Money & Banking Class 12 Economics
Introduction
Money is a universally accepted medium of exchange. In an economy with only one person, there are no exchanges, and thus no need for money. However, when multiple people engage in market transactions, money becomes essential for facilitating exchanges. Without money, barter systems require a double coincidence of wants, which is difficult to achieve. Money simplifies the process, allowing individuals to sell goods for money and then purchase what they need. Its primary function is to ease exchanges, but it serves other roles in a modern economy too.
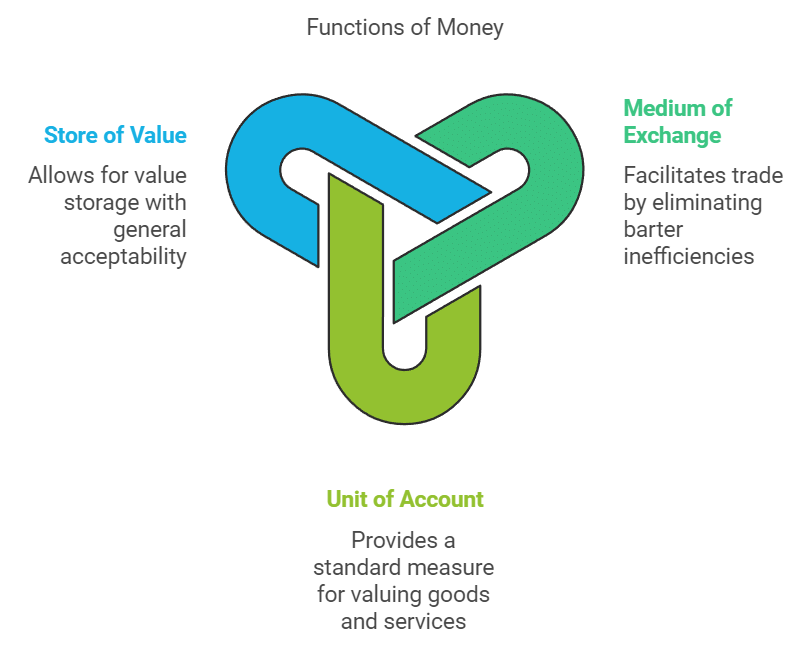
Functions of Money
1. Medium of Exchange
- Money simplifies exchanges in large economies, avoiding the high costs and difficulties of barter systems.
- Barter requires finding suitable partners with complementary needs, which can be inefficient.
2. Unit of Account
- Money provides a standard measure for valuing goods and services.
- Example: A wristwatch valued at Rs 500 means it can be exchanged for 500 units of money (rupees).
- Relative prices can be calculated, e.g., a pen (Rs 10) is worth 5 pencils (Rs 2 each).
3. Store of Value
- Money has removed the major difficulty of the double coincidence of wants.
- It is very convenient, easy and economical to store the value and has got general acceptability which was lacking in the barter system.
- Other assets like gold, property, or bonds can store value but lack easy convertibility and universal acceptance.
- Money must maintain its value over time, but inflation may erode its purchasing power.
Digital Transactions
- Some countries aim for a cashless economy, relying on digital transactions instead of physical currency.
- Digital money transfers replace cash (notes and coins).
- The Indian government has invested in financial reforms for greater inclusion, such as Jan Dhan accounts, Aadhaar-enabled payment systems, e-wallets, and the National Financial Switch (NFS).
- Mobile and smartphone penetration has made financial inclusion more achievable.
Demand For Money and Supply Of Money
Demand For Money
The demand for money explains why people want to hold a certain amount of money such as:
- Money for Transactions: People need money to make transactions. The more transactions they need to conduct, the more money they will want.
- Income and Demand: As income increases, people will engage in more transactions, so their demand for money will also rise.
- Savings and Interest Rates:
1-If people save money instead of investing in interest-earning accounts, their demand for money increases
2-When interest rates go up, people prefer to earn interest rather than hold onto cash, so their demand for money decreases.
