Locating Places on the Earth Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Exciting World of Maps |

|
| A Map and Its Components |

|
| Mapping the Earth |

|
| Understanding Time Zones |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Key Words |

|
The Exciting World of Maps
Imagine you're a pirate searching for buried treasure on a mysterious island with an old, crumpled map. This map, filled with strange symbols and arrows, is your guide to hidden treasure. Just like a pirate’s map, every map tells a story and helps us find places we’ve never been. Maps are not just for treasure hunts; they help us navigate cities and explore new lands. Let’s embark on a journey to discover the secrets of maps and their magical components!
A Map and Its Components
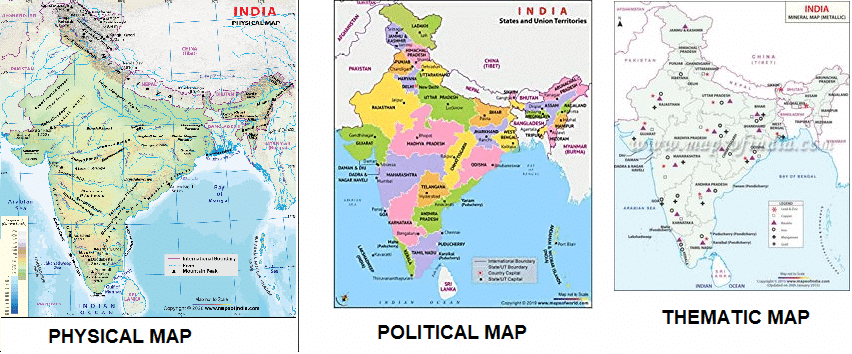
A map is a visual representation of an area, showing the locations of different features such as mountains, rivers, cities, and roads. Maps can be simple or complex, depending on the amount of detail they include.
There are different types of maps, each serving a specific purpose:
- Physical Maps: Show natural features like mountains, rivers, and lakes.
- Political Maps: Show boundaries of countries, states, and cities.
- Thematic Maps: Focus on specific types of information, such as population density or climate zones.
Components of a Map
Maps have several important components that help us understand the information they provide:
- Distance: Maps use a scale to represent distances. The scale shows the relationship between the distances on the map and the actual distances on the ground. For example, a scale might show that 1 cm on the map equals 500 meters in reality.
- Direction: Maps use main directions (North, South, East, and West) and in-between directions (Northeast, Southeast, Southwest, and Northwest) to help us find places. Most maps have an arrow pointing to the north to show which way is north. The four big arrows in the following picture show the four main directions: North, South, East, and West.
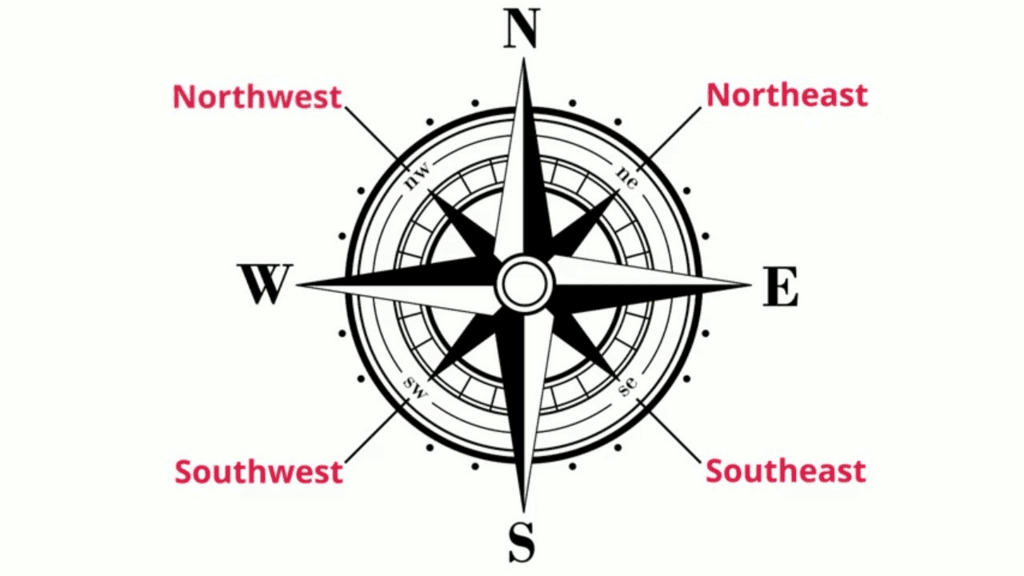 Cardinal and Intermediate Directions
Cardinal and Intermediate Directions
- Symbols: Maps use symbols to represent different features. For example, a small drawing of a tree might represent a forest, or a dotted line might represent a road. These symbols are explained in the map's legend or key.
