travels in a straight line under normal conditions, a property known as rectilinear propagation.
When light passes through aligned holes in a straight line, it creates a bright spot on a screen.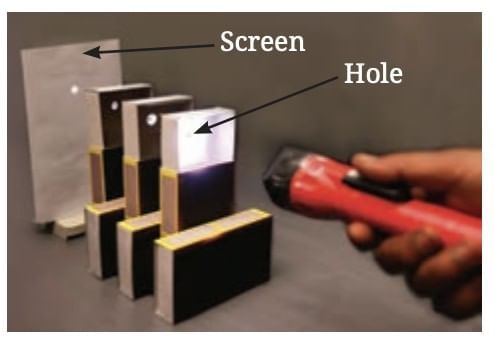
If the holes are misaligned, no spot appears, indicating that light does not bend around obstacles.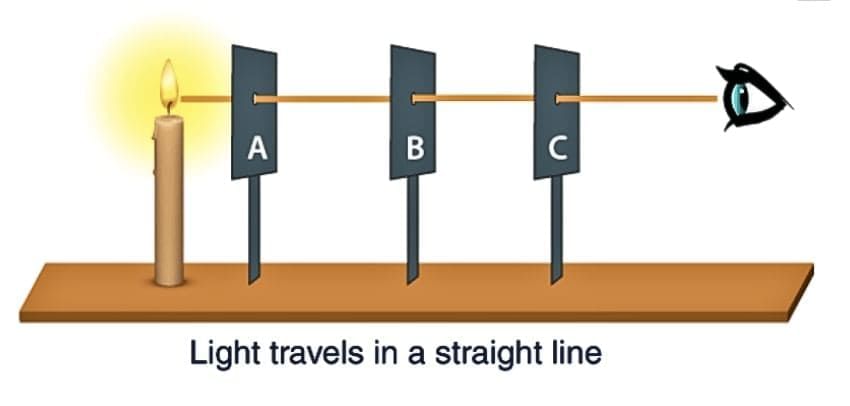
Similarly, a candle flame is visible through a straight pipe but not a bent one, confirming that light follows a straight path.
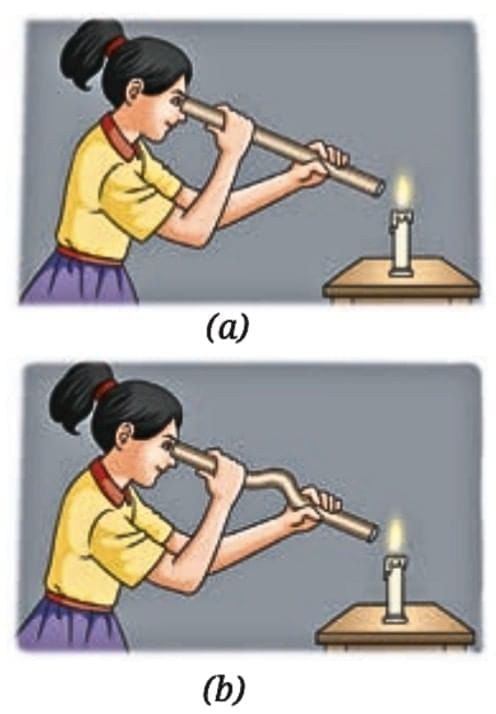 Viewing candle flame through (a) a straight pipe (b) a bent pipe
Viewing candle flame through (a) a straight pipe (b) a bent pipe
Dive Deeper
Light generally travels in a straight line. This can be seen clearly when a laser beam passes through a medium like water. However, under special conditions, light can also bend — a fascinating concept you’ll explore in higher grades.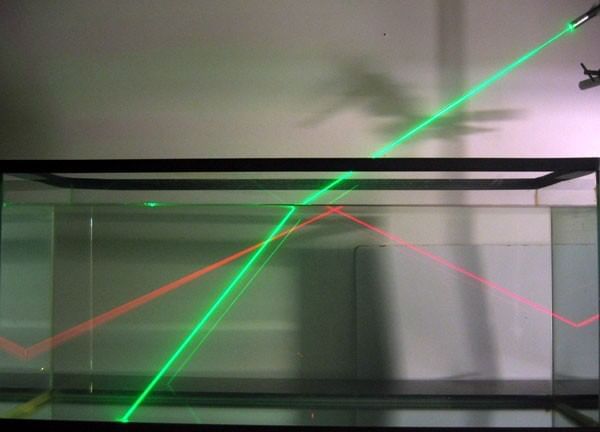
Caution: Lasers should always be used under teacher supervision. Only low-power laser pointers are safe for basic use. Never point a laser at anyone’s eyes — it can cause serious injury.