Supply of Money
In a modern economy, money includes both cash and bank deposits. There are various measures of money based on the types of bank deposits considered.
These are created by a system comprising two types of institutions
1. The central bank
2. The commercial banking
Central Bank
The central bank plays a crucial role in a modern economy, with almost every country having one. India's central bank that is The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), was established in 1935. It performs several key functions:
- Issuing currency for the country.
- Controlling the money supply through methods like adjusting the bank rate, open market operations, and reserve ratios.
- Acting as a banker to the government and holding the country's foreign exchange reserves.
- Serving as a bank to other banks.
- In terms of money supply, its primary role is currency issuance. The money issued by the central bank, known as high-powered money or reserve money or monetary base forms the basis for credit creation in the economy.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks play a key role in creating money in the economy. They accept deposits from the public and lend out part of these funds to borrowers. Banks pay depositors a lower interest rate than they charge borrowers, and this difference, known as the spread is how banks make a profit.
Banks act as intermediaries between people or firms with extra funds and those who need money. People prefer to keep their money in banks because:
- Banks offer interest on deposits.
- It’s safer to store money in a bank than at home.
- With modern banking tools like checks and debit cards, keeping money in a demand deposit account makes transactions safer and more convenient.
When banks receive deposits, they lend out a portion of the funds, assuming not all depositors will withdraw their money at the same time. However, banks must ensure they have enough funds to repay depositors when needed. While banks aim to lend as much as possible to earn interest, they must balance this with the need to have sufficient funds on hand for withdrawals to maintain depositor confidence.
Key Points
1. Deposit and Lending: Banks take deposits from the public and lend out a portion of the funds to borrowers.
2. Interest Rate Spread: The difference between the interest paid to depositors and charged to borrowers is the bank’s profit, called the spread.
3. Intermediation: Banks connect people or businesses with extra money to those who need loans (home loans, crop loans, etc.).
4. Safety and Convenience: People prefer to keep money in banks for safety and convenience (e.g., checks and debit cards for large transactions).
5. Lending Strategy: Banks lend a portion of the deposited funds, keeping enough aside to repay depositors when they withdraw their money.
6. Balance: Banks must carefully manage lending and available funds to ensure they can repay depositors on demand, maintaining trust and confidence.

Money Creation by Banking System
Money creation by the banking system is an essential process in modern economies. It describes how commercial banks can increase the money supply by lending money and creating new deposits. This process is vital for boosting economic activity, funding investments, and supporting growth. Generally, banks lend money because they know that not all depositors will withdraw their funds at the same time. When a bank lends money, it creates a new deposit in the borrower’s name, increasing the overall money supply (existing deposits plus new deposits plus currency).
Balance Sheet Structure
Balance sheet: It is a sheet that records a bank's assets (what it owns) on the left and liabilities (what it owes) on the right. Both sides must be equal.
Assets: These are things a firm owns or what a firm can claim from others .They Include
- Reserves: Deposits that the bank holds with the central bank (e.g., Reserve Bank of India) and any cash held by the bank.
- Loans: Amounts lent by the bank to individuals or businesses.
- Formula: Assets= Reserves+ Loans
Liabilities: They refer to what a bank owes, primarily the deposits from customers.
- Deposits: The total amount of money that people or businesses have deposited in the bank. This is the primary liability of the bank since depositors can demand their money back at any time.
- Formula: Liabilities= Deposits
Net Worth: If assets (reserves + loans) exceed liabilities (deposits), the difference is recorded as the bank's Net Worth.
Net Worth = Assets – Liabilities.
Balance Sheet of a Fictional Bank
We can start our fictional bank with deposits (liabilities) amounting to Rs 100 which could come from Ms. Fernandes depositing Rs100 into the bank. The bank then deposits this same amount as reserves with the Reserve Bank of India. The table below shows the bank's balance sheet.