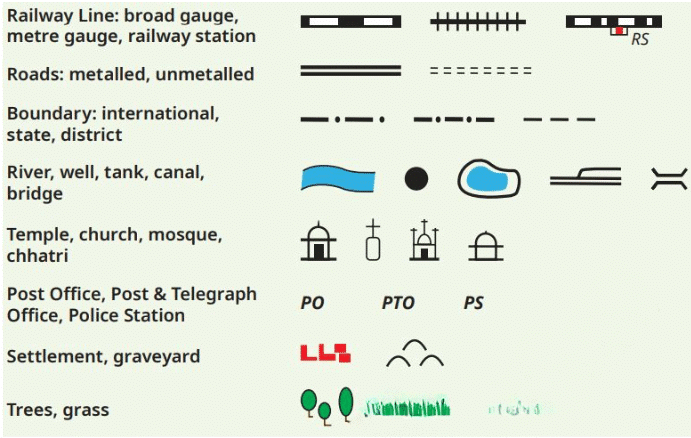 A selection of symbols commonly used in maps
A selection of symbols commonly used in maps
Mapping the Earth
The Earth is a sphere, so representing it on a flat map can be challenging. A globe is a more accurate way to represent the Earth because it maintains the correct proportions and distances. However, maps are more convenient for many purposes.
To accurately locate places on the Earth, we use a coordinate system based on latitudes and longitudes.
(a) Understanding Coordinates
- A coordinate system uses one or more numbers to uniquely determine or identify the position of a particular point.
- In the case of earth, latitudes and longitudes are used to determine or pinpoint the position of a particular place.
- These are imaginary lines drawn on the earth that assist in location and navigation across the planet.
- The position of a point on earth written in terms of its latitude and longitude is called its coordinates.
(b) Latitudes
- Equator: The Equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth halfway between the North and South Poles. It is at 0° latitude. The equator divides the earth into southern and northern hemispheres.
- Parallels of Latitude: These are imaginary lines that run parallel to the Equator. They measure the distance north or south from the Equator. For example, the Tropic of Cancer is at approximately 23.5°N latitude, and the Tropic of Capricorn is at approximately 23.5°S latitude.
- Climate Zones: The Earth is divided into different climate zones based on latitude. The area near the Equator is generally hot and is called the torrid zone. The areas between the tropics and polar circles are called temperate zones and have moderate climates. The areas near the poles are called frigid zones and are very cold.
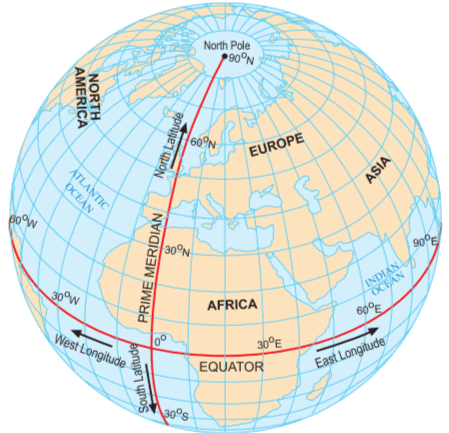 This globe shows both parallels of latitude and meridians of longitudes
This globe shows both parallels of latitude and meridians of longitudes
(c) Longitudes
- Prime Meridian: The Prime Meridian is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England. It is at 0° longitude. The prime meridian divides the earth into the eastern and western hemispheres.
- Meridians of Longitude: These are imaginary lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole. They measure the distance east or west from the Prime Meridian. For example, New York is at approximately 74°W longitude, and Tokyo is at approximately 140°E longitude.
- Local Time: The Earth's rotation causes different places to experience day and night at different times. Local time is determined by a place's longitude. Places with the same longitude have the same local time.
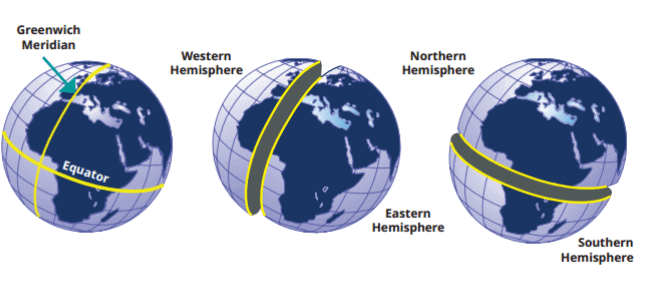 This sketch shows how the Prime Meridian divides the Earth into the Western and Eastern Hemispheres, while the Equator divides it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
This sketch shows how the Prime Meridian divides the Earth into the Western and Eastern Hemispheres, while the Equator divides it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Don't Miss Out
- The Greenwich Meridian is not the first prime meridian. There were others in the past.