Light Through Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Materials
When light encounters different materials, its behavior depends on the material’s properties.
Transparent Materials
- These allow light to pass through almost completely, enabling clear visibility of objects on the other side.
- Examples include glass and clear plastic.

Translucent Materials
- These allow light to pass through partially, causing diffused or blurred visibility.
- Examples include tracing paper and frosted glass.

Opaque Materials
- These block light completely, preventing any light from passing through.
- Examples include cardboard and thick cloth.

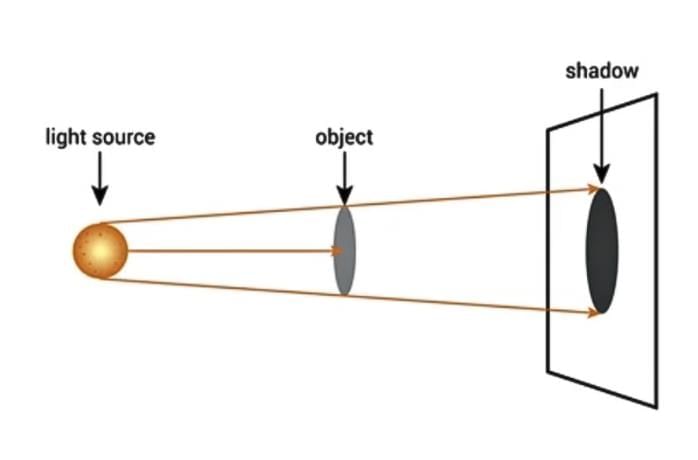
A shadow is a dark region formed when an object blocks light from reaching a surface.
Conditions for Shadow Formation
Shadows require three components:
- A light source (e.g., Sun or torch),
- An opaque or partially opaque object to block the light,
- A screen (e.g., wall, floor, or ground) where the shadow appears.
Types of Shadows
- Opaque objects create the darkest, most defined shadows.
- Translucent objects produce lighter, less distinct shadows.
- Transparent objects may create faint shadows or none at all.
Shadow Characteristics and Observations
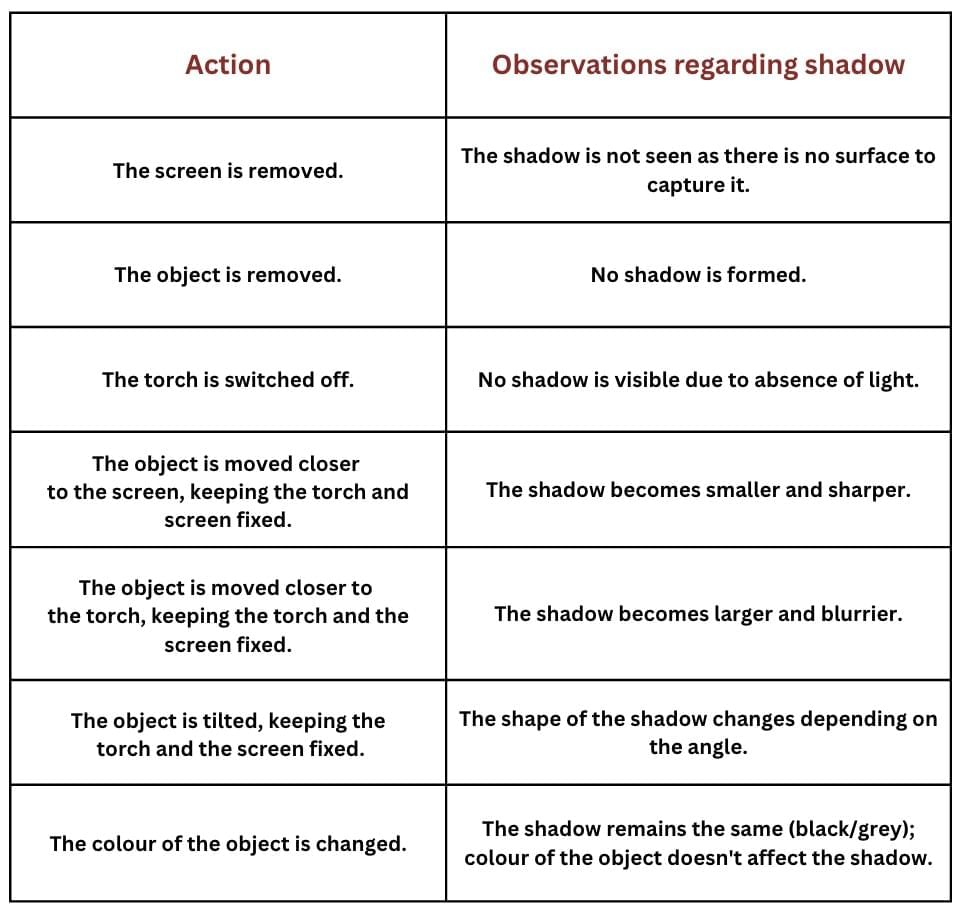
From the above observations we can conclude:
- Shadows are formed when an opaque object blocks light from reaching a surface, which acts as a screen.
- To observe a shadow, we need a light source, an opaque object, and a screen.