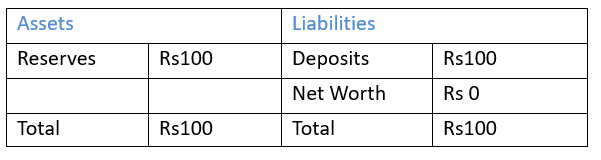 Balance sheet of a Bank
Balance sheet of a Bank
If we assume that there is no currency in circulation, then the total
money supply in the economy will be equal to Rs 100.
M1= Currency + Deposits = 0 +100 = 100
Limits to Credit Creation and Money Multiplier
Let's assume that a borrower comes to the bank for a loan of Rs 1000. If it gives the loan and borrower deposits the loan amount in the bank itself, the total bank deposits and total money supply will rise . But there is a limit to money or credit creation by banks and it is determined by the Central Bank of India that is Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
The RBI sets a specific percentage of deposits that each bank must hold as reserves. This is to prevent banks from lending too much. It is a legal requirement that all banks must follow. This is known as the Required Reserve Ratio, Reserve Ratio or Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR).
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) refers to the percentage of deposits that a bank must keep as cash reserves.
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)-A percentage of a bank's deposits that must be maintained as liquid assets such as cash, gold, and government-approved securities, held in the bank's vault.
Process of Credit Creation
Suppose there is an initial deposit of Rs. 1000 and CRR. is 20% i.e., the banks have to keep Rs. 200 and lend Rs. 800/-. All the transactions are routed through banks. The borrower withdraws his Rs. 800/- for making payments which are routed through banks in the form of deposits account.
The Bank receives Rs. 800/- as deposit and keeps 20% of Rs.800/- i.e., Rs.160/- and lends Rs.640/- . Again the borrower uses this for payment which flows back into the banks thereby increasing the flow of deposits.
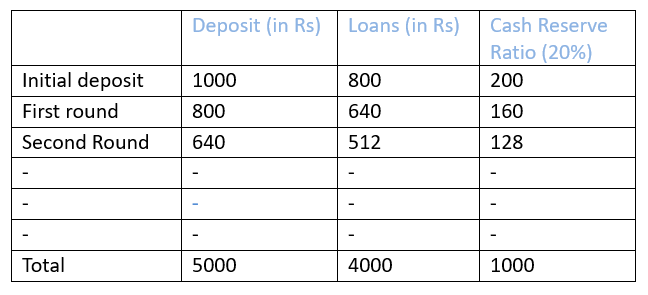 Here-
Here-
- The first column shows each round
- The second column displays the total deposits held by the bank at the start of each round.
- 20% of these deposits must be deposited with the RBI as required reserves (shown in column 4).
- The amount the bank lends in each round is added to the deposits in the next round.
- Column 3 shows the loans made by the bank.
- The bank is required to keep 20% of its deposits as reserves.
- Therefore, reserves of Rs1000 (which is 20% of Rs5000) are enough to support deposits of Rs 5000.This means the bank can lend out Rs 4000(5000-1000)
- The total money supply is calculated : M1 = Currency + Deposits = 0 + 5000 = Rs5000.Thus, the money supply grows from Rs1000 to Rs5000.
- With a Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) of 20%, the bank cannot lend more than Rs 4000.The reserve requirement limits the amount of money the bank can create.
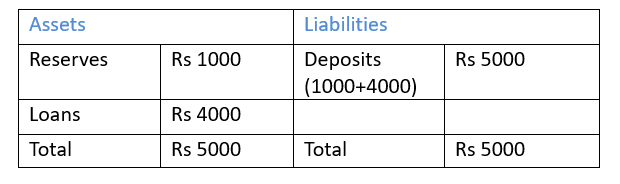 Balance Sheet of a Bank
Balance Sheet of a Bank
Money Multiplier
Money multiplier refers to the mechanism through which commercial banks generate credit based on the reserve ratio and initial deposits.
Money Multiplier = 1/CRR.
In the above example
CRR = 20% i.e. 0.2, so money multiplier is equal to 1/0.2=5 .Thus Reserves of Rs1000 create deposits of Rs 5000 (5 X 1000)
Why only a fraction of deposits is kept as Cash Reserve?