- In fact, many centuries before Europe, India had a prime meridian of its own!
- It was called madhya rekhā (or ‘middle line’) and passed through the city of Ujjayinī (today Ujjain), which was a reputed centre for astronomy over many centuries.
- Varāhamihira, a famous astronomer, lived and worked there some 1,500 years ago.
- Indian astronomers were aware of concepts of latitude and longitude, including the need for a zero or prime meridian.
- The Ujjayinī meridian became a reference for calculations in all Indian astronomical texts.
- The map shows a few ancient Indian cities close to the Ujjayinī meridian.
- Some are very close to it, while others are a little away.
- That is because measuring longitude required accurate timekeeping, which was not as precise then as it is today.
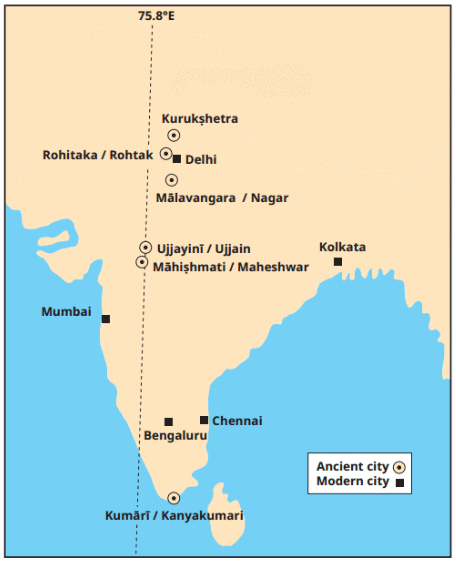 The Ujjayinī prime meridian used in ancient Indian astronomy. Cities marked with a circle are mentioned in astronomical texts as being on this meridian (the modern name is given after the oblique bar).
The Ujjayinī prime meridian used in ancient Indian astronomy. Cities marked with a circle are mentioned in astronomical texts as being on this meridian (the modern name is given after the oblique bar).
Understanding Time Zones
- The Earth spins from west to east, completing a full rotation of 360° every 24 hours. This means it rotates 15° every hour.
- To mark time zones, we divide the globe into meridians of longitude every 15°.
- Moving east from the Prime Meridian (0°), the meridians are 15°E, 30°E, 45°E, and so on, up to 180°E. Each meridian represents an additional hour of local time.
- For example, if it is 12 pm at the Prime Meridian, it is 1 pm at 15°E, 2 pm at 30°E, and so forth.
- Moving westward from the Prime Meridian means subtracting time: 11 am at 15°W, 10 am at 30°W, etc.
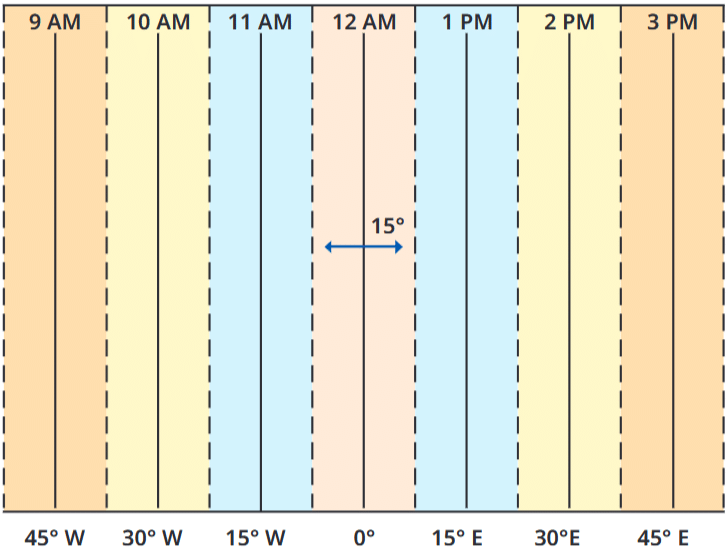 . This graph shows longitudes at the bottom and the local time at the top, with reference to the Prime Meridian at 0° . Each colour is a zone of 15° centred on a meridian.
. This graph shows longitudes at the bottom and the local time at the top, with reference to the Prime Meridian at 0° . Each colour is a zone of 15° centred on a meridian.
Standard Time and Time Zones
- Most countries adopt a standard time based on a meridian that passes through them, as having multiple local times would be impractical.