- The size, shape, and clarity of the shadow depend on the positions of the object, light source, and screen.
- Changing the colour of the object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
- Shadows help us understand the presence and shape of objects but do not reveal their colour.
Fascinating Facts
Shadow play, or shadow puppetry, is an ancient art where flat cut-out puppets are placed between a light source and a screen to create lifelike movements.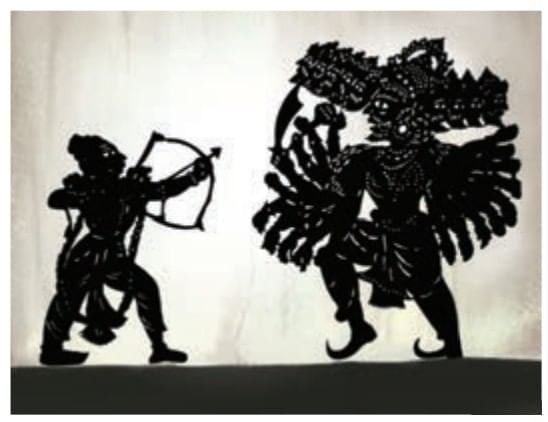 
Different Indian regions have unique styles like Charma Bahuli Natya (Maharashtra), Keelu Bomme and Tholu Bommalata (Andhra Pradesh), Togalu Gombeyaata (Karnataka), Ravana Chhaya (Odisha), Tholpavakoothu (Kerala), and Bommalattam (Tamil Nadu).
These performances entertain and convey important community messages.
Question for Chapter Notes: Light: Shadows and Reflections
Try yourself:
What type of materials allows light to pass through almost completely?Explanation
Transparent MaterialsThese materials allow light to pass through almost completely, enabling clear visibility of objects on the other side. Examples include:
Report a problem
Reflection of Light
Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, changing its direction.
Reflection by Shiny Surface
- Shiny surfaces, such as polished steel plates or plane mirrors, reflect light efficiently, creating bright spots on nearby surfaces.
- For example, tilting a mirror can direct sunlight onto walls not directly lit.