- All depositors do not withdraw the money at the same time.
- There is constant flow of new deposits into the banks.
Policy Tools to Control Money Supply
The Reserve Bank is the sole authority responsible for issuing currency. When commercial banks require additional funds to expand credit, they can either seek funds from the market or approach the Central Bank. The Central Bank supplies these funds through various means. One key function of the RBI is its readiness to lend to banks whenever needed, which is why it is referred to as the lender of last resort.
The RBI regulates money supply using both quantitative and qualitative tools.
Quantitative Tools: These tools adjust the overall money supply by modifying the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), bank rate, or through open market operations.
- Changing CRR: Changes in the reserve ratio (CRR) directly affect banks' lending capacity, which influences deposits and thus the money supply. For example, an increase in the reserve ratio reduces the amount of money banks can lend, decreasing money supply.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs):It refers to the buying and selling of securities by the Central Bank from/ to the public and commercial banks.
It sells government securities during inflation/excess demand and buys the securities during deflation/deficient demand.
Types of OMOs
1. Outright OMOs: Permanent transactions where the central bank either injects or withdraws money without future promises to reverse the action. These are permanent in nature.
2.Repo Agreement/ Repurchase agreement: When the central bank buys securities with an agreement to sell them back at a later date at a specific price. The lending interest rate is the repo rate.
Similarly
-Reverse Repo Agreement: When the central bank sells securities with a promise to buy them back at a later date. The interest rate for this is the reverse repo rate.
-Repo and Reverse Repo Operations: These operations, often conducted over various maturities (overnight, 7-day, 14-day, etc.), are the main tools of the RBI's monetary policy. - Bank Rate- It refers to the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks as a lender of the last resort.
Central Bank increases the bank rate during inflation (excess demand) and reduces the same in times of deflation (deficient demand)
Qualitative Tools: These involve the Central Bank using influence to encourage or discourage lending by commercial banks, typically through methods like moral suasion and adjusting margin requirements.
- Moral suasion, which means persuading banks to follow certain lending practices.
- Adjusting margin requirements, which are rules about how much money banks need to hold onto when they give out loans.
- These tools are used to either encourage or discourage lending by a commercial ban.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes - Money & Banking
|
Download as PDF |
Demand and Supply of Money : A Detailed Discussion
- Money is the most liquid asset: It can easily be exchanged for other goods and services.
- Opportunity cost of holding money: Keeping money in hand has a cost, as one loses the interest that could be earned by investing it, like in a Fixed Deposit.
- Trade-off in money holding: While deciding how much money to hold, people must balance the advantage of having liquid cash with the disadvantage of not earning interest.
- Liquidity preference: The demand for holding money is referred to as liquidity preference, representing the trade-off between liquidity and earning interest.
- Two main reasons for holding money:
1. Transaction Motive: To carry out day-to-day transactions.
2. Speculative Motive: To take advantage of changes in future asset prices.

Transaction Motive
- The main reason people hold money is to make transactions.
- Income and expenditure don’t always match; income is received at certain intervals, but spending is continuous.
- Example: If someone earns Rs 100 on the first day of the month and spends it evenly over the month, their average cash holding would be Rs 50 (calculated as (Rs 100 + Rs 0) ÷ 2).
- Hence, the average transaction demand for money is typically half of the monthly income or half of the monthly transaction value.
Two-Person Economy Example
- In a basic economy with just a firm and a worker:
- The firm gives the worker Rs 100 at the beginning of the month.
- The worker uses this Rs 100 to buy things that the firm produces throughout the month.
- Both the firm and the worker keep an average of Rs 50 in cash.
- Therefore, the total amount of money needed for transactions in this economy is Rs 100.
Relationship between Money and Transactions
- The number of times a unit of money changes hands in a period is called the velocity of circulation of money.
- In the example, Rs 100 supports Rs 200 worth of transactions because money changes hands twice in a month (velocity = 2).
Transaction Demand and Nominal GDP
- Transaction demand for money is related to nominal GDP.