- For instance, Indian Standard Time (IST) is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- Standard times are organized into time zones, which generally follow the 15° divisions.
- The boundaries of these time zones on the world map are not perfectly straight; they adjust to align with each country's standard time and international borders.
Countries with Multiple Time Zones
- While it may seem that every country has a single standard time, large countries like Russia, Canada, and the USA have multiple time zones.
- For example, the USA has six time zones, and Russia has eleven.
- Traveling across Russia from east to west requires adjusting your watch ten times to match the local time.
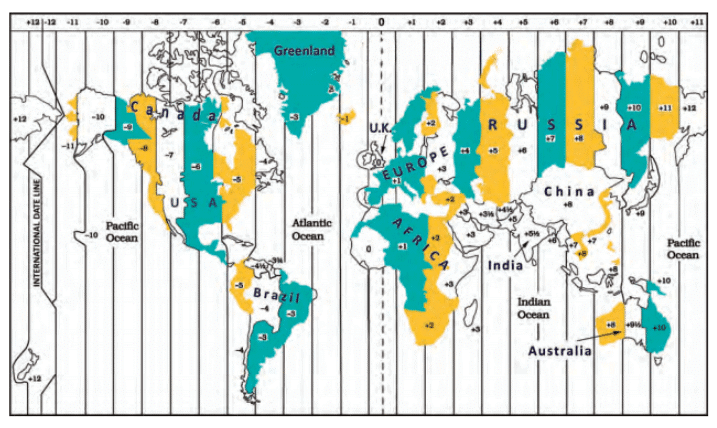 A world map of the time zones, showing the standard times (with respect to GMT) for a few countries.
A world map of the time zones, showing the standard times (with respect to GMT) for a few countries.
The International Date Line
- The Prime Meridian was established at Greenwich, while the line opposite it, around 180° longitude, is called the International Date Line.
- At the International Date Line, the +12 and -12 time zones meet. Crossing this line requires changing the date on your watch.
- If you travel eastward, you subtract a day (e.g., from Monday to Sunday); if you travel westward, you add a day (e.g., from Sunday to Monday).
- The International Date Line is "approximately" at 180° longitude because it deviates in certain areas to avoid splitting countries into two different days.
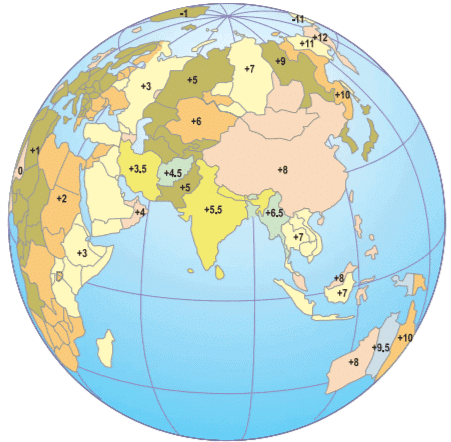 A few time zones (with respect to GMT) in Africa and Eurasia.
A few time zones (with respect to GMT) in Africa and Eurasia.
Conclusion
So, whether you're a pirate looking for treasure, an explorer charting new lands, or just someone trying to find the nearest ice cream shop, maps are your best friend. They guide us through unknown territories, help us understand the world around us, and show us how to get from point A to point B. With the knowledge of latitudes and longitudes, you can pinpoint any location on Earth, and understanding time zones will help you know what time it is anywhere in the world. Maps are more than just pieces of paper—they are keys to adventure and discover
Key Words
Representation – This means a way of showing something, like using pictures or symbols to show real things.
Thematic – This word means related to a specific theme or topic, like a map that shows only climate or population.
Coordinate – A coordinate is a pair of numbers used to find the exact location of a place on the Earth.
Imaginary – Something that is not real but made up in the mind to help explain or understand things, like imaginary lines on a globe.
Meridian – A meridian is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and helps measure distance east or west.
Longitude – These are vertical lines on the globe used to measure how far east or west a place is from the Prime Meridian.
Latitude – These are horizontal lines on the globe that measure how far north or south a place is from the Equator.
Astronomer – A person who studies stars, planets, and space.
Hemisphere – One half of the Earth, like the northern or southern part divided by the Equator.
Deviation – A small change from the usual or straight path, like when a line moves slightly away from its regular direction.
FAQs on Locating Places on the Earth Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the main components of a map? |  |
| 2. How do maps represent the Earth's surface? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of understanding time zones? |  |
| 4. How do you locate a place on Earth using coordinates? |  |
| 5. What are some common types of maps, and what are their uses? |  |
