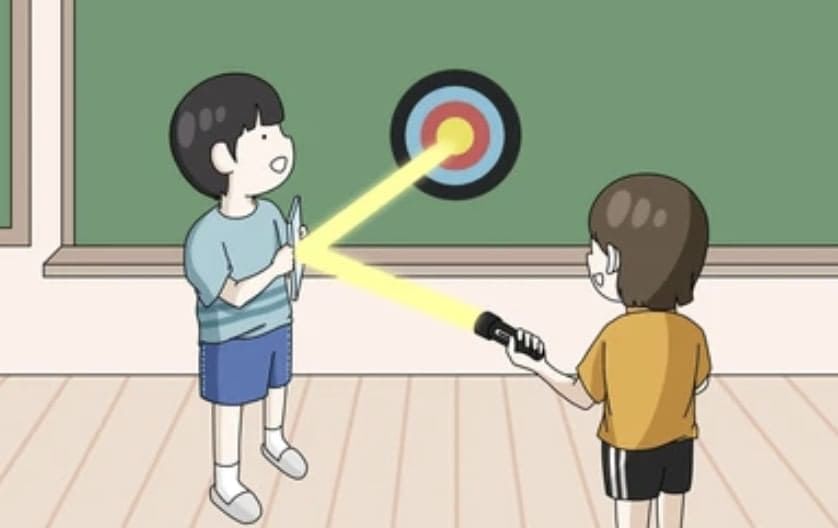

- When a light beam hits a plane mirror, it changes direction as a reflected beam, which is why mirrors are used to redirect light in many applications.
A plane mirror is a flat mirror that forms a virtual image of an object placed in front of it.
Image Characteristics
- Same Size: The image is the same size as the object.
- Erect: The image is upright, with the top of the object appearing at the top.
- Laterally Inverted: The left side of the object appears as the right side in the image, and vice versa
For example: raising your left arm makes the image raise its right arm). This is called lateral inversion.)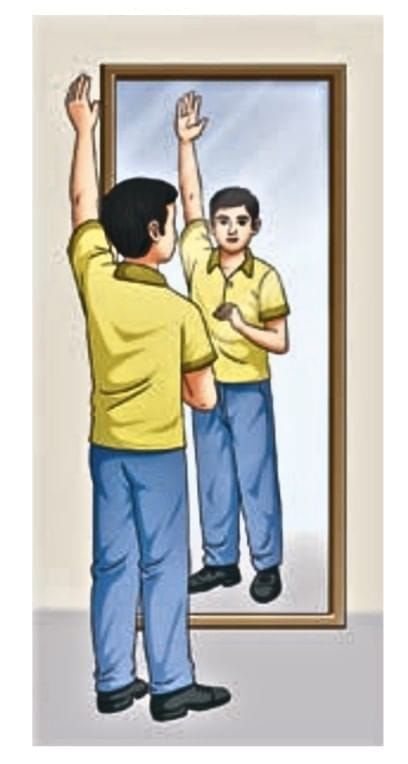
Another example: word "AMBULANCE" is written in reverse letters on the front of ambulances so that drivers in vehicles ahead can see the word correctly in their rear-view mirrors. This helps them quickly recognize an approaching ambulance and give way.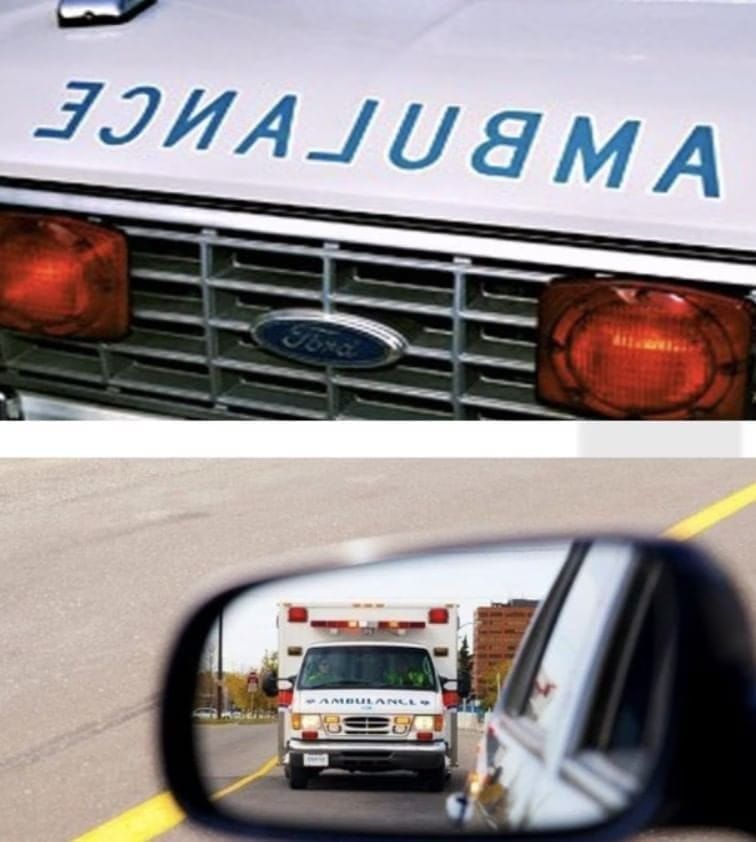