- As nominal GDP increases, the total value of transactions rises, leading to a higher demand for money.
Modified Equation
- Transaction demand for money (MdT) is represented as:
MdT = kPY,
where
Y is the real GDP,
P is the general price level (GDP deflator),
K is a constant fraction. - This shows that transaction demand for money is positively related to real income and the price level of the economy.
Speculative Motive
- Speculation refers to assumptions about the future value of an asset or commodity.
- When people expect asset prices (e.g., bonds) to rise, they convert their money holdings into those assets to gain future profits.
- Conversely, if they anticipate a drop in asset prices, they sell their assets (e.g., bonds) and hold money to avoid potential losses.
Bonds
- Individuals can hold wealth in two main forms: money and bonds.
- Bonds are promises of future returns and are tradable in the market.
Example
- A firm issues a 2-year bond with a face value of Rs 100 and a coupon rate of 10%.
- The bond promises Rs 10 after 1 year and Rs 110 (Rs 100 principal + Rs 10 interest) at the end of the 2nd year.
Comparison with Bank Interest:
- Suppose the interest rate in your savings account is 5%. You would calculate how much you need to invest in the bank to generate Rs 10 after one year.
- The present value (PV) of Rs 10 at a 5% interest rate is calculated as

- Similarly, the present value of Rs 110 at the end of two years is

- Total present value (PV) of the bond is Rs 109.29, meaning the bond's returns are better than saving Rs 100 in a savings account
Competitive Bidding:
- Since the bond offers a better return (Rs 109.29) than the face value of Rs 100, people will rush to buy the bond.
- Competitive bidding increases the bond price until it matches its present value.
Relationship Between Bond Prices and Interest Rates:
- If the market interest rate increases, the present value (PV) of the bond decreases.
- For example, if the interest rate rises to 6%, the present value of the bond becomes Rs 107.33.
- This shows that bond prices are inversely related to interest rates: when interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and vice versa.
Speculative Demand for Money:
- If people expect interest rates to rise in the future, they will expect bond prices to fall (leading to a capital loss).
- To avoid this loss, they will sell bonds and hold money instead, creating a speculative demand for money.
- Conversely, if interest rates are high, people expect them to fall and bond prices to rise (leading to a capital gain), so they buy bonds and reduce their speculative demand for money
Speculative Demand Formula:
- The speculative demand for money Msd can be expressed as

- As interest rates decrease from rmax to rmin, the speculative demand increases.
Liquidity Trap:
- If the interest rate is very low close to rmin everyone expects rates to rise in the future and bond prices to fall.
- In this situation, everyone holds money instead of bonds, and the speculative demand for money becomes infinitely elastic. This is called a liquidity trap.
Total Demand for Money
- Total demand for money in an economy consists of:
1. Transaction demand (proportional to real GDP and price level).
2. Speculative demand (inversely related to interest rates). - The total money demand equation is

- In simpler terms, money is demanded both for transactions and for speculative purposes, depending on economic activity (GDP) and interest rates.

Key Points
- Bond prices fluctuate inversely with market interest rates.
- Speculative demand for money arises from people's expectations of future interest rate movements and their desire to avoid capital losses.
- When interest rates are very low, a liquidity trap can occur, where people hold money rather than bonds, preventing further declines in interest rates.
The Supply of Money- Various measures
What money consists of
- Currency notes and coins are the primary forms of money.
- In India:
1. Currency notes are provided by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
2. Coins are produced by the Government of India.
Deposits in Banks as Money
- Money also includes balances in savings or current accounts at commercial banks.
- Cheques from these accounts can be used for payments.
- These bank balances are known as demand deposits because they must be paid out when requested by the account holder.
- Time deposits, like fixed deposits, have a specific maturity period and cannot be withdrawn immediately.
Value of Currency
- A 100-rupee note or a 5-rupee coin does not have a real value equal to its face value (the actual material is worth much less).
- The reason people accept currency is due to
1.The value is backed by a guarantee from the issuing authority (RBI).
2.The RBI assures that the note will be accepted for buying goods and services.