Distance Relationship: The image’s distance from the mirror equals the object’s distance from the mirror. Moving closer to the mirror makes the image appear closer, and moving farther makes it appear farther.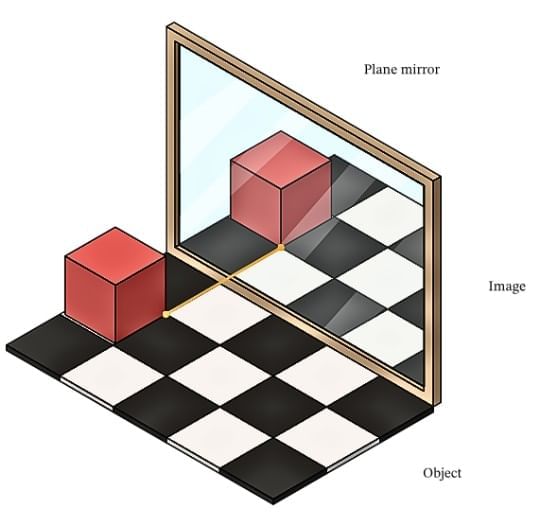
Fascinating Fact
The exact time when mirrors were invented is unknown. Early mirrors were made by polishing stone or metal. With the invention of glass mirrors, the traditional art of making metal mirrors faded but still survives in places like Kerala, where the unique Aranmula Kannadi metal mirror has been crafted for centuries.
Pinhole Camera
A pinhole camera is a simple device that uses a tiny hole to form an image on a screen.
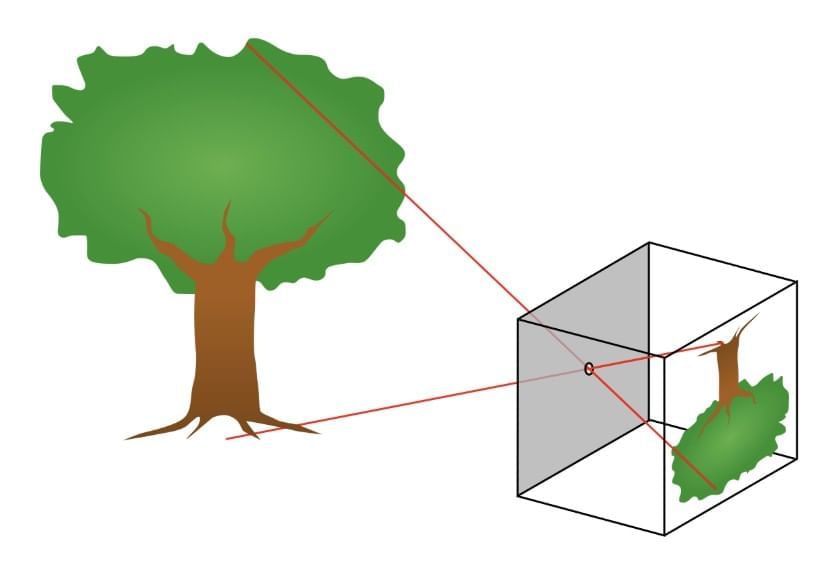
Working Principle
Light rays from an object pass through a small hole (pinhole) and form an inverted (upside-down) image on a screen, such as tracing paper. The image shows the object’s colors but is reversed vertically.