Fiat Money
- Fiat money includes currency notes and coins that do not have intrinsic value, like gold or silver coins.
- They are accepted because of the government's guarantee.
Legal Tender
- Currency notes and coins are referred to as legal tender.
- They must be accepted by everyone in the country for transactions.
- Cheques, however, can be declined as a payment method and are not considered legal tender.
Legal Definitons : Narrow and Broad Money
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI)identifies four categories of money supply:
- M1 = CU + DD
CU = Currency (notes and coins) that people have.
DD = Net demand deposits in commercial banks. - M2 = M1 + Savings deposits in Post Office savings banks.
- M3 = M1 + Net time deposits in commercial banks.
- M4 = M3 + Total deposits in Post Office savings (excluding National Savings Certificates).
Types of Money Supply
- M1 and M2 are referred to as narrow money -which is category of money that includes physical money and other liquid assets that are easily accessible to central banks
- M3 and M4 are known as broad money-It represents the total amount of liquid financial assets in an economy that can either be used directly as a medium of exchange or quickly converted into one. It includes currency, deposits with maturities up to two years, redeemable deposits with up to three months' notice, repurchase agreements, money market fund shares, and debt securities with maturities of up to two years.
- M1 is the most liquid, meaning it is the easiest to use for transactions.
- M4 is the least liquid.
Most Common Measure
- M3 is the most commonly used measure of money supply and is also called aggregate monetary resources.
Exclusions
- Interbank deposits (deposits of one bank held in another bank) are not included in the money supply.
Demonetisation
- Demonetisation was a significant step taken by the Government of India in November 2016 to combat issues such as corruption, black money, terrorism, and fake currency.
- Old currency notes of Rs 500 and Rs 1000 were declared invalid.
- New currency notes of Rs 500 and Rs 2000 were introduced.
Process of Exchanging Old Notes
- People could deposit old notes into their bank accounts until 31 December 2016 without needing to declare anything.
- After 31 December 2016, old notes could be exchanged at the RBI until 31 March 2017, but a declaration was required.
- Each person was allowed to exchange up to Rs 4000 per day in new currency.
- Until 12 December 2016, old notes were still accepted at petrol stations, government hospitals, and for paying government dues like taxes and utility bills.
Impact of Demonetisation
- Initially, there were challenges like long lines outside banks and ATMs, and a lack of cash disrupted economic activities.
- Over time, the situation improved, and things returned to normal.
Positive Effects of Demonetisation
- Increased tax compliance: More people began paying taxes, helping to reduce black money.
- Savings in the formal system: Individuals moved their savings into banks, giving banks more money to lend.
- Lower interest rates: With more money available, banks could offer loans at lower rates.
- Curb on tax evasion: The government showed it was serious about tackling black money and made it clear that tax evasion would lead to penalties.
- Shift to electronic payments- Demonetisation prompted a move from cash transactions to digital payments.

Long term Benefits
- Reduction in corruption: Demonetisation targeted the hoarding of large amounts of black money in cash. By invalidating high-denomination notes, it forced people to deposit or exchange their old currency, bringing unaccounted wealth into the formal banking system
- Improved tax administration: When people deposited large amounts of cash into their accounts during demonetisation, it became easier for tax authorities to track undeclared income. This increased tax compliance widened the tax base, and helped the government identify potential tax evaders, leading to better tax collection and administration.
- Increased use of digital payments: Demonetisation led to a temporary cash shortage, encouraging people and businesses to adopt digital payment methods such as mobile wallets, online banking, and card transactions. This shift reduced dependency on cash, improved transparency in financial transactions, and helped promote a more formal and accountable economy.
|
64 videos|275 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Money & Banking Class 12 Economics
| 1. What are the primary functions of money in an economy? |  |
| 2. How does the demand for money differ from the supply of money? |  |
| 3. What role does the banking system play in money creation? |  |
| 4. What are some policy tools used by central banks to control the money supply? |  |
| 5. What are the economic impacts of demonetisation? |  |