Making a pinhole camera
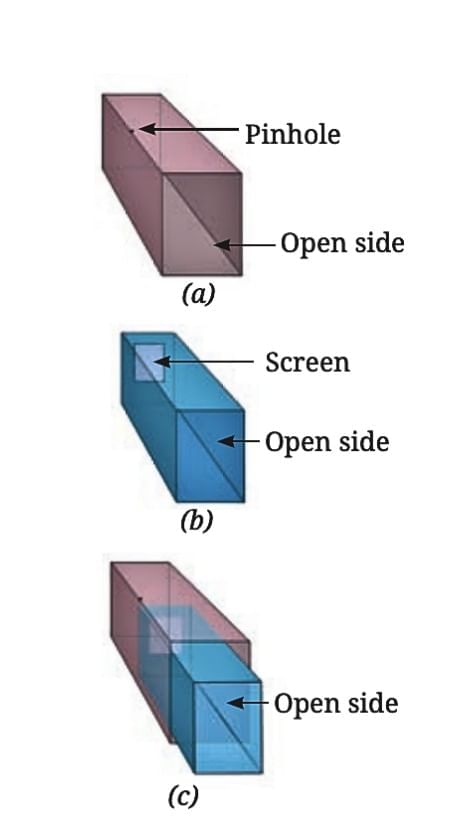 A sliding pinhole camera
A sliding pinhole cameraUse two cardboard boxes, one slightly smaller to slide inside the other.Make a small hole in one side of the larger box.
Cut a square on the opposite side of the smaller box and cover it with thin translucent paper (like tracing paper) to act as a screen.
Slide the smaller box inside the larger one so the tracing paper is inside.
Point the pinhole side towards a distant object in bright sunlight.
Look through the open side, cover your head and camera with a dark cloth to see the image clearly.
Adjust the smaller box forward or backward until the image appears on the tracing paper.
Question for Chapter Notes: Light: Shadows and Reflections
Try yourself:
What is a characteristic of the image formed by a plane mirror?Explanation
Image Characteristics in a Plane Mirror:- The image is the same size as the object.
- It is upright, with the top of the object appearing at the top.
- The left side of the object appears as the right side in the image, and vice versa.
Report a problem
Characteristics of Image Formed
Dive Deeper
A pinhole camera forms an upside-down image, while a mirror produces a laterally inverted image that is not upside down. These concepts will be explored further in higher grades.
Making Some Useful Items
The properties of light, such as its straight-line travel and reflection, are used to create practical devices.
Periscope
- A simple periscope is made by placing two plane mirrors inside a Z-shaped box.
- The reflection from these mirrors allows us to see objects that are not directly visible.
- Periscopes are commonly used in submarines, tanks, and by soldiers to see outside their bunkers. You can also use one to see over taller people.
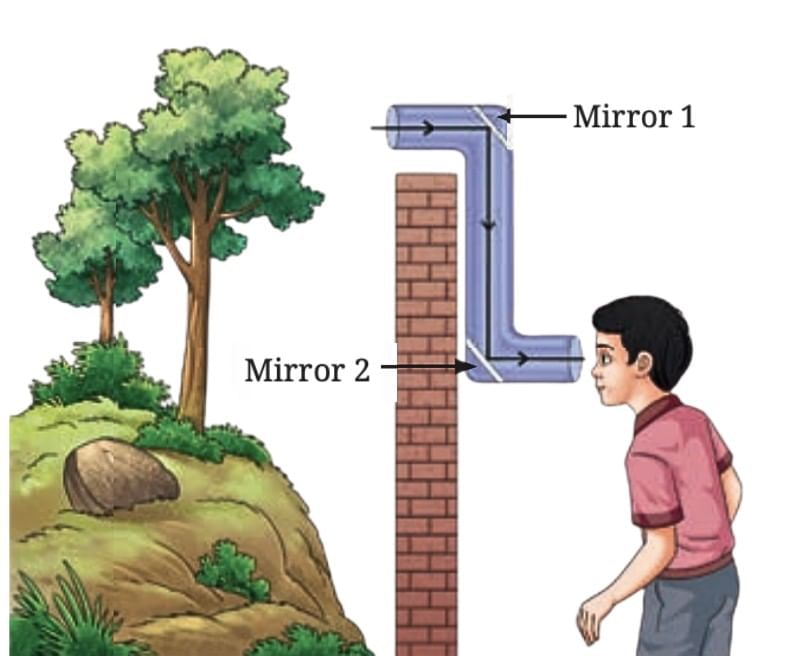 A Periscope
A Periscope
Kaleidoscope
- A kaleidoscope is made by joining three rectangular plane mirrors in a triangular shape and placing them inside a circular tube.
- Colored pieces like broken bangles or beads are placed on one end, covered with a transparent sheet and tracing paper.
- Looking through the open end shows beautiful, ever-changing patterns due to multiple reflections from the three mirrors.
- Artists often use kaleidoscopes to find inspiration for new designs.
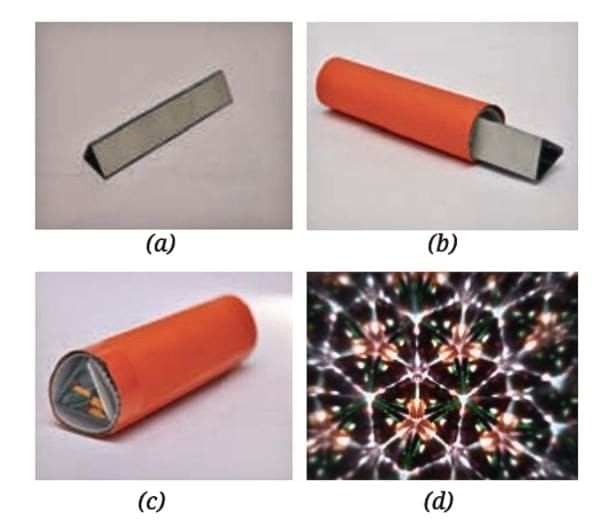 A kaleidoscope
A kaleidoscope
Difficult Words
- Luminous Objects: Objects that emit their own light, such as the Sun, stars, or fireflies.
- Non-Luminous Objects: Objects that do not emit light but reflect light from other sources, such as the Moon or a mirror.
- Rectilinear Propagation: The property of light traveling in a straight line.
- Transparent Materials: Materials that allow light to pass through almost completely, like glass.
- Translucent Materials: Materials that allow light to pass through partially, causing diffused visibility, like tracing paper.
- Opaque Materials: Materials that block light completely, like cardboard.
- Shadow: A dark region formed when an object blocks light from reaching a surface.
- Reflection: The change in direction of light when it bounces off a surface, such as a mirror.
- Lateral Inversion: The left-right reversal of an image in a plane mirror, where the left side appears as the right side.
- Pinhole Camera: A device that uses a tiny hole to form an inverted image of an object on a screen.
- Periscope: A device with two plane mirrors that allows viewing of objects not directly visible, used in submarines and bunkers.
- Kaleidoscope: A device with three mirrors forming symmetrical patterns from reflected objects, used for design inspiration.






